NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Quwat Sahl Nīnawā: Iraq’s Shia Shabak Get Their Own Militia
By Phillip Smyth

Figure 1: Quwat Sahl Nīnawā’s logo. The Iraqi (left) and Shabak (right) flags emerge out of a map of the Hamdaniya region of the Nineveh Plain. The symbol also features an AK-102 rifle.
Quwat Sahl Nīnawā (A.K.A. Liwa Sahl Nineveh or QSN) purports to be a Shia Shabak militia associated with the Democratic Assembly of Shabaks (Tajema’ al-Shabak al-Dimokrati or DAS).1 QSN announced itself via a November 23, 2014 official statement posted on the website and social media apparatus belonging to the DAS. The group has also already claimed to take casualties in the fight against the Sunni jihadist “Islamic State” (A.K.A. IS, ISIS, or ISIL).2
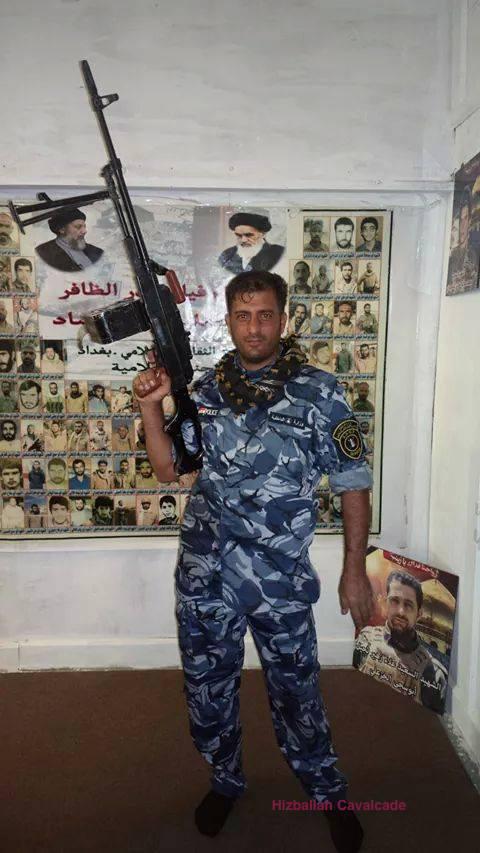

Figure 2: A QSN fighter poses with martyrdom posters (one featuring the dome of Sayyida Zaynab in Syria – bottom right) and other posters featuring Badr Organization founder Ayatollah Muhammad Baqir Sadr and the first Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khomeini.
Present in the symbols and photos, QSN mixes a limited quantity of Shabak particularism and an added emphasis on Shia identity. On some pages the group has simultaneously promoted links to Iran’s proxy forces. While the group may have relations with Iran’s proxies, its official statements have announced a commitment to “gladly serve the supreme religious authority in Najaf [Grand Ayatollah Sistani].”3 This would likely indicate the group is not an equivalent (in terms of ideology and/or levels of control) to newer Iraqi Shia Iran-proxy militias such as Hizballah al-Abrar.
Photos claiming to show the group training also indicate that they may be assembled along the lines of a “Popular Assembly/Mobilization” or “al-Hashd al-Sha’abi” type group. Photographs of claimed QSN fighters holding flags promoting al-Hashd al-Sha’abi add further credence to this likelihood. Organization along those lines would mean many of the fighters are possibly newer recruits trained and likely led by more experienced personnel and advisors.
In photos of QSN, around 100 fighters were shown posing in ranks. This suggests the numbers for the group are likely in the range of 100-500 combatants.
The creation and promotion of the group may exemplify another method Iran and its proxies are using to place pressure on Kurdish organizations. QSN, as organized along lines of the more dominant Iraqi Arab Shia militias in the south of the country, also demonstrates the direction in which other new militias may be organized. QSN further exemplifies how some of Iraq’s minority groups are mobilizing against ISIS.
The Name & Symbols
QSN’s name directly refers to an area of heavy Shabak habitation, Iraq’s Ninewa (or Nineveh) Plain. Their logo and a post by the Shabak Democratic Assembly describes the group as “Quwat Sahl Nīnawā” or the “Nineveh Plain’s Forces.”4 Albeit, via social media, one page purporting to belong to the group claimed it also went by the name of “Liwa Sahl Nīnawā” or the “Nineveh Plains Brigade”. However, such minor alterations in name are common during the early stages of many new militias.5
The group’s logo also demonstrates a rather rudimentary approach to create symbolism for the new group. Readily available images (including the pictures of an AK-102 rifle, the Shabak and Iraqi flags, and a map of the Hamdaniya area of the Nineveh Plains) were likely pasted together following a simple image search online.6

Figure 3: A QSN fighter poses with a flag associated with the Popular Mobilization type militias.
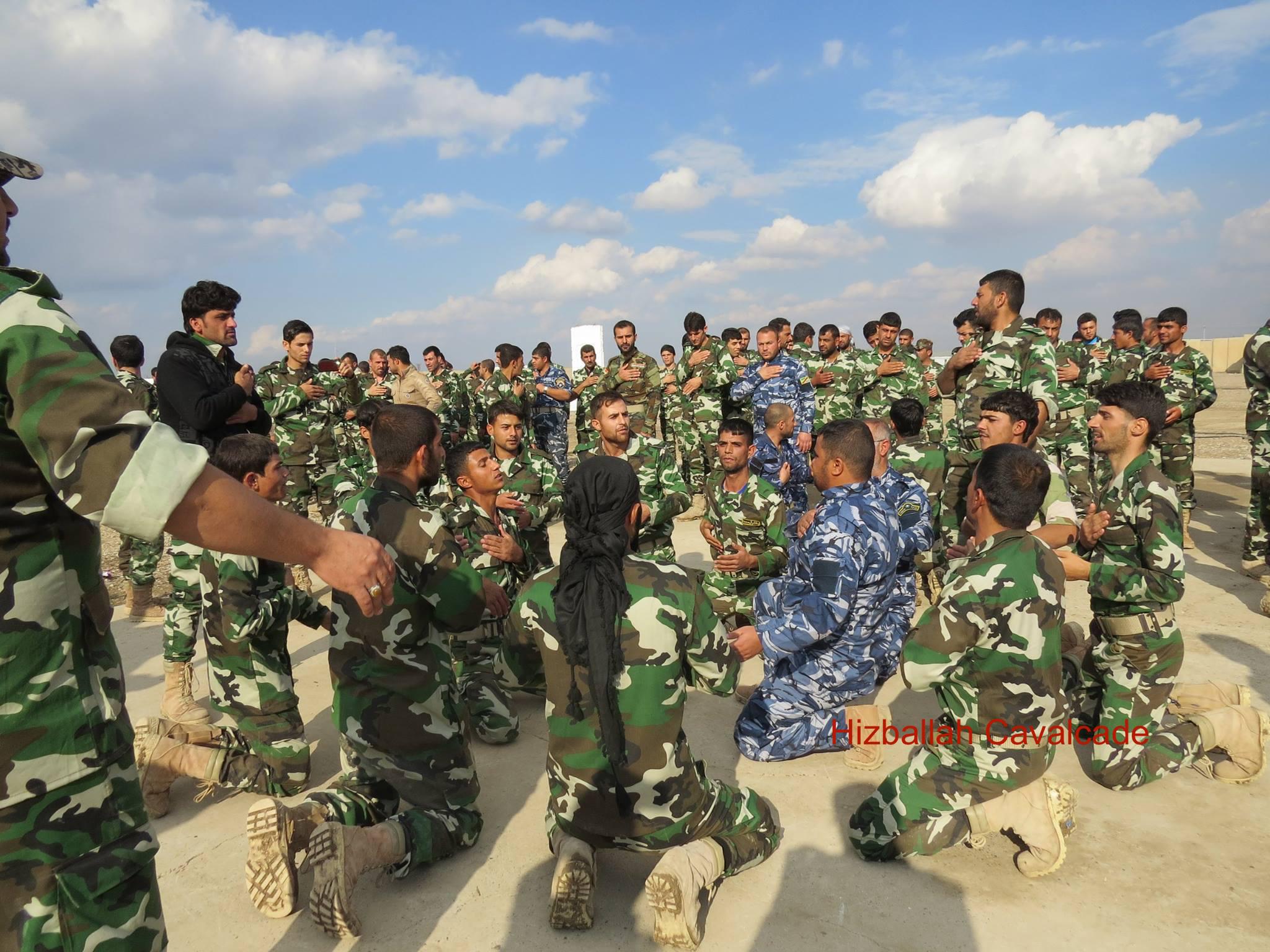

