NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
The Big Picture Behind Kata’ib Hizballah’s Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) Threats
By Phillip Smyth
First appearing on March 15, 2014 and posted to social media accounts linked to Kata’ib Hizballah (these included simultaneous posts on Facebook and Youtube)1, a video showing what appeared to be SA-7-type and SA-18-type Man-Portable Air-Defense System (MANPADS) was shown in the hands of Kata’ib Hizballah militiamen.
Interestingly, sections of one of the MANPADS serial numbers were also exposed in the video clip. It is possible the missile systems were not SA-7 and SA-18s, but might actually be an Iranian produced Misagh-type or Chinese produced QW-1-type MANPAD.2 This would not be the first time Kata’ib Hizballah has shown off a MANPAD capability. In 2010, the group released a video showing it possibly launching a QW-1-type missile system.
Technical details on what type of missile system was deployed aside, the video serves as a cap on a developing narrative line which has been promoted by Iran’s Shia militia proxies and via some Tehran’s own media organs.
Claims emanating from Iranian and their other proxy Shia militias have stated that the U.S. and other Coalition allies have supplied the so-called “Islamic State” (ISIS) via aerial deliveries. This was particularly the case in the month of February, during the run-up to the predominantly Shia militia push on Tikrit.3
As early as February 7, 2015, Kata’ib Hizballah statements were repeated in Iranian media. One report claimed the group had confirmed the U.S. was supplying ISIS via helicopter.4 Other accusations by Kata’ib Hizballah of U.S. supplies being routed to ISIS were continued. On February 20, a flurry of stories hit the media. Al-Etejah TV published a report that alleged that U.S. helicopter landed near the home of Sheikh Qasim al-Janabi.5 Janabi, a moderate Sunni tribal leader who worked with the Iraqi government was kidnapped and assassinated in Baghdad on February 14th.6 Janabi’s son and other moderate Sunni parliamentarians blamed Shia militias for his kidnapping and murder.7 Also on the 20th, Al-Etejah published a story citing representatives in Babil who claimed U.S. aircraft were dropping supplies to ISIS.8 Other outlets also published that Kata’ib Hizballah had threatened to deploy anti-aircraft missile systems in the wake of these claims that the U.S. was supplying ISIS.9
Three days later, the Badr Organization-linked Al Ghadeer TV reported that forces of the Hashd al-Sha’abi (Popular Mobilization, a term used to describe the umbrella grouping of numerous Iranian-backed and other local Shia militia forces) claimed to have recorded landings in Babil Province.10 This also coincided with even more baseless claims distributed via the IRGC-linked Fars News that two British planes had been “shot down” while carrying weapons to ISIS.11
These types of accusations continued, and on March 5, 2015, the head of the Badr Organization’s parliamentary bloc, Qasim Muhammed Jalal Hussein Al-Araji,12 stated that the group had documents proving the U.S. was aiding ISIS.13 In an article published a day after the Kata’ib Hizballah video release, Harakat Hizballah al-Nujaba leader, Akram Ka’abi threatened U.S.-led Coalition aircraft. In the interview he stated, “Our air defenses are ready to target their planes, which are helping IS by giving them weapons and ammunition.”14
What Does It All Mean?
Needless to say, an active campaign by Kata’ib Hizballah and other Iranian-backed Iraqi Shia militia/jihadist organizations has been aimed at the U.S. and other Coalition allies (namely, the U.K.). The display of MANPAD systems underlines what likely appears to be messaging aimed at reducing the Coalition’s willingness to undertake further anti-ISIS air operations. In turn, if the threats succeed in that goal, it would grant more responsibility and control for Iran and its proxies on the battlefields of Iraq.
Another, more ideologically based goal is also included within these threats. The claim that the U.S. and other Western entities have supported radical Sunni extremist groups is a theme well honed by Iran and its proxies since the U.S. occupied Iraq (2003-2011) and in the war in Syria.15 The further push for these lines demonstrates another longer-term type of goal, even if it is only marginally effective, to alter the narrative and build broader distrust for the U.S. and other Western states.
1 Kata’ib Hizballah, an Iraq-based, direct Iranian proxy, was registered by the U.S. State Department as a Foreign Terrorist Organization in 2009: https://www.state.gov/r/pa/prs/ps/2009/july/125582.htm.
2 See: https://blogs-cdn.fas.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/The_MANPADS_Threat.pdf.
Note: Adam Rawnsley published a very comprehensive analysis of Kata’ib Hizballah’s MANPAD capabilities: https://medium.com/war-is-boring/iran-backed-terror-group-parades-new-anti-aircraft-missiles-in-iraq-ca0204079eb0 in the piece, Rawnsley assessed that one of the missile systems shown was a Chinese QW-1M.
3 See: https://www.cbsnews.com/news/isis-iraq-iran-shiite-militias-tikrit-questions-about-mosul/.
4 See: https://www.alalam.ir/news/1674215.
5 See: https://aletejahtv.org/index.php/permalink/47550.html.
6 See: https://www.wsj.com/articles/leading-iraqi-sunni-tribal-sheik-killed-1423951260.
7 Note: It is possible that Kata’ib Hizballah was attempting to craft another anti-U.S. conspiracy theory (or theories) with the inclusion Janabi in their reportage.
See: https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/sunni-parties-consider-leaving-iraqi-parliament-after-slaying-of-sheik/2015/02/14/7e164a8c-b463-11e4-bf39-5560f3918d4b_story.html.
8 See: https://aletejahtv.org/index.php/permalink/47558.html.
9 See: https://www.alsumaria.tv/news/125515/كتائب-حزب-الله-سننشر-صواريخ-مضادة-للطائر/ar.
10 See: https://alghadeer.tv/news/detail/23789/.
11 See: https://english.farsnews.com/newstext.aspx?nn=13931204001534.
12 See: https://www.iraqiparliament.info/en/node/673.
13 See: https://almasalah.com/ar/news/48777/%D8%A8%D8%AF%D8%B1–%D8%A7%D8%AF%D9%84%D8%A9-%D8%AA%D8%AB%D8%A8%D8%AA-%D9%85%D8%B3%D8%A7%D8%B9%D8%AF%D8%A9-%D8%A7%D9%85%D8%B1%D9%8A%D9%83%D8%A7-%D9%84%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B9%D8%B4.
14 See: https://www.al-monitor.com/pulse/originals/2015/03/iraq-shiite-hezbollah-nujaba-victory-islamic-state.html#.
15 In my monograph, “The Shiite Jihad In Syria and Its Regional Effects,” I outlined the ideological roots for claiming that Western states backed ISIS and other radical Sunni extremist elements. See: https://bit.ly/ShiiteJihadPDF. See the section marked, “Takfiris: A Perfect Enemy.”
Category: Badr Organization
Hizballah Cavalcade: Quwat Sahl Nīnawā: Iraq’s Shia Shabak Get Their Own Militia
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Quwat Sahl Nīnawā: Iraq’s Shia Shabak Get Their Own Militia
By Phillip Smyth

Figure 1: Quwat Sahl Nīnawā’s logo. The Iraqi (left) and Shabak (right) flags emerge out of a map of the Hamdaniya region of the Nineveh Plain. The symbol also features an AK-102 rifle.
Quwat Sahl Nīnawā (A.K.A. Liwa Sahl Nineveh or QSN) purports to be a Shia Shabak militia associated with the Democratic Assembly of Shabaks (Tajema’ al-Shabak al-Dimokrati or DAS).1 QSN announced itself via a November 23, 2014 official statement posted on the website and social media apparatus belonging to the DAS. The group has also already claimed to take casualties in the fight against the Sunni jihadist “Islamic State” (A.K.A. IS, ISIS, or ISIL).2
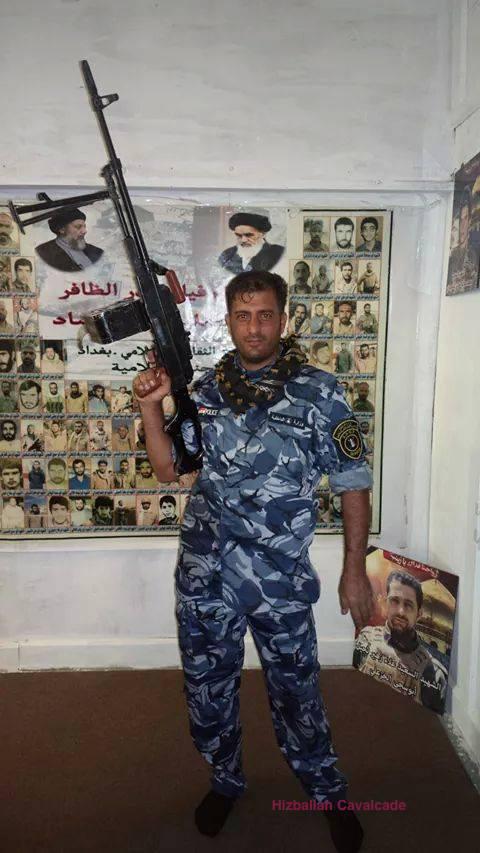

Figure 2: A QSN fighter poses with martyrdom posters (one featuring the dome of Sayyida Zaynab in Syria – bottom right) and other posters featuring Badr Organization founder Ayatollah Muhammad Baqir Sadr and the first Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khomeini.
Present in the symbols and photos, QSN mixes a limited quantity of Shabak particularism and an added emphasis on Shia identity. On some pages the group has simultaneously promoted links to Iran’s proxy forces. While the group may have relations with Iran’s proxies, its official statements have announced a commitment to “gladly serve the supreme religious authority in Najaf [Grand Ayatollah Sistani].”3 This would likely indicate the group is not an equivalent (in terms of ideology and/or levels of control) to newer Iraqi Shia Iran-proxy militias such as Hizballah al-Abrar.
Photos claiming to show the group training also indicate that they may be assembled along the lines of a “Popular Assembly/Mobilization” or “al-Hashd al-Sha’abi” type group. Photographs of claimed QSN fighters holding flags promoting al-Hashd al-Sha’abi add further credence to this likelihood. Organization along those lines would mean many of the fighters are possibly newer recruits trained and likely led by more experienced personnel and advisors.
In photos of QSN, around 100 fighters were shown posing in ranks. This suggests the numbers for the group are likely in the range of 100-500 combatants.