Figure 4: QSN fighters congregate.
Who Are the Shabak & What is the Nineveh Plain?
The Nineveh Plain is a minority rich area; home to the Shabak, numerous Christian sects (including the Assyrians, Chaldeans, and Syriac Orthodox and Syriac Catholics), Turkmen, Yezidis, and Kurds.7 Considered a heartland for Iraq’s Christians, Assyrian Christian and other Syriac (Aramean, Syriac, and Chaldean) Christian nationalist organizations and political parties have pushed for autonomy in the area.8 There has also been a campaign to make the Nineveh Plain its own province (under primarily Christian leadership) within the Iraqi federal framework.9 Nevertheless, the Plain has not been granted a truly autonomous standing.
Many Shabak insist they have a unique ethnic identity, which is neither Arab nor Kurd (albeit, primarily non-Kurdish).10 The group also speaks its own language, Shabaki.11 Most Shabak are also religiously (Twelver) Shia.12
Within the Nineveh Plain, the Shabak primarily live in villages to the east of the city of Mosul, in the Hamdaniya area, and a few thousand also lived in the city of Mosul (before the invasion). Due to ISIS advances, many Shabak hamlets have been overrun.
The Democratic Assembly of Shabak & Issues With the Kurds
While QSN was ostensibly created as a Shabak arm to fight back ISIS threats and offensives targeting the Shabak, there are other underlying trends present with the creation of the militia associated with Shabak-Kurdish relations.
Kurdish groups have shown interest in further incorporating areas of Shabak habitation into Kurdistan.13 As early as 2008, minority groups including the Shabak claimed there was an effort to “Kurdify” areas they inhabited.14
Along with the promotion of a separate non-Kurdish identity, the DAS’s leader and parliamentarian Hanin Qaddo has specifically called out Kurdish parties for claimed abuses against the Shabak. In 2008 Qaddo opposed the incorporation of Shabak inhabited areas into Iraqi Kurdistan.15 Two years later, Qaddo denounced the Kurdish Democratic Party (KDP) for “intimidating” Shabak voters.16 In 2012 the Shabak leader demanded the expulsion of Kurdish and Christian armed forces from the Nineveh Plain.17
With this in mind, QSN’s establishment also recalls the 2012 decision by then Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki to allow for the creation of a 500-man Shabak militia force referred to as, “The Shabak Regiment of Doom.”18
For their part, many Kurdish political leaders have not been supportive of independent Shabak efforts to create their own militias. Nevertheless, some of those Kurdish apprehensions were downgraded following the ISIS advance. Thus, QSN has not been the only Shabak armed group to come into existence. However, its other counterpart is under the control of Kurdish military commanders.19 Whereas QSN is organized along lines set by Baghdad-supported Shia militias and Iran’s proxy groups and does not appear to be taking order from Kurdish commanders.
Tensions between QSN’s DAS parent party and Kurdish parties may explain for QSN’s retention of its independence. The DAS, the largest Shabak Party, is also part of the ruling Iraqi State of Law Coalition. This is the same coalition which included former Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki, the current Iraqi Prime Minister, the Badr Organization and Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada, among other Iranian proxy groups. Nevertheless, Qaddo has “wavered between the Hakim and Maliki factions,” and then ran on the Badr Organization’s electoral list.20
The increase in Iranian proxy cooperation via training, equipping, and other support also speaks to other issues related to Iran’s and their proxies’ policies in Iraq. The policies in question are particularly focused on Kurdistan. From the summer of 2014 until the present, there has been increased tension between Iran’s Iraqi Shia proxies and Kurdish Peshmerga forces.21 Additionally, Iran’s proxies have also threatened Kurdish leaders such as Masoud Barzani.22
A push for support for a group which has already had problems with Kurdish leadership seems to be another avenue for Tehran to exert pressure on the Kurds. Nevertheless, QSN’s main goals and activities have and will likely remain oriented against the existential threat that is ISIS.
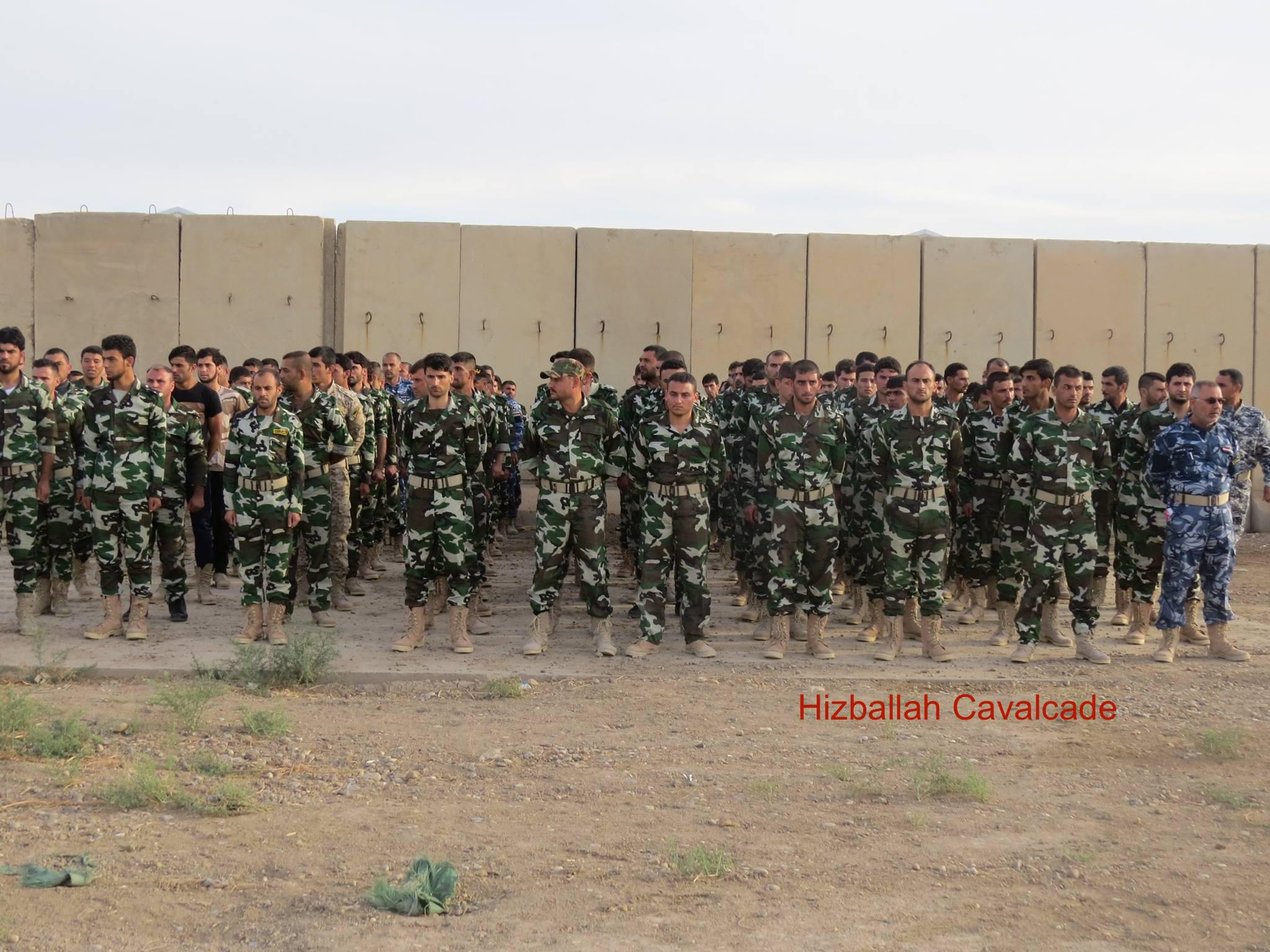

Figure 5: Around 100 QSN are shown in this photo.
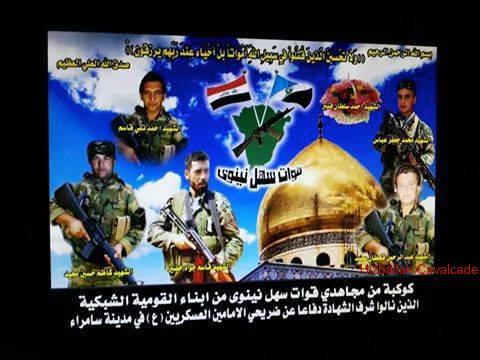
Figure 6: QSN Martyrs are shown on a poster featuring the dome of Syria’s Sayyida Zaynab. It is possible the dome was included by graphics designers to demonstrate that the fight in Syria and Iraq, marketed as “protection for shrines”, are one in the same.

Figure 7: The martyrdom poster for Kazem Husayn al-Asharaf (Abu Sajad).
Videos
Notes:
_____________
Category: Iran
Hizballah Cavalcade: The Shia Militant Response to Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr’s Death Sentence
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
The Shia Militant Response to Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr’s Death Sentence
By Phillip Smyth

Ayatollah Sheikh Nimr Baqr al-Nimr, an outspoken radical Saudi Arabian Shia cleric, has been the center of controversy and brewing conflict between Shia protesters, militant Shia groups of Saudi Arabia and Bahrain, and their respective Sunni governments. According to a 2012 article by Toby Matthiesen, al-Nimr was, “long a peripheral figure in the local Shia power struggle but now seems to have become the most popular Saudi Shia cleric among local youth.”1 His cause and image is spreading across the Middle East as the latest example of Sunni oppression of Shia in the region and his recent death sentence has become a potent rallying cry for regional Shia militant organizations, particularly those with links to Iran.
Arrested in 2012, Nimr was accused by the Saudi government’s Special Criminal Court of making sectarian statements to cause strife, inviting foreign intervention (shorthand for Iranian influence), and disobeying the king. Following his 2012 arrest, thousands took to the streets and Saudi police shot and killed two protesters.2 In mid-October 2014, Nimr was sentenced to be “crucified”, a process where the sheikh will be beheaded and his body displayed.3
Protests in Saudi began in early 2011 and in part addressed anti-Shia discrimination suffered by the group in the Shia majority area in Saudi Arabia’s oil-rich Eastern Province; primarily zones around the Shia-majority towns and villages near the city of Qatif.4 Following the 2011 Saudi intervention in Bahrain, protests against the Saudi government increased in Bahrain and Saudi Arabia among Shia protesters.5 Following the 2011-2012 protests, links between Bahrain’s and Saudi Arabia’s protest movement spilled over into the more militant circles which actively promoted Nimr’s defiant stance and a hope to combine their fronts against common foes.
Of further interest are Nimr’s own ideological leanings and how they may relate to Shia militant responses. In Frederic Wehrey’s Sectarian Politics in the Gulf, the sheikh is described as a follower of the late Ayatollah Muhammad al-Shirazi.6 Shirazi was one of the founders of a radical Shia political school of thought referred to as the “Shiraziyya.” Shiraziyya clerics have been some of the most influential in the Arab Shia world. Initially al-Shirazi agreed with the Islamic revolutionary ideology of Ayatollah Khomeini, only to split from Khomeini over issues regarding how the new Islamic state (in Iran post 1979 revolution) should be led.7 In one BBC Arabic report, Nimr had been accused by Riyadh of attempting to spread Wilayat al-Faqih.8 Absolute Wilayat al-Faqih is the Khomeinist concept that serves as the basis for the Islamic Republic of Iran. Nevertheless, it was not clarified whether this was the type of Wilayat al-Faqih Nimr was accused of propagating.
Despite the history of strife between Shirazi’s school of thought and that of Ayatollahs Khomeini and Khamenei, al-Nimr appeared to increase public support for Tehran and send other more mixed messages. In 2008, he had also reportedly stated he supported Iran’s nuclear program by saying any attack against it should be met by a response from the Islamic world. That same year, he also said that Saudi Shia may need to call on foreign support (implying Iran) to help press their issues in Saudi Arabia.9 Later in 2009, Nimr reportedly called for secession, stating during a sermon, “Our dignity is more precious than the unity of this land.”10 His statement came as a response to discrimination against Shia in the kingdom and reflected possible repercussions if certain demands made by Shia protesters were not addressed.
Since 2013, in a piecemeal fashion, social media accounts associated with Iranian proxy groups in Iraq have promoted the images and other supportive statements for Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr.11 While this does not necessitate that Nimr is a true ally or proxy of Tehran, his message and influence is likely seen by Iran as a cause to be promoted in that country’s wider struggle for the leadership of Shia Islam and as a counter to Saudi Arabia.
Nimr’s deep links and strong voice within the Saudi Shia community, particularly among youthful radicals and other more non-violent protestors, has led to Shia militant groups championing his cause from Bahrain and Iraq. Even in Yemen, Shia supporters of Ansar Allah, more commonly known as the Houthis, even launched demonstrations for the jailed cleric.12 Some Bahraini militant groups, which view the struggle of their coreligionists in a geographically close region of Saudi Arabia, as part and parcel to their conflict with the Khalifa monarchy and their Saudi government supporters. Additionally, powerful Iranian proxy groups based in Iraq—which have also maintained anti-Saudi and anti-Bahraini government narratives—have taken to issuing stern threats against Riyadh for his sentence.
The Violent Replies From Saudi Arabia’s and Bahrain’s Militants
Bahraini militant groups demonstrated the most concerted effort in terms of orchestrating violent retorts to Nimr’s jailing and sentence. While other threats and attacks were conducted since the start of 2014, this piece will focus on more recent threats and attacks beginning in the summer of 2014.
Bahrain’s Saraya al-Mukhtar (SaM), a group which once said the Saudi Shia of the Qatif and the Shia of Bahrain constituted one people with common foes, launched the most attacks over the longest period specifically addressing Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr’s arrest, trial, and death sentence.
Starting in August, SaM attacked an electricity tower in Ar-Rifā near a Bahraini military base. The group filmed the attack and stated it had been a warning related to the imprisonment and trial of Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr. Around the same time, SaM also began an online countdown for the Nimr verdict and increased their threats against Saudi Arabia. The group also ratcheted up it’s pro-Nimr messaging with the release of numerous images.
This messaging coincided with Saraya al-Mukhtar making its first direct threat against U.S. military personnel in Bahrain on August 11. Through an image posted to Facebook, SaM stated that, “The American cover on al-Saud and Al_Khalifa crimes,,Marines in bahrain will pay the price. [sic]” The message essentially claimed that the U.S. was the real backer for the Khalifa and Saud monarchies. As a result, they bore equal responsibility and could be targeted.