The creation and promotion of the group may exemplify another method Iran and its proxies are using to place pressure on Kurdish organizations. QSN, as organized along lines of the more dominant Iraqi Arab Shia militias in the south of the country, also demonstrates the direction in which other new militias may be organized. QSN further exemplifies how some of Iraq’s minority groups are mobilizing against ISIS.
The Name & Symbols
QSN’s name directly refers to an area of heavy Shabak habitation, Iraq’s Ninewa (or Nineveh) Plain. Their logo and a post by the Shabak Democratic Assembly describes the group as “Quwat Sahl Nīnawā” or the “Nineveh Plain’s Forces.”4 Albeit, via social media, one page purporting to belong to the group claimed it also went by the name of “Liwa Sahl Nīnawā” or the “Nineveh Plains Brigade”. However, such minor alterations in name are common during the early stages of many new militias.5
The group’s logo also demonstrates a rather rudimentary approach to create symbolism for the new group. Readily available images (including the pictures of an AK-102 rifle, the Shabak and Iraqi flags, and a map of the Hamdaniya area of the Nineveh Plains) were likely pasted together following a simple image search online.6

Figure 3: A QSN fighter poses with a flag associated with the Popular Mobilization type militias.
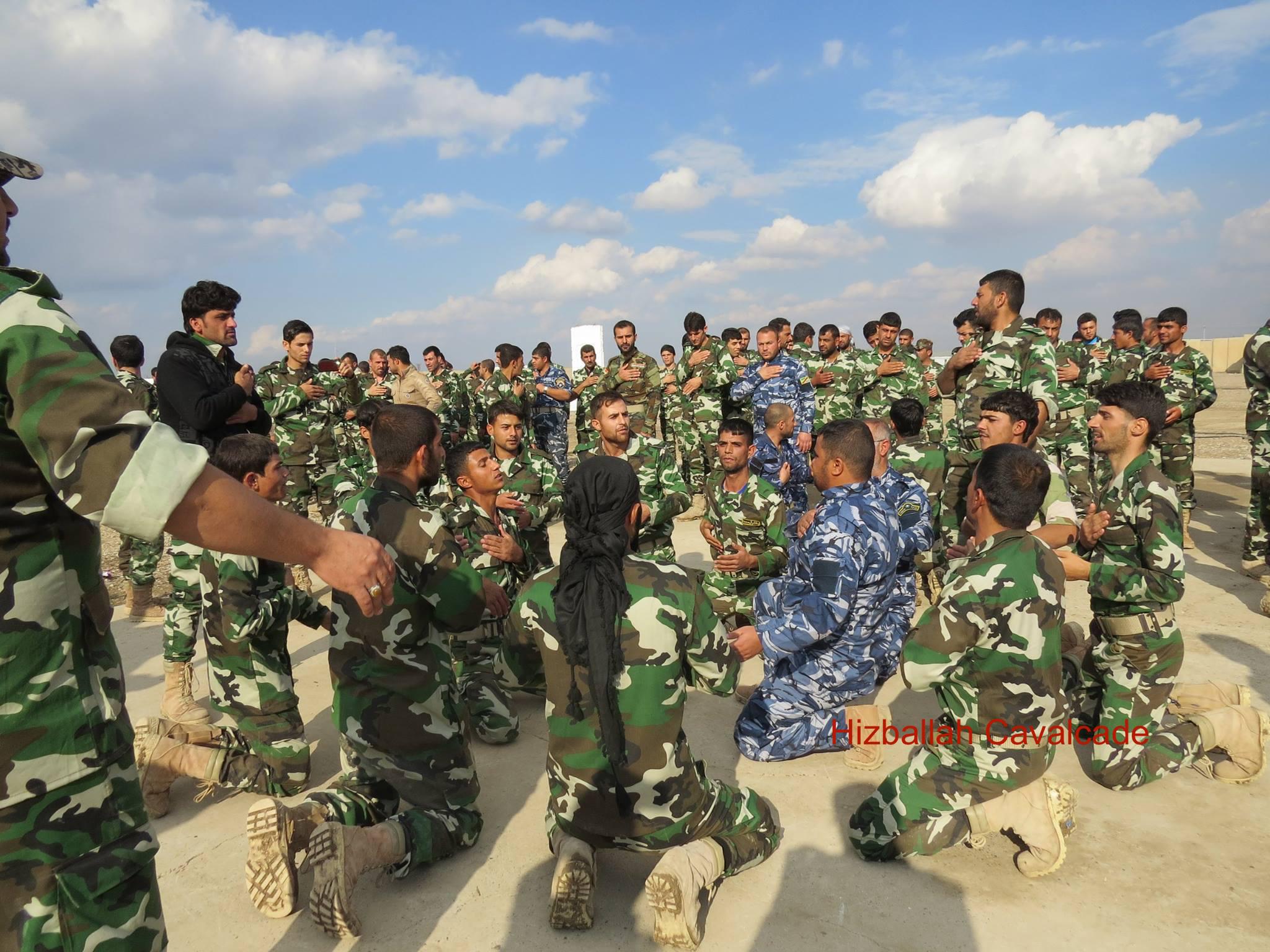

Figure 4: QSN fighters congregate.
Who Are the Shabak & What is the Nineveh Plain?
The Nineveh Plain is a minority rich area; home to the Shabak, numerous Christian sects (including the Assyrians, Chaldeans, and Syriac Orthodox and Syriac Catholics), Turkmen, Yezidis, and Kurds.7 Considered a heartland for Iraq’s Christians, Assyrian Christian and other Syriac (Aramean, Syriac, and Chaldean) Christian nationalist organizations and political parties have pushed for autonomy in the area.8 There has also been a campaign to make the Nineveh Plain its own province (under primarily Christian leadership) within the Iraqi federal framework.9 Nevertheless, the Plain has not been granted a truly autonomous standing.
Many Shabak insist they have a unique ethnic identity, which is neither Arab nor Kurd (albeit, primarily non-Kurdish).10 The group also speaks its own language, Shabaki.11 Most Shabak are also religiously (Twelver) Shia.12
Within the Nineveh Plain, the Shabak primarily live in villages to the east of the city of Mosul, in the Hamdaniya area, and a few thousand also lived in the city of Mosul (before the invasion). Due to ISIS advances, many Shabak hamlets have been overrun.
The Democratic Assembly of Shabak & Issues With the Kurds
While QSN was ostensibly created as a Shabak arm to fight back ISIS threats and offensives targeting the Shabak, there are other underlying trends present with the creation of the militia associated with Shabak-Kurdish relations.
Kurdish groups have shown interest in further incorporating areas of Shabak habitation into Kurdistan.13 As early as 2008, minority groups including the Shabak claimed there was an effort to “Kurdify” areas they inhabited.14
Along with the promotion of a separate non-Kurdish identity, the DAS’s leader and parliamentarian Hanin Qaddo has specifically called out Kurdish parties for claimed abuses against the Shabak. In 2008 Qaddo opposed the incorporation of Shabak inhabited areas into Iraqi Kurdistan.15 Two years later, Qaddo denounced the Kurdish Democratic Party (KDP) for “intimidating” Shabak voters.16 In 2012 the Shabak leader demanded the expulsion of Kurdish and Christian armed forces from the Nineveh Plain.17
With this in mind, QSN’s establishment also recalls the 2012 decision by then Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki to allow for the creation of a 500-man Shabak militia force referred to as, “The Shabak Regiment of Doom.”18
For their part, many Kurdish political leaders have not been supportive of independent Shabak efforts to create their own militias. Nevertheless, some of those Kurdish apprehensions were downgraded following the ISIS advance. Thus, QSN has not been the only Shabak armed group to come into existence. However, its other counterpart is under the control of Kurdish military commanders.19 Whereas QSN is organized along lines set by Baghdad-supported Shia militias and Iran’s proxy groups and does not appear to be taking order from Kurdish commanders.
Tensions between QSN’s DAS parent party and Kurdish parties may explain for QSN’s retention of its independence. The DAS, the largest Shabak Party, is also part of the ruling Iraqi State of Law Coalition. This is the same coalition which included former Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki, the current Iraqi Prime Minister, the Badr Organization and Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada, among other Iranian proxy groups. Nevertheless, Qaddo has “wavered between the Hakim and Maliki factions,” and then ran on the Badr Organization’s electoral list.20
The increase in Iranian proxy cooperation via training, equipping, and other support also speaks to other issues related to Iran’s and their proxies’ policies in Iraq. The policies in question are particularly focused on Kurdistan. From the summer of 2014 until the present, there has been increased tension between Iran’s Iraqi Shia proxies and Kurdish Peshmerga forces.21 Additionally, Iran’s proxies have also threatened Kurdish leaders such as Masoud Barzani.22
A push for support for a group which has already had problems with Kurdish leadership seems to be another avenue for Tehran to exert pressure on the Kurds. Nevertheless, QSN’s main goals and activities have and will likely remain oriented against the existential threat that is ISIS.