Figure 1: Saraya al-Mukhtar’s anti-American message posted on August 11, 2014.

Figure 2: A Saraya al-Mukhtar photo for Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr posted on August 8, 2014. The poster reads: “Sheikh Nimr[‘s trial and poor treatment] will make us put all options on the table.”

Figure 3: A Saraya al-Mukhtar photo posted on August 10, 2014. This poster reads: [in the red box] “A warning from Saraya al-Mukhtar to the mafia of the Sauds [in white text] Harming Sheikh Nimr will make us put all options [on the table]. Harming the Faqih Nimr means every single Saudi national will enter our country in a coffin.”

Figure 4: A Saraya al-Mukhtar photo for Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr posted on August 11, 2014. The poster reads: “Do not hesitate, Do not underestimate, No red lines.. after [the] discrimination [against] the Faqih al-Nimr.”
On September 16, SaM announced it had planted 6 explosive devices in retaliation for al-Nimr’s incarceration. Albeit, these bombs did not target U.S. interests and there was little confirmation as to whether any devices were actually planted.
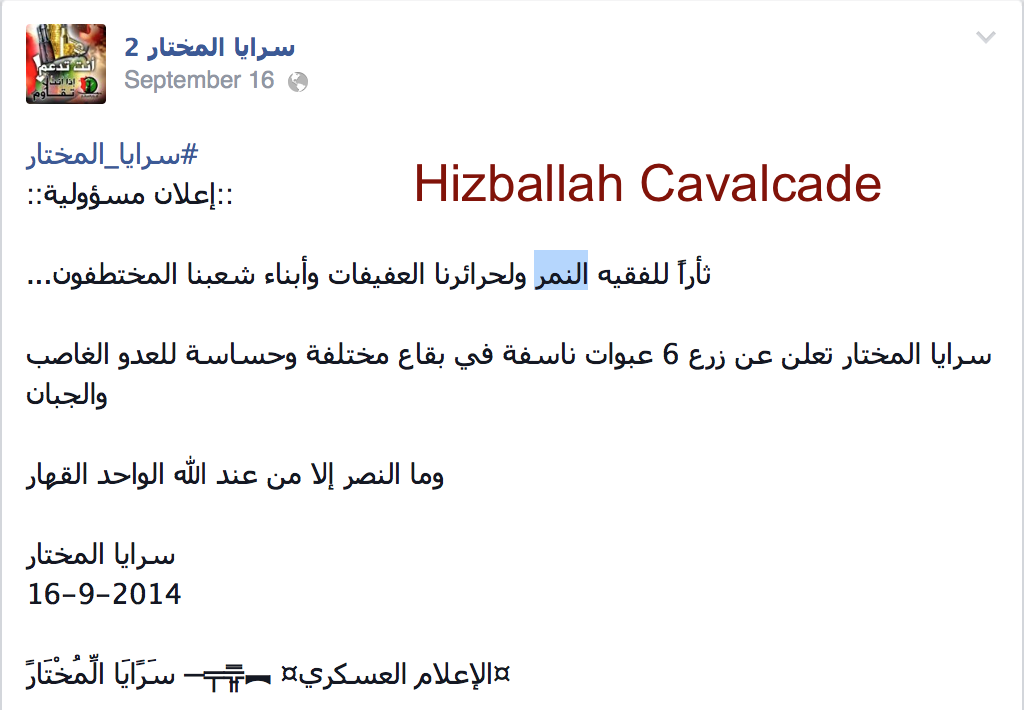
Figure 5: Saraya al-Mukhtar’s September 16 claim to have planted 6 bombs.

Figure 6: Saraya al-Mukhtar’s claim of 2 attacks on October 18, 2014.
Then on October 9, SaM claimed to conduct an attack in the town of Karana, Bahrain utilizing an improvised firearm. SaM’s claim of responsibility stated they attacked, “herds of mercenaries” (shorthand for Bahraini police and other security entities). On October 15, SaM claimed to have launched attacks in Sanabis and Aker, Bahrain targeting “mercenaries”. In another statement from that day, the group threatened, “The occupying mafia of al-Saud and al-Khalifa [would face]…consequences for the death sentence.” Later, on October 18, SaM claimed two attacks, referring to them as “Revenge of the Faqih [an expert in Islamic jurisprudence] Nimr.” SaM’s statement declared that it had injured “ranks of the enemy occupier.”
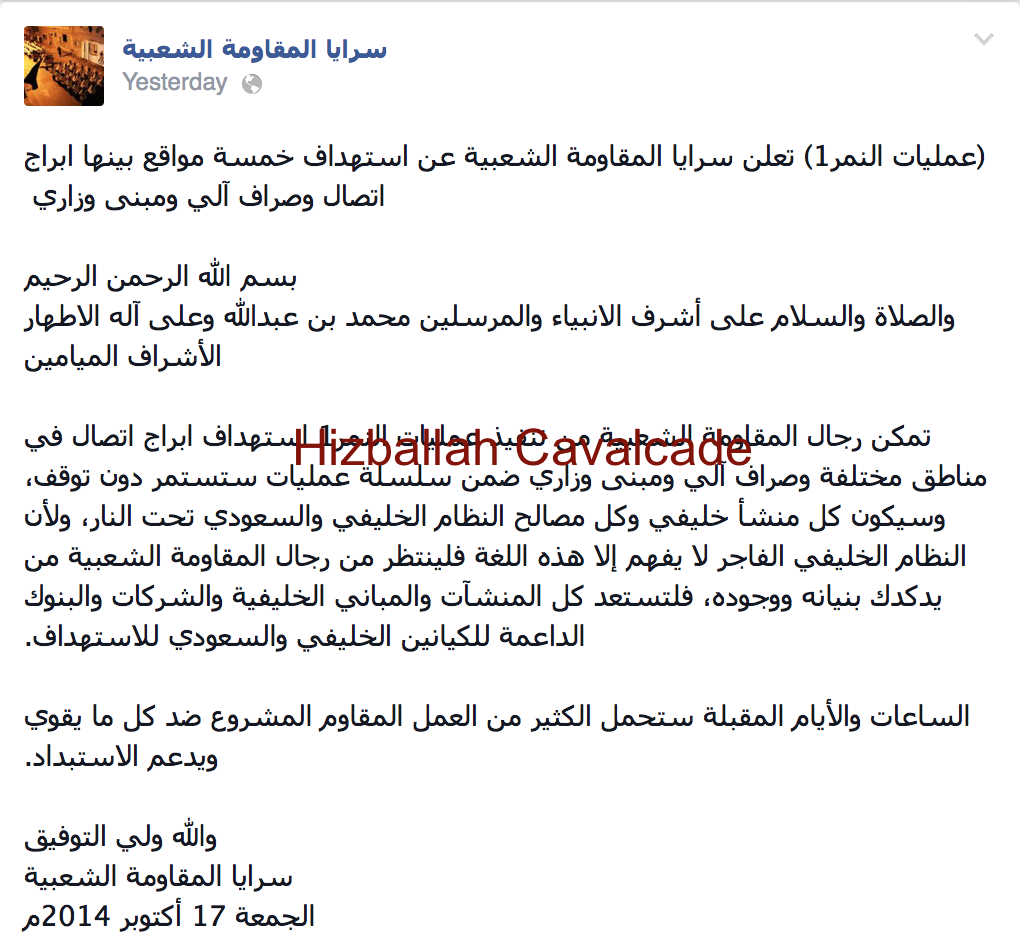
Figure 7: SMS’s claim of attack in honor of Sheikh Nimr.
Bahraini militant group, Saraya
Hizballah Cavalcade: Ansar Allah al-Awfiyya: One of Many New Khomeinist Militias in Iraq
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
–
Ansar Allah al-Awfiyya: One of Many New Khomeinist Militias in Iraq
By Phillip Smyth

Figure 1: AAA’s logo. The symbol features the fist-gripping-a-Kalashnikov symbol, which is nearly ubiquitous among Iranian proxy groups.
On August 10, 2014, Ansar Allah al-Awfiyya (The Loyal Partisans of God or AAA), a Shia jihadi militia, announced its existence via Facebook and cast itself as a militia whose purpose is to assist in fighting Sunni Jihadi groups such as the Islamic State (IS, also known as ISIS or the Islamic State of Iraq and al-Sham) and the “Ba’athists” (likely a reference to the Naqshbandi Army or JRTN). Two weeks following its declarations of existence, the group had already reported its first losses.
The group has cast itself as supportive of the Iranian Supreme Leader and attempts to appeal to Iraq’s large Sadrist Movement (Al-Tayyar al-Sadri) by incorporating images of the late Ayatollah Muhammad Muhammad Sadiq Sadr.
Proxy Overlap

Figure 2: A “martyrdom” poster released for a Liwa al-Hamad militant killed in Syria. The poster was circulated by and featured the logo of KSAI’s media wing.
While new and relatively unheard of, AAA did not emerge from a void. As with other Iranian proxies, the group has listed itself as one of the many groups belonging to “al-Muqawama al-Islamiyyah fi al-Iraq” (“The Islamic Resistance in Iraq”). Yet, its “Muqawama” credentials are simply one piece to a larger interconnected Iranian proxy network.
Shaykh Haydar al-Gharawi, Secretary General of Kayan al-Sadiq w al-‘Atta fi al-Iraq (KSAI or The Group of Honesty and Caring in Iraq) announced AAA as a militia associated with his small Maysan Province based party. LSAI has been politically active since 2012 and has had members serve on Maysan’s provincial council. In June, one LSAI leader on Maysan’s provincial council declared the province would allocate billions of Iraqi dinars to assist with training for volunteer fighters.1
KSAI has also promoted its association with Akram Kaabi, the Secretary General of Liwa al-Hamad’s parent group, Harakat Hizballah al-Nujaba. Since HHN has sub-militia groups, such as Liwa Ammar Ibn Yasir and Liwa al-Imam al-Hasan al-Mujtaba, it appears that KSAI has the most extensive links with HHN’s Liwa al-Hamad. These associations were exposed via Facebook posts earlier in 2014 via the posting of “martyrdom” notices from the group about a member killed fighting as part of Liwa al-Hamad. Additionally, the same style of graphics used for Liwa al-Hamad’s online posts are replicated. Further demonstrating the deep links between Liwa al-Hamad and AAA, Liwa al-Hamad’s official Facebook pages have even adopted the logo of AAA.