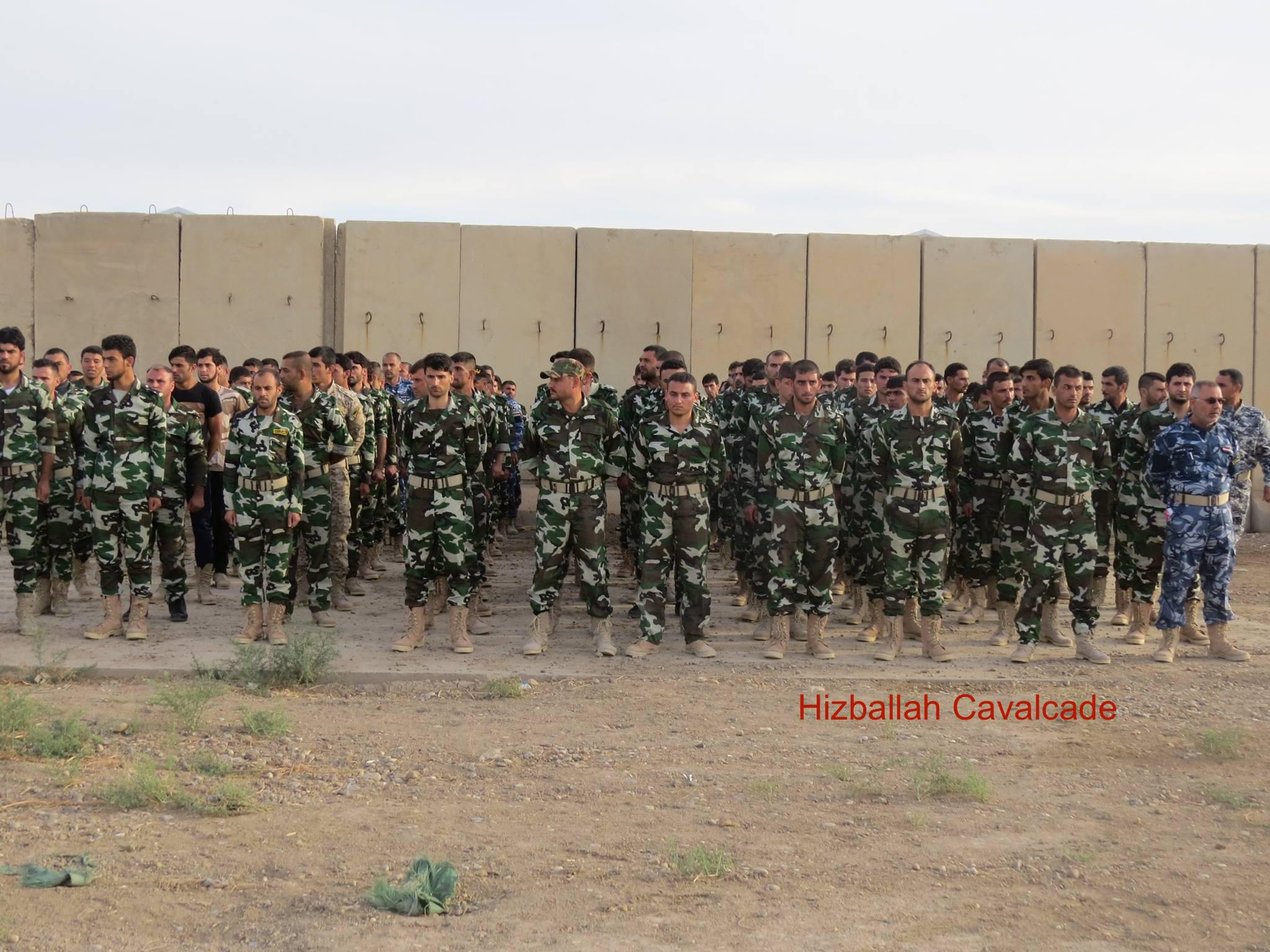

Figure 5: Around 100 QSN are shown in this photo.
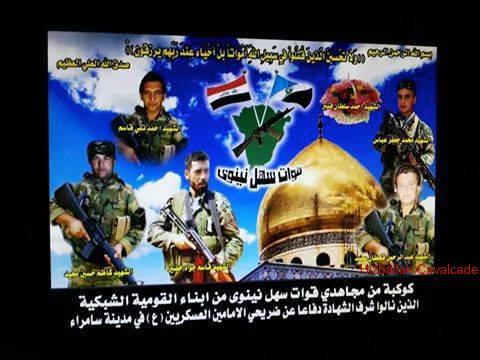
Figure 6: QSN Martyrs are shown on a poster featuring the dome of Syria’s Sayyida Zaynab. It is possible the dome was included by graphics designers to demonstrate that the fight in Syria and Iraq, marketed as “protection for shrines”, are one in the same.

Figure 7: The martyrdom poster for Kazem Husayn al-Asharaf (Abu Sajad).
Videos
Notes:
_____________
Hizballah Cavalcade: Khamenei’s Cannon: .50 Caliber Anti-Material Rifles & Shia Fighters in Syria
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
–
Khamenei’s Cannon: .50 Caliber Anti-Material Rifles & Shia Fighters in Syria
By Phillip Smyth
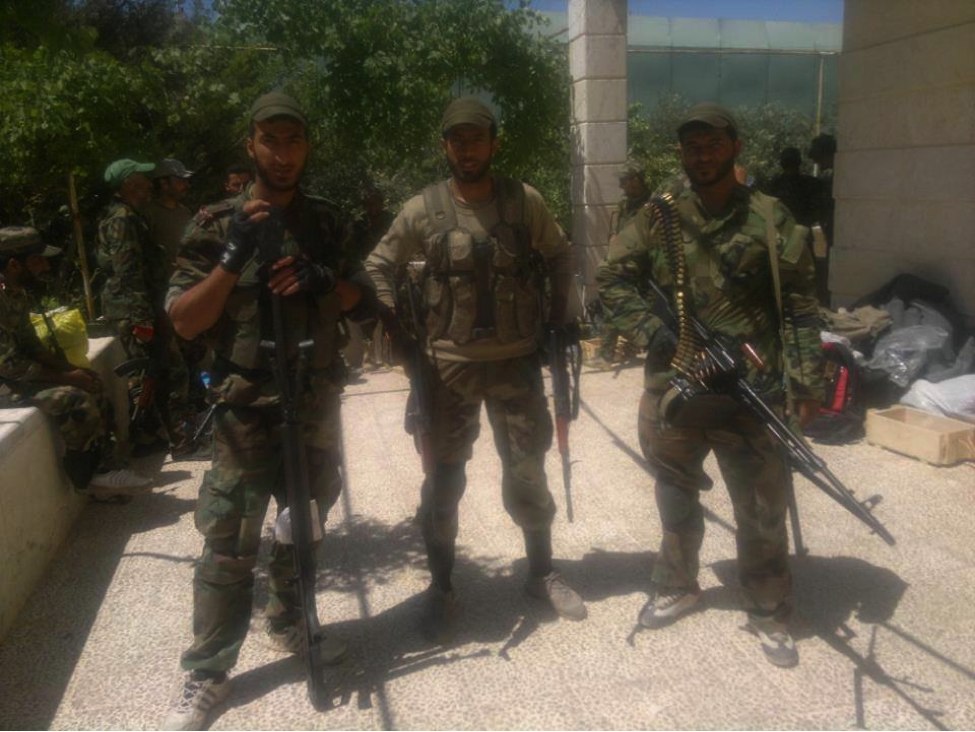

Figure 1: Combatants from Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir. The fighter on the left likely holds an Iranian-copy of the HS.50 rifle.
Since April 2013, around the same time Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas was first gaining broader exposure and name-recognition, another sub-trend started to appear in the photos showing Shia Islamist fighters in Syria. This trend remained minor and occasional. However, starting in October, there have been increasing examples of foreign Shia Islamist fighters being pictured with long range bolt-action anti-material rifles.[1]
It is possible these weapons were the bolt-action HS.50, .50 caliber (12.7x99mm) rifles produced by Austria’s Steyr Mannlicher. According to The Telegraph, 800 of the rifles were shipped to Iran in 2007.[2] However, according to the Brown Moses Blog, it is far more probable that these rifles are actually Iranian copies which were shipped to Syria.[3] Since the winter of 2012, pro-Iranian social media has also praised the Iranian-made copy of the rifle.[4] Still, serial numbers on the weapons are often hidden, making absolute confirmation difficult.
The original Steyr Mannlicher sale of these long-range weapons caused worries among British and U.S. policymakers and military personnel due to the fear they would be supplied to Iranian-created and supplied Shi’a Islamist “special groups” in Iraq. These groups included Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq and Kata’ib Hizballah. Both of these organizations are now sending forces to Syria.
Anti-material sniper rifles of this caliber have found a welcome place in Western military services. The U.S. military fields the M107 semi-automatic .50 caliber rifle as do a number of other militaries. In October, 2012 one of these weapons killed a Taliban member in Afghanistan from a distance of 2,475 meters.[5]
Presently in Syria, these types of rifles have been used by both rebels and pro-Assad forces. Nevertheless, the outfitting of highly organized foreign Shia fighter manned organizations may demonstrate a shift in tactics and training.
Groups using the rifle in Syria span the full spectrum of organizations backed by Iran. Lebanese Hizballah has been a primary poster of images with the weapon. Additionally, Iraq-based Harakat Hizballah al-Nujaba’s (a front for Kata’ib Hizballah and Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq) Syria-based front militias, Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir and Liwa’a al-Hamad have posted photos of their militants with the rifle. Iraq’s Badr Organization’s Quwet Shahid Muhammed Baqir Sadr and Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada have posted their own images of their fighters with the HS.50 type rifle. Other Shia fighters from unnamed organizations have also been pictured with the weapon.
Films featuring Shia militia groups using the HS. 50 type rifles in combat in Syria have been extremely rare. Usually only photos are posted.
The first film showing Shia Islamist militias in Syria using the rifle was posted to Facebook and YouTube pages associated with the Badr Organization’s Quwet Shahid Baqir Sadr (BOQSBS), the group’s expeditionary unit in Syria. The BOQSBS has also been a main poster of high-quality images showing their combatants wielding these types of anti-material rifles. Around a minute of footage showing BOQSBS fighters using the weapon was inserted into a much longer film made to demonstrate the group’s activities in Syria (see below at minute markers 1:59-2:23).
Due to the high level of operational security employed by these groups, potential failures or successes of the rifle in combat are often not showcased. Operations using the rifle have also not been detailed on the many social media pages run by Iranian-backed Shia militia groups inside Syria. In fact, the rifle has rarely been named or described by Shia Islamist militia pages. Nevertheless, these rifles have become a regular feature in images featuring fallen fighters.
Such a capability, even if deliberately showcased for propaganda purposes, should be taken seriously by regional and global military forces. Iranian equipped and trained snipers, utilizing smaller caliber rifles, demonstrated a lethal efficiency during the Iraq War (2003). Their utilization of smaller caliber-wielding snipers (particularly using the SVD-type rifles) demonstrates a concentration on sniping tactics.
Some Possible Reasons Why the Rifles Are Appearing More
- Propaganda Purposes: Some of the photos of fighters holding the rifle appear to be posed images meant to showcase the size of the weapon (representing power) in comparison to the fighter. Additionally, since it is probably a copy, showing the rifle in operations overseas is a sign that Iranian-made weapons are of a high quality. Proxy organizations may also see the rifle as a symbol of advancement and as a sign they are comparable to first-world armies. The weapon may also be a sign to rebel groups that Shia militants have more advanced capabilities.