Figure 3: A “martyrdom” poster for a HHN member. The image is the same model used by AAA.

Figure 4: A “martyrdom” poster for Liwa al-Hamad. This model is the same as AAA’s “martyrdom” imagery.

Figure 5: Liwa al-Hamad’s official Facebook page has also adopted the AAA logo.
Ansar Allah al-Awfiyya has also claimed it is affiliated with Harakat Ansar Allah al-Awfiyya, (The Movement for the Loyal Partisans of God). It is unknown whether the group is attempting to market itself as a separate or unified movement with LSAI, or simply using the term “Harakat” (“Movement”) to appear larger and/or more developed. Nevertheless, the creation of multiple interlinked groups utilizing commanders who were members of other established organizations is a common strategy within the realm of Iran proxy militias.2
Ansar Allah al-Awfiyya Joins the Battle
AAA has not yet announced the areas of Iraq in which their armed forces are operating. However, other details have emerged. Shaykh Haydar al-Gharawi, the Secretary General of KSAI has now been simultaneously described as AAA’s Secretary General. From released images, the group appears to follow the same types of tactics utilized by other groups when they have gone about asserting their presence in the arena of Iraqi Shia militias. The group has pressed civilian vehicles into service and declared the deaths of two members, including a commander, Muhammad Abdul Amir Ibrahim al-Assadi.
It is likely AAA is organized along the lines of other Iranian proxies, with the militia borrowing fighters from other established organizations in order to appear more powerful and established. Nevertheless, since the group already has a strong regional influence, it is possible it can count on the regional populace it represents to assist with the recruitment of new fighters.

Figure 6: “Martyrdom” poster for an AAA member announced killed on August 31, 2014.

Figure 7: AAA commander Muhammad al-Assadi was declared killed while fighting in Iraq in a number of posts on August 24, 2014.
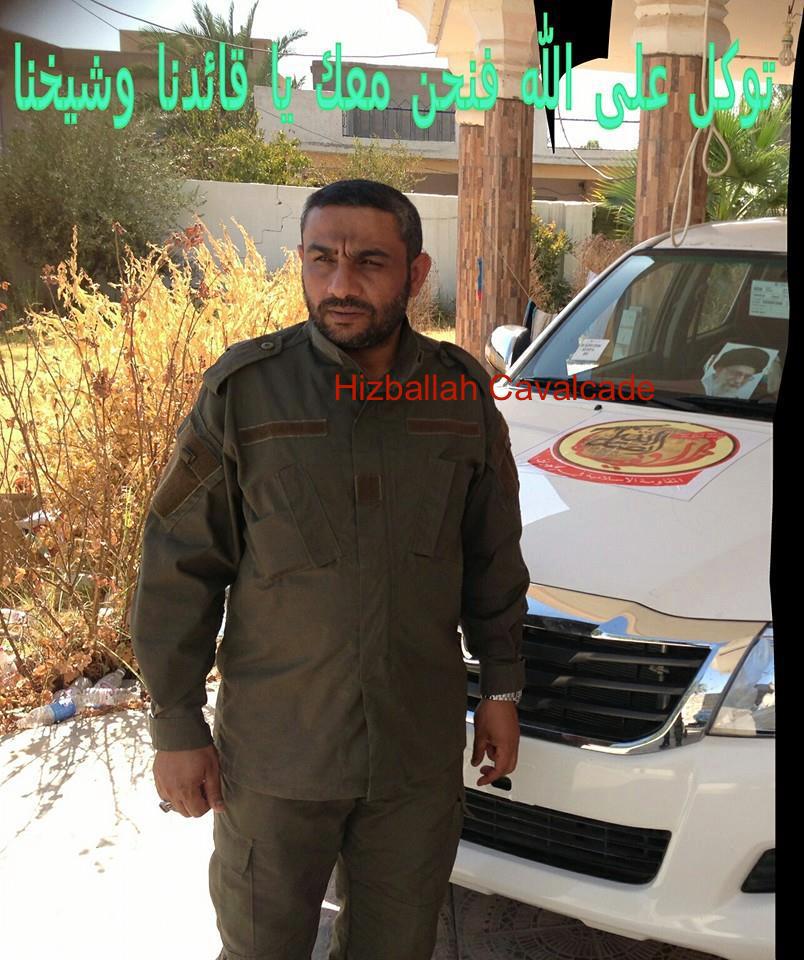

Figure 8: AAA’s secretary general, is shown in uniform posing in front of a car featuring the group’s logo and a poster of Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei.
_____________
NOTES:
New article from Shaykh Abū Basīr al-Ṭarṭūsī: "The Sunnah of Iraq Between Two Swords: The Sword of the Ghulāt al-Rawāfiḍ and the Sword of the Ghulāt al-Khawārij"

Click the following link for a safe PDF copy: Shaykh Abū Basīr al-Ṭarṭūsī — “The Sunnah of Iraq Between Two Swords- The Sword of the Ghulāt al-Rawāfiḍ and the Sword of the Ghulāt al-Khawārij”
___________
To inquire about a translation for this article for a fee email: [email protected]
Hizballah Cavalcade: IRGC's First Martyr vs. ISIS in Iraq?
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
IRGC’s First Martyr vs. ISIS in Iraq?
By Phillip Smyth
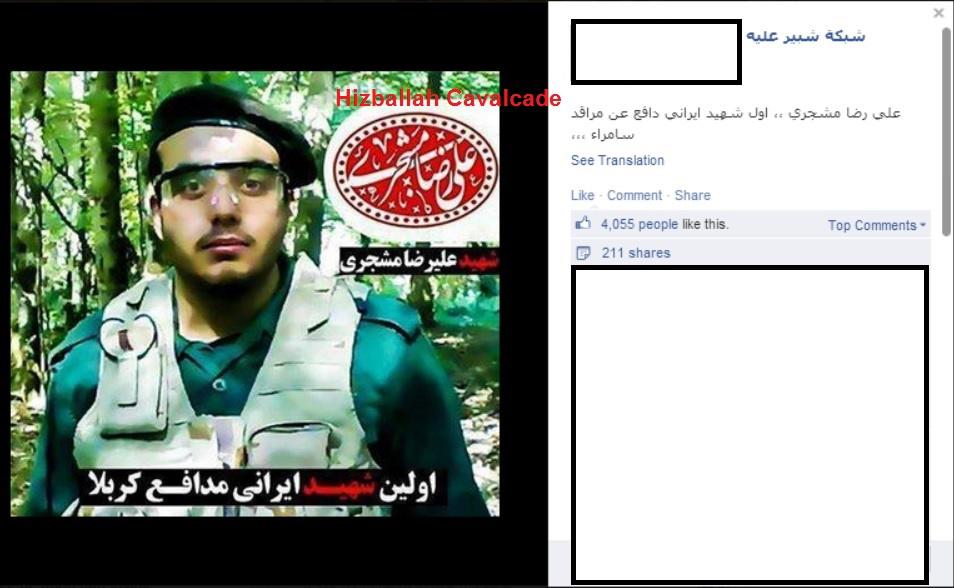
Figure 1: Post claiming the IRGC member was killed fighting in Samarra.
According to Iranian media outlets Ali Reza Moshajari, a member of Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), was reportedly killed in an accident on June 14, 2014.1 In another article written by the IRGC-linked Tasnim News, Moshajari was killed in “Western Iran” while on “a mission.” In all of the articles he is described as a “martyr” or “hero martyr.” However, his death was not such an open and shut case. In fact, Moshajari’s death may be further evidence of direct IRGC presence in Iraq.
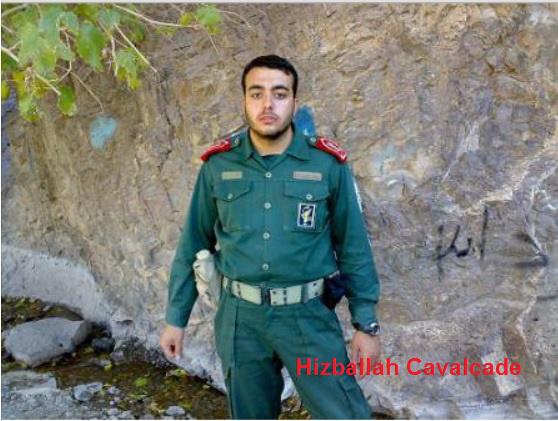

Figure 2: Moshajari in his IRGC uniform.
Before official announcements were made by groups such as Kata’ib Hizballah or Lebanese Hizballah stating they were both involved in fighting in Syria, both organizations would give vague explanations for the funerals of their members. The former would claim members had died due to illness or for other non-combat related reasons. Lebanese Hizballah would often only state that their fallen fighter had been “killed doing his jihadist duty.” Nevertheless, on social media run by many of these elements, it would be stated that the fallen fighters had in fact been killed in Syria. This may be the same type of structured announcement.
In some ways, this mirrors the announcements for the fallen IRGC member who was not only listed as a martyr for battle on a mission of some sort, but had competing accounts for how and where he died.
On Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps-linked (often these pages are run directly by the IRGC for internal and narrative purposes) social media networks–which run the gambit from Twitter and Facebook to Google Plus and YouTube—have cast Moshajari as an IRGC fighter who had been “martyred” in the IRGC deployment to Iraq.
It is possible that Moshajari was actually killed in an accident while deploying with IRGC units to sections of Iraq bordering Iran. CNN reported that 500 IRGC had been deployed to Diyala, an Iraqi province on the border with Iran.2 In Diyala Province, Kata’ib Hizballah and other Iraqi Shia Islamist groups backed by Iran have also reported being engaged in combat against units belonging to the Islamic State of Iraq and al-Sham (ISIS).
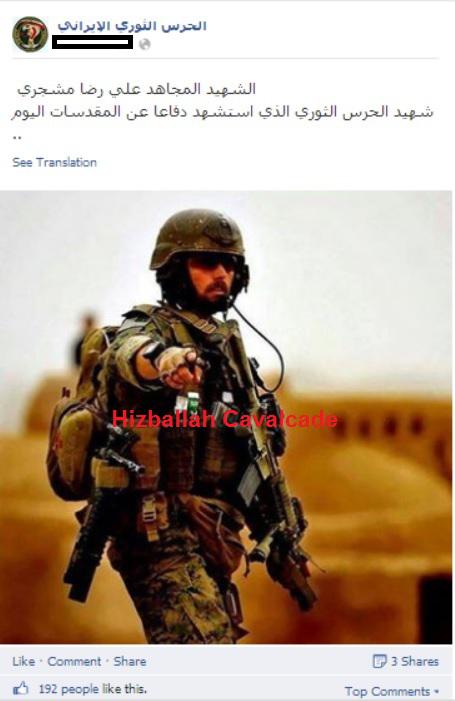
Figure 3: An IRGC Facebook page claiming Moshajari was the first IRGC martyr in Iraq while defending the shrines.
However, other Facebook-based sites with links to Iran’s regional Shia Islamist proxies and the IRGC also claimed that he had been involved in the “defense of Samarra.” Samarra has been a city of heavily publicized deployments by Iran’s Shi’a Islamist proxies within Iraq, mainly due to the fact that the holy Askari Shrine is located in the city.