- General Incorporation into the Order of Battle: The rifle could have possibly become more prolific with increased foreign-manned Shia militia operations.
- Offensive Operations: Since the start of main offensives in October and increase in numbers of Shia fighters, it is possible the rifle has found more use and acceptance by fighters.
The Rifle & Its Shia Islamist Users
Lebanese Hizballah:
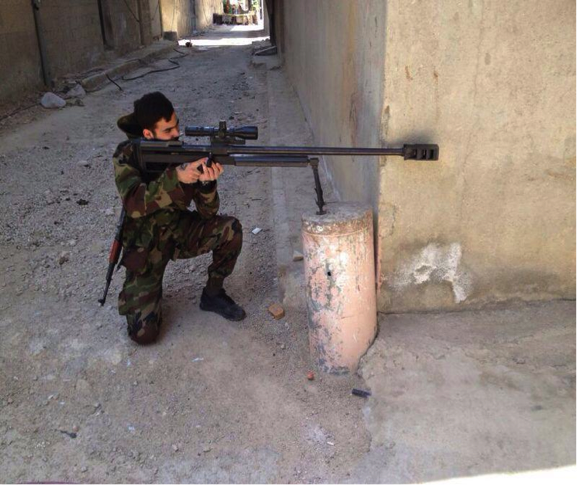


Figure 2: Lebanese Hizballah’s Ali al-Hadi Nuwn shown holding the weapon on his shoulder. (Left)
Figure 3: Another posed-photo of Lebanese Hizballah’s Ali al-Hadi Nuwn. In this picture he is taking aim with the .50 caliber rifle. (Right)

Figure 4: Hizballah commander Ja’afar Husayn Hashim with the rifle. He was reported to have been killed in Syria on November 1, 2013.
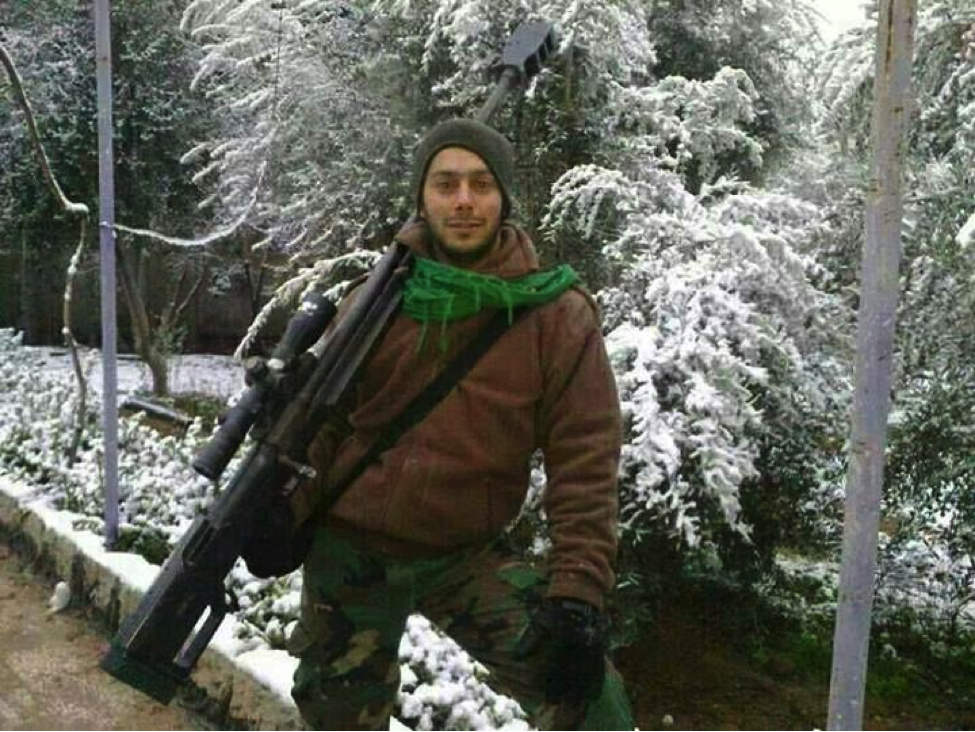

Figure 5: Hizballah’s Khadr Ahmed Matar, declared killed in Syria on December 2
0, is shown standing in the snow with the rifle.