Figure 4: Killed IRGC member’s martyrdom poster. The poster was circulated primarily on Facebook and Twitter. It claims he was an “Iranian defender of Karbala.”
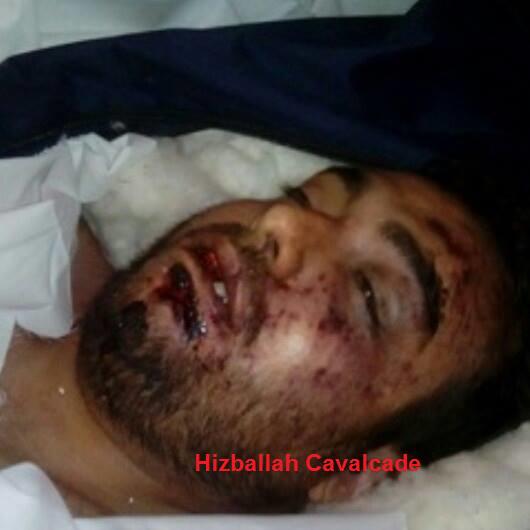

Figure 5: A photo of Moshajari’s face prior to his funeral.
_________
NOTES:
Hizballah Cavalcade: Singing Hizballah’s Tune in Manama: Why Are Bahrain’s Militants Using the Music of Iran’s Proxies?
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
–
Singing Hizballah’s Tune in Manama: Why Are Bahrain’s Militants Using the Music of Iran’s Proxies?
By Phillip Smyth
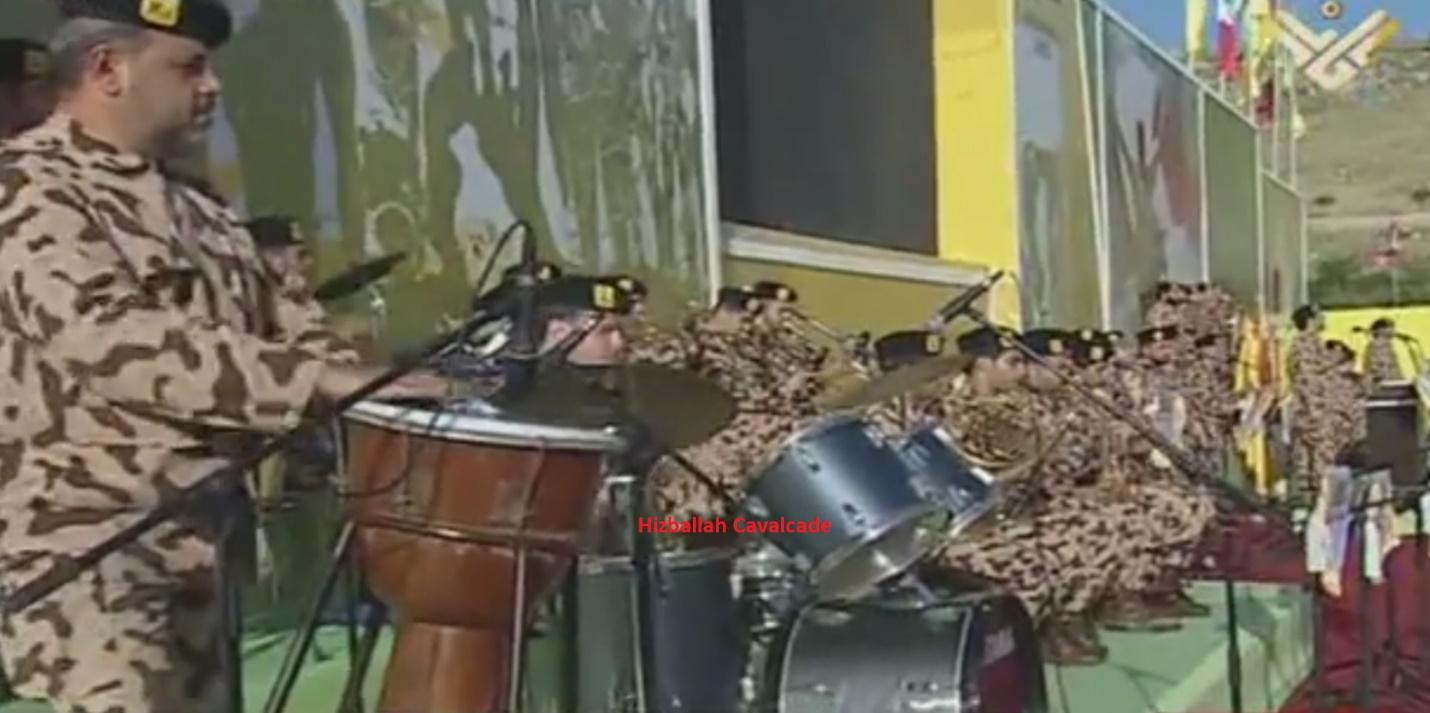

Figure 1: A screenshot of a Hizballah musical band performing at the 2013 “Resistance and Liberation Festival”
Bahraini officials have repeatedly accused anti-government militants and protesters in the country of being supplied, trained, and supported by Iran and its numerous regional proxies. Still, the government of Bahrain has done little to bolster their claims of deep and intrinsic links between Bahraini militants and Tehran. Along with official Iranian denials, the issue of Iran-Bahraini militant links is still quite hazy. Nonetheless, this does not mean that within the material released by Bahraini militant organizations that there are not hints of some level of Iranian influence. One of the more intriguing pieces pointing to influence from Iranian-backed organizations comes from the utilization of specific types of music in the many propaganda videos released by Bahraini militants, their sympathizers, and amplifiers.
Numerous instances of Bahraini militants producing propaganda videos with different varieties of music created and utilized by Iranian-backed proxies could indicate a connection with Iran’s proxies. Nevertheless, this type of overlap should not be viewed as a “smoking gun” affirming Iranian involvement. However, it does assist in piecing together direct and indirect influences.
The pieces of music in question were originally developed and used by Iranian proxy organizations, particularly Lebanese Hizballah, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq (AAH), and Kata’ib Hizballah. In fact, some of the songs that have been promoted fit a long standing media strategy employed by the aforementioned groups and Iran when manufacturing narratives and perceptions for themselves and other armed groups.
The use of music as a transferable propaganda medium follows a very formulaic strategy used by Iran and its “Islamic Resistance” proxy organizations for many years. Often, songs produced for one group are repackaged for newer organizations in other geographic locations. The songs are then altered in a way to make them appeal to the populations and target audience where the new group is located.
Possible Reasons for Using Specific Songs
Why would Bahraini militant groups utilize Hizballah and its Iraqi clones’ music and with such frequency? Some possible answers include:
- Direct Iranian influence or assistance provided to the developing militant groups.
- Video editing/production was offered to Bahraini militants by Iran and/or its proxies as a means to influence and shape militant organizations and to encourage the adoption of a more bellicose strategy to the broader (and more peaceful) protester audience.
- Bahraini militants sympathize with Iranian-proxy groups, their exploits, and with the general concept of “Al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya” (“The Islamic Resistance”). The hope to be as successful, feared, and/or respected as those organizations has led them to adopt the same varieties of music.
- Thumbing their nose at the government: With the government of Bahrain accusing protesters and militants of being Iranian proxies, militant groups may use the material as a way to subtly frighten or encourage speculation among Bahraini government and other observers.
- Narrative Goals: One song by Lebanese Hizballah’s Ali al-Attar called “Wa’ad al-Asra” or “The Prisoner’s Promise” was written to celebrate the release of prisoners Hizballah sought to free during the 2006 Hizballah-Israel War. While the song makes clear references to Lebanese Hizballah and themes related to the 2006 war, the same song was employed by some Bahraini protesters (as background music for their uploaded clips) when they protested the government’s detention of key protest-leaders.
Auto-Tuning the Revolution: Examples of the Musical Overlap
In March 2014, a music video which was claimed to have been produced by “Saraya al-Bahrainiyya al-Muqawama” or the Bahraini Resistance Brigades, (which is likely another name used by The February 14 Youth Coalition’s Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya [Popular Resistance Brigades]) was posted by the popular Revolution Bahrain’s YouTube Channel. The video featured a montage of edited clips, which purported to show Bahraini militants engaged in training. The music video also included a number of videos of bombings orchestrated by militant Bahraini organizations.
Yet, the music used was strikingly familiar in the circles of Iranian-backed Shi’a Islamist groups. In fact, Iranian-backed Iraqi group, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq had released the exact tune back in 2011 to commemorate attacks the group orchestrated against U.S. targets to demonstrate solidarity with Bahrain’s protesters. Later in 2011, when fellow Iranian proxy Kata’ib Hizballah released footage of attacks it had also launched in solidarity with Bahraini protesters, it too used the same song.
However, the song was neither originally Bahraini nor Iraqi, instead its origins were rooted father to the west, in Lebanon. The original song, “Risalat al-Thuwar” (“Message of the Rebels”), was performed by one of Lebanese Hizballah’s official bands, Firqat al-Fajr (The Dawn Band), following the 2006 Hizballah-Israel War. It first appeared on the band’s 2007 “Lahan al-Turab” or “Melody of the Soil” album. Still, the rendition dealing with Bahrain was not the only version of the song. Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq had their own Iraq/Grand Ayatollah Muhammad Muhammad Sadiq Sadr (as opposed to Sayyid Hassan Nasrallah) themed “Risalat Thuwar” produced in 2011.
“Risalat al-Thuwar” is not the only Hizballah song which has been adopted and rebranded by Bahraini militants and their amplifiers. Another song used by Bahraini militants also comes from Firqat al-Fajr. The song, “Ya Wa’ad Allah” (“O Promise of God”) can be found on the group’s 2008 album, “Sharit Wa’ad Allah” (“Take the Promise of God”). The song has been released in different formats, with more recent music video varieties showcasing the assassinated Hizballah terror-mastermind Imad Mughniyeh. The album also included an instrumental version of the song. Both versions have been prominent features on productions done by Hizballah’s Al-Manar TV network.
In Bahrain, “Ya Wa’ad Allah” was used as background for clips released to the popular (particularly with militant groups) Revolution Bahrain’s YouTube account. One of these videos included the firebombing of an armored car used by Bahraini government forces.
It is not just the polished music video-quality material finding its way into Bahraini militant propaganda productions. Bahraini militant group Saraya al-Mukhtar released a video of their April 2014 targeting of Bahraini police with an improvised explosive device. Another bomb attack in Bani Jamra also utilized the same background music.
The musical selection in the background matched with instrumentals used by Iraq’s Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq. This music was first featured on the AAH-affiliated Al-Ahad TV in the late summer/fall of 2013 to commemorate Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq members killed fighting in Syria. Further pointing to some level of Iranian or Iranian proxy influence, is highly unlikely that this particular musical element could find its way into so many pieces of released footage. This may indicate some Bahraini militant footage being sent abroad (possibly to Iraq) where the footage is re-edited and put back together for a later introduction.
Another similar instrumental used by Bahraini militants with Saraya al-Mukhtar and Saraya al-Ashtar was also the same exact tune utilized in a number of Kata’ib Hizballah video releases (see: 00.17-00.40 on “Kata’ib Hizballah Anti-America Video”).
The use of the last two instrumentals create further questions. Why would these groups, which have resorted to using a variety of improvised weapons, and exist under increasing heavy security crackdowns, spend the time to find, edit, and utilize background instrumentals which already have obscure points of origin. Why pick these two exact instrumentals, which have only been found in the repertoire of Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq and Kata’ib Hizballah? Other Bahraini protest organizations have utilized a variety of different musical accompaniments. Thus, the use of these particular musical pieces seem out of place when compared to the rest of what has been released.
Whatever the reasons, closely assessing the propaganda published by these organizations may provide insight into rather opaque organizations. While assessing the musical selections may appear to be a tangential escapade, AAH, Kata’ib Hizballah, and Lebanese Hizballah have all demonstrated their strategy of using this material as another method to push the narrative of the “Islamic Resistance.”
Hizballah Cavalcade: Asa’ib al-Muqawama al-Bahrainia: An Emerging Militant Group in Bahrain?
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Asa’ib al-Muqawama al-Bahrainia: An Emerging Militant Group in Bahrain?
By Phillip Smyth

Figure 1: Asa’ib al-Muqawama al-Bahrainia’s logo.
Asa’ib al-Muqawama al-Bahrainia (The League of Bahraini Resistance or AMB) was first established and marketed as an independent militant organization on February 22, 2014. The group’s founding announcement claimed that the time had become ripe for armed opposition against Bahrain’s ruling monarchy due to the government’s actions. As with other Bahraini militant groups, little is known about AMB’s manpower or armed capabilities.
Regardless, unlike other Bahraini militant organizations, AMB’s founding announcement has found its way onto many different online venues catering to a wide range of readers.[1]
AMB’s statements appear online in bursts. February 22 and February 28, 2014 have been the two dates this organization has placed a series of announcements in public. This pattern is reminiscent of another Bahraini organization, a proto-militant group which went by a similar name, Asa’ib al-Muqawama (The Resistance League). Using Twitter, Asa’ib al-Muqawama released 33 announcements (in both Arabic and English) between April 21 and 22, 2012. Asa’ib al-Muqawama’s threats centered on Bahrain’s controversial Formula One race. One of these statements claimed responsibility for planting three homemade bombs at the race location. At time, there were also instances of Molotov cocktails being thrown at some (from Team India) affiliated with the race.[2] Additionally, on April 9, 2012, seven Bahraini police were wounded due to an improvised bomb planted in the town of Akr.[3] Albeit, neither of these attacks were linked to Asa’ib al-Muqawama.
After their last tweet on April 22, 2012, Asa’ib al-Muqawama went quiet. This is similar to how AMB went silent after their last February 28, 2014 statement. There is a possibility of a link between AMB and Asa’ib al-Muqawama, considering the groups espouse the same militarism, utilized a similar name, and have released announcements in bursts over two-day periods. In fact, AMB’s official Twitter account also describes itself as “Asa’ib al-Muqawama.” It is possible that AMB developed out of the original Asa’ib al-Muqawama. However, beyond these assumptions, there is little substantiating open-source information to assist in confirming any links.

Figure 2: Asa’ib al-Muqawama’s English language Tweet-announcement, declaring they had planted 3 bombs at the Bahrain F1 race.

Figure 3: Asa’ib Muqawama’s logo.

Figure 4: AMB’s first announcement.
On February 28, 2014 AMB announced the launch of their, “Fist of Righteousness” operation to avenge the death of Ja’afar al-Derazi. Derazi, whose burial occurred the day of the announcement, was a 22 year old anti-government activist. According to opposition and pro-Iran sources, Derazi died due to torture and other forms of maltreatment when he was detained within a government jail cell.[4] In revenge for Derazi’s death, on April 11, 2014, Saraya al-Mukhtar claimed responsibility for an attack targeting Bahraini police. Nevertheless, AMB has not yet claimed any other attacks as part of their “Fist of Righteousness” campaign.

Figure 5: AMB’s second announcement from February 28, 2014.
AMB Joins YouTube
AMB’s official YouTube account claimed to release a video introducing the group on February 21, 2014. However, the first publicly accessible copy of the video was uploaded and released on February 22, 2014. In the video, supposed AMB members are shown marching in formation, extending their arms in a Roman salute. Demonstrating their potential roots as militant offshoots of the larger Bahraini protest movement, young balaclava wearing men hold tires in one of their displays. Tires are a regular feature in some protests; often laid across stretches of road, coated in gasoline, and lit on fire.
Furthering religious themes was also a feature of the film. Young marching militants are seen holding Qurans, wearing white (in addition to other colors) burial shrouds symbolizing a willingness to be martyred, and holding flags with “Ya Husayn” (“O Husayn”) written on them. The “Ya Husayn” flags symbolize a Shia-centric theme, recalling Husayn’s martyrdom via beheading, at the pivotal Battle of Karbala.[5] These flags have also made regular appearances during anti-government protests.
The promotional clip also claims to show AMB launching operations against internal security elements (primarily the Bahraini police). Segments of film featuring Molotov throwing youths are a main theme. However, these clips are usually from earlier films recorded by more violent activists associated with the February 14 Youth Coalition. It is possible this footage demonstrates a further link to the February 14 Youth Coalition or it was simply repackaged by AMB to show a broader theme surrounding the “resistance” against the Bahraini government and their forces.
AMB also appears to have a preoccupation with utilizing weapons which can burn their foes. This may be the result of protester use of Molotov cocktails. Utilizing the limited available tools, some Bahraini protesters, particularly younger male militants, have often thrown Molotov cocktails at Bahraini internal security forces. The theme of the Molotov thrown at Bahraini police, particularly their vehicles, was regularly utilized in AMB’s introductory video. However, the focus on using weapons which can kill and injure using fire does not appear to stop with Molotovs. In one part of their video, AMB shows Bahraini police engulfed in a wall of flame, likely caused by a bomb or another incendiary device.
AMB’s Badge
AMB’s logo may also show links to Saraya al-Ashtar (SaM), one of the first publicly established Bahraini militant organizations. Featuring two crossed M16-style rifles within a circle (which could potentially symbolize a pearl, a recognized emblem of Bahrain), the group’s logo mirrors SaM’s official symbol. This logo also included two crossed rifles (albeit, of the Kalashnikov variety) within a circle representing a pearl.
An Asa’ib of Their Own?
When investigating potential links between AMB, Iran, or Iranian-backed proxies, there was some evidence of overlap between AMB & Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq (AAH). On March 13, 2014, AMB’s founding statement was circulated on AAH’s extensive network of Facebook pages. This often coincided with claims that AMB was representative of AAH’s spreading brand. Claims of this nature may be an Iranian proxy attempt to demonstrate a substantial link to the Bahraini militant group. Both groups utilize similar language, with AMB describing itself as the “Bahraini Resistance” and AAH calling itself the, “Islamic Resistance in Iraq.” Still, there is the possibility that AAH could be jumping on an organically constructed (in Bahrain) group while skillfully playing on AMB’s similar name, all in an effort to claim a connection and demonstrate a broader reach. It is important to note that it took AAH nearly a month before pages associated with the group started to carry AMB’s founding statement.
Another potential link includes religious and ideological themes. The AMB’s founding statement mentioned the group was following their taklif. A taklif, or religiously mandated order, was developed and utilized for political and social events by those embracing Iranian Islamic Revolutionary concepts.[6] The mention of a taklif mirrors a similar statement made by fellow Bahraini militant group, Saraya al-Mukhtar, which also mentioned they were picking-up arms against the government due to a taklif.
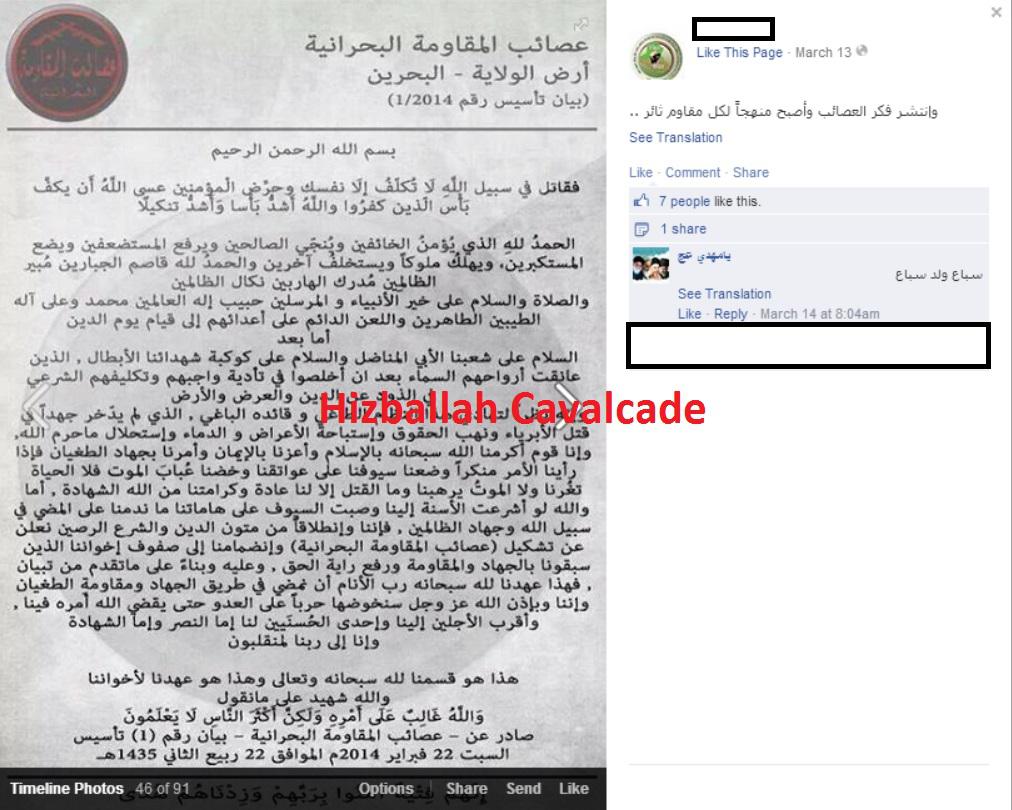
Figure 6: A post promoting the first AMB declaration on an official Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq Facebook page.
Is AMB Dormant?
At the time of this writing, the last statement issued by AMB was released via their Twitter account on February 28. Since that time, AMB has not itself claimed any new attacks, seen related militant groups, protest organizations, or the official Bahraini media, cite any new actions by the group. While little has been heard from this organization since it’s nearly 2 month-long period of silence, AMB’s release of formal statements, broad web-presence (including their YouTube video release), overlap between itself and other Bahraini militant groups, and other attack claims, may indicate AMB is still active.
AMB’s activities may be continuing as members of the organization act as integral elements within other Bahrain militant groups. If there is a true link between the AMB and Asa’ib al-Muqawama, it is possible that following the established model, a new wave of attack-claims could be registered on an entirely new online/social networking apparatus.
Nevertheless, until AMB claims another attack or has an allied organization claim an attack for them, it will be impossible to know what has become of this group
_____________
[1] Note: Numerous Sunni Islamist and Shia Islamist forums, Facebook
New statement from Jabhat al-Nuṣrah in Lebanon: "Blessed Martyrdom Operation on the Stronghold of the Dreaded Ḥizb Irān in the Region of al-Nabī 'Uthmān”

Click the following link for a safe PDF copy: Jabhat al-Nuṣrah in Lebanon — “Blessed Martyrdom Operation on the Stronghold of the Dreaded Ḥizb Irān in the Region of al-Nabī ‘Uthmān”
__________
To inquire about a translation for this statement for a fee email: [email protected]
Hizballah Cavalcade: Bahrain’s Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya: Militants of the February 14 Youth Coalition
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Bahrain’s Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya: Militants of the February 14 Youth Coalition
By Phillip Smyth

Figure 1: Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya’s logo.
Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya (The Popular Resistance Brigades or SMS), sometimes also called Saraya al-Muqawama (The Resistance Brigades), was listed by the government of Bahrain as a terrorist organization following the deadly March 3, 2014 bombing. The group, along with fellow militant group Saraya al-Ashtar, claimed responsibility for the attack. SMS has been operationally active and publishing its activities online since April 2012. Importantly, Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya does not hide that they are affiliated with one of the main anti-government protest groups, the February 14 Youth Coalition (which was also listed as a terrorist organization by the government of Bahrain). This is hardly a minor connection, since, both the February 14 Youth Coalition and SMS have also distributed images sharing one another’s logos, organized events (such as protests) together, and share a similar narrative. Other militant groups—namely Saraya al-Ashtar and Saraya al-Mukhtar—have only vaguely claimed to represent links to protestors, let alone main protest organizations.
In June 2013, the Bahraini government accused the February 14 Youth Coalition of having a “spiritual leader” based in Karbala, Iraq and of, “frequently travel[ing] between Iran, Iraq and Lebanon to obtain financial and moral support as well as weapons training.” However, Bahraini authorities provided little substantiating evidence dealing with claims of Iranian or Iranian proxy involvement. Nevertheless, according to Iranian reports, February 14 Youth Coalition representatives have thanked Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei for his comments supportive of their activities. Iranian media has also expressed their support for the “revolutionary activities” of the Bahraini group. Despite these pronouncements, the actual relationship between Iran and the February 14 Youth Coalition, particularly dealing with any attempts at training or equipping militant elements attached to the organization, is still unknown.

Figure 2: Both the February 14 Youth Coalition and Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya’s logos on a promotional image released onto multiple February 14 Youth Coalition pages.
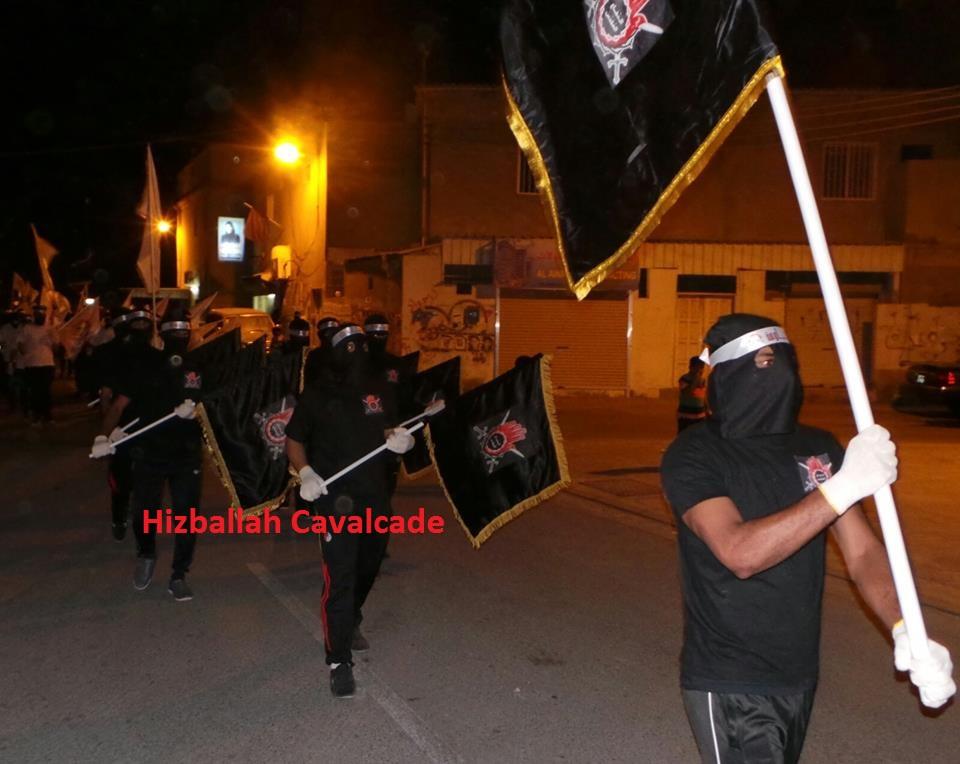

Figure 3: SMS supporters carry the group’s flag during a march.
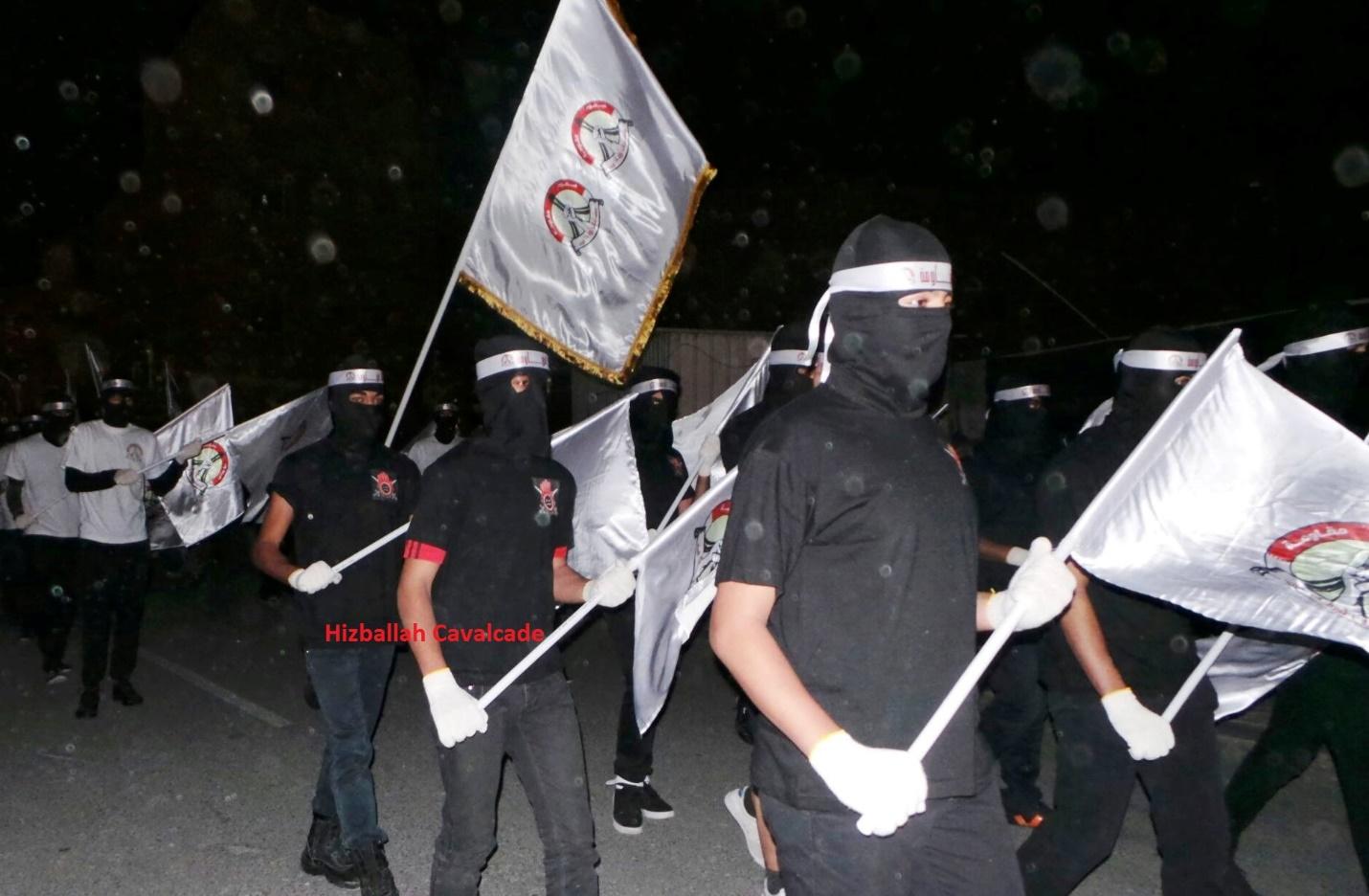

Figure 4: SMS and February 14 Youth Coalition supporters march together and carry February 14 Youth Coalition flags.
Initially, the February 14 Youth Coalition did not embrace violence. However, after publishing a series of “warnings” to the Bahraini government, Gulf Arab states (namely, Saudi Arabia and the UAE) which have deployed forces to Bahrain, and foreigners recruited into the Bahrain’s internal security forces (often referred to by the group and other Bahraini militants as, “mercenaries”), the coalition issued communiques demonstrating they would choose a more militant path of “resistance.” In a January 27, 2012 English-language statement made by a February 14 Youth Coalition affiliated page, the group issued a statement reading:
“We have so far preserved our right to use force for self-defense, hoping that would make you hesitant from attacking peaceful protestors, women and children. However, common sense and human logic do not seem to work on you…Our people have decided to bring an end to the illegitimate regime…We shall take no responsibility for whatever might happen to the mercenaries after this final warning.”

Three months after this announcement, SMS pushed for a response to the holding of the controversial 2012 Bahrain Grand Prix Formula 1 race. The group released images urging protestors to throw the gas (the group claimed it was poisonous) used by Bahraini police at the race cars. However, no armed action was taken against the race by SMS. It is likely that in such an early stage of development and combined with Bahraini government crackdowns, the group was unable to act.

Figure 5: One of SMS’s English language posters calling for action against the 2012 Grand Prix race.
Narrative Structure
SMS considers its fighters to be “jihadists,” refer to their attacks as “jihadist operations,” and believe they are fighting a “jihad against the infidel Khalifas [Bahrain’s ruling royal family].” While the message of jihad is repeated in many SMS statements, these statements do not share the same level of more complicated religious and ideological messaging found with other non-Bahraini Shia jihadist elements.
SMS also lacks a specific goal for what type of government will rule in Bahrain following a theoretical collapse of the currently ruling Khalifa royal family. Still, this has not stopped the group from constructing complex narratives via militant activity for their enemies.
Following Saraya al-Ashtar’s and SMS’s claim of responsibility for the March 3, 2014 bombing (which killed two Bahraini police officers and a police officer sent by the United Arab Emirates [UAE] to Bahrain), SMS used the opportunity to criticize government claims that forces of the Peninsula Shield Force were being used in conjunction with local Bahraini police forces to counter protests and riots.
Sent to Bahrain in 2011, the Peninsula Shield Force included hundreds from the Saudi military and the UAE’s police force. Officially, these units claimed they were not involved in internal matters in Bahrain and were only interested in securing strategic bases and locations from “external influence.” Regardless, the death of a UAE police officer attached to Bahraini police served as a propaganda coup for SMS.
The timing of the SMS’s bombing claim and messages which proceeded it also fit into a broader message dealing with the Peninsula Shield Force and particularly Saudi Arabia. SMS has demonstrated a specific ire for the Saudis. The organization’s communiques have called Saudi Arabia the “usurper of land,” “occupiers,” and have stated their operations are to “purge the land of its Saudi and Khalifa occupiers.”
In part, this may tie back to February 14 Youth Coalition links to Saudi Shia activists. Researcher Fredric M. Wehrey noted that an “important attribute of the February 14 Youth Coalition is its strong affinity with Shi’a activists in neighboring Saudi Arabia.” Wehrey went on to explain how coordinated protests were conducted by Bahraini and Saudi groups out of solidarity. The February 14 Youth Coalition’s and SMS’s links to the Saudi Shia is also important when viewed in context with announcements by fellow militant organization, Saraya al-Mukhtar. Saraya al-Mukhtar has issued a number of announcements saying they share the cause of the “people of the [Saudi] Eastern Region” –an area heavily populated by Saudi Shia. The shared narrative may demonstrate deeper links between Saraya al-Mukhtar, SMS, and the February 14 Youth Coalition.

Figure 6: A poster released by the February 14 Youth Coalition asking, “Who are the terrorists?” The photo shows Saudi forces crossing the King Fahd Causeway which links Bahrain to Saudi Arabia.
As part of the view casting the Saudis as foreign occupiers, activists from SMS and the February 14 Youth Coalition have drawn parallels between Israel and Saudi Arabia; accusing both counties of using the same techniques of occupation. Prior to a series of March 2014 protests against “Saudi occupation”, the February 14 Youth Coalition and SMS circulated images attempting to link Saudi Arabia and Israel as fellow occupying states. This also extended into the realm of February 14 Youth Coalition partisans attempting to directly link the causes of Palestinian and Bahraini demonstrators.

Figure 7: The Israeli flag flies behind Jerusalem’s Dome of the Rock (left) while a bulldozer is shown destroying the 400 year old Amir Mohammed Braighi Mosque with a Saudi flag behind it (right). The latter incident occurred in 2011 along with the Bahraini government destruction of other Shia mosques. This picture was used as a tool to organize activists for protests and events against the “Saudi occupation.”

Figure 8: A poster showing a Bahraini protester (with February 14 Youth Coalition) and a Palestinian activist. The former looks to the now demolished Pearl Roundabout statue, the latter looks to the Dome of the Rock. The picture attempts to show a unity of purpose and cause between Palestinian and Bahraini demonstrators.
Symbols of the “Popular Resistance”
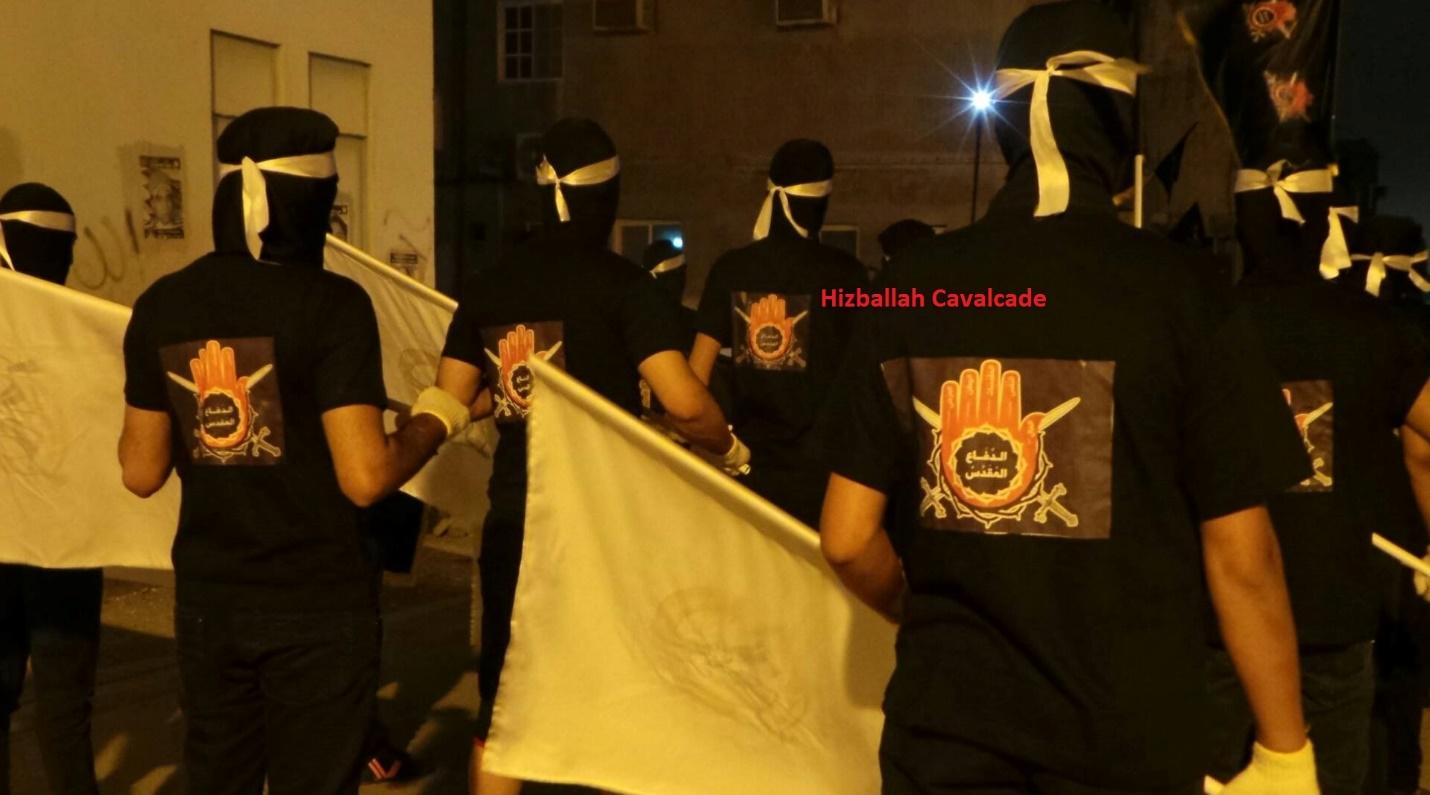

Figure 9: SMS protesters at a February 14 Youth Coalition event demonstrating against “The Saudi Occupation.”
Shia symbolism is heavily featured in the group’s logo. The most prominent image is the symbolic hand of Shia leader Abbas Ibn Ali; son of the first Shia imam and loyal aid and military leader for the third Shia imam, Husayn ibn Ali. Serving as Husayn’s flag bearer during the historic Battle of Karbala, Abbas’s hand was cut off by one of the forces of Yazid, the reviled leader of the Umayyads, as Abbas went alone to collect water for Husayn’s dehydrated camp. Abbas went on to fight singlehandedly until his other arm was cut off by sword strikes from Yazid’s forces and was then killed. Abbas’s loyalty and steadfastness until being cut down remains an important message for many Shia Muslims.
Another unique feature from the logo is that “The Sacred Defense” is written within the symbolic hand of Abbas. This helps convey that the group’s conflict with the government is viewed as both a defensive and religiously justified action. Intriguingly, the Shia jihad in Syria and the Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988) have (by Shia actors) both been described as “The Sacred Defense.”
Behind the
al-Awzā’ī Foundation for Media Production presents a new statement from the ‘Abd Allah ‘Azzām Brigades: "On the Raid of the Iranian Cultural Center in Beirut"

Click the following link for a safe PDF copy: ‘Abd Allah ‘Azzām Brigades — “On the Raid of the Iranian Cultural Center in Beirut”
_____________
To inquire about a translation for this statement for a fee email: [email protected]