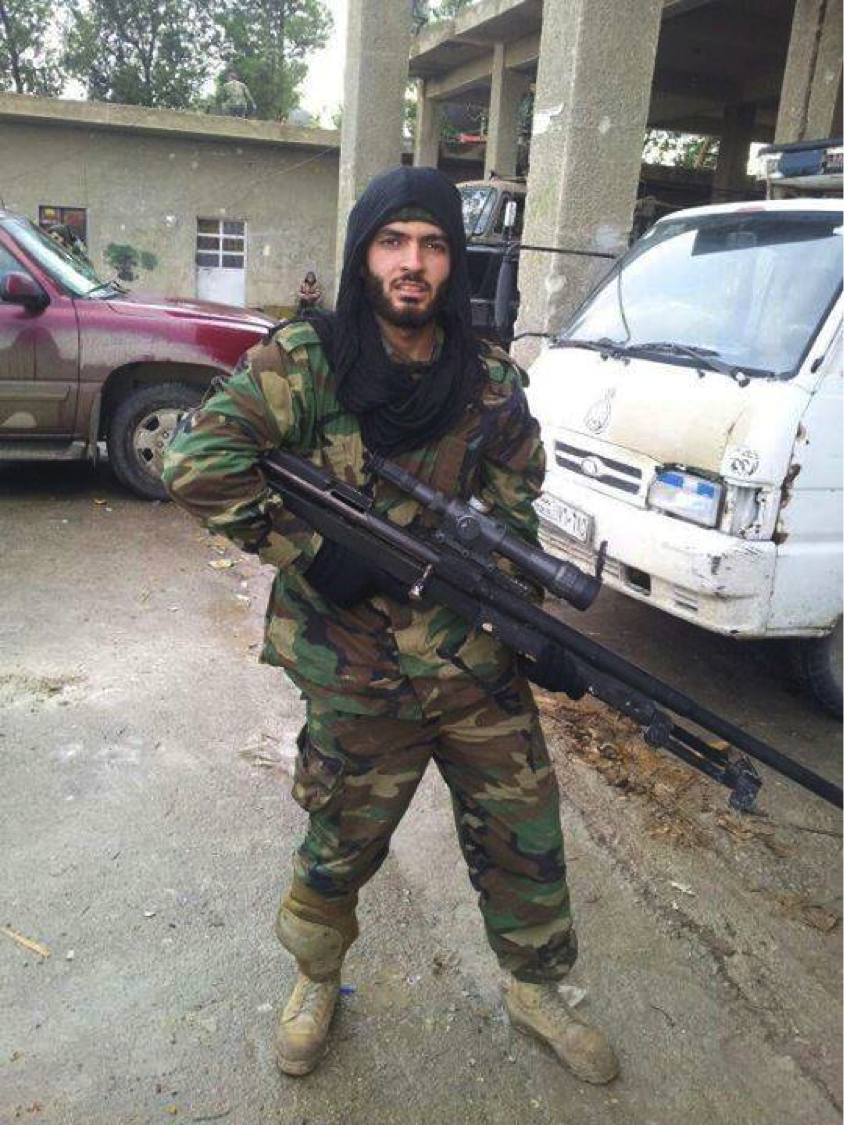

Figure 6: Qasim Ghamloush is shown holding the .50 caliber rifle. His death was announced by Hizballah on December 7, 2013.
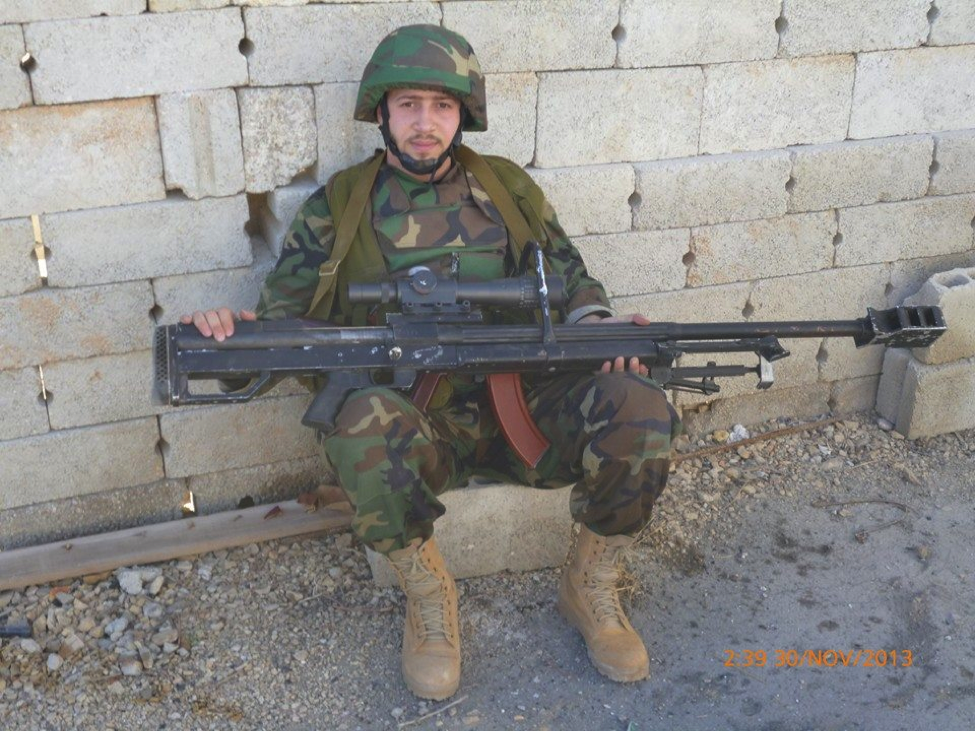

Figure 7: Ali Husayn Salah (A.K.A. Sheikh Hadi) is seen holding the rifle over his Kalashnikov-pattern weapon. Salah was also reported to have been killed in Syria on December 7, 2013.
Liwa’a al-Hamad:
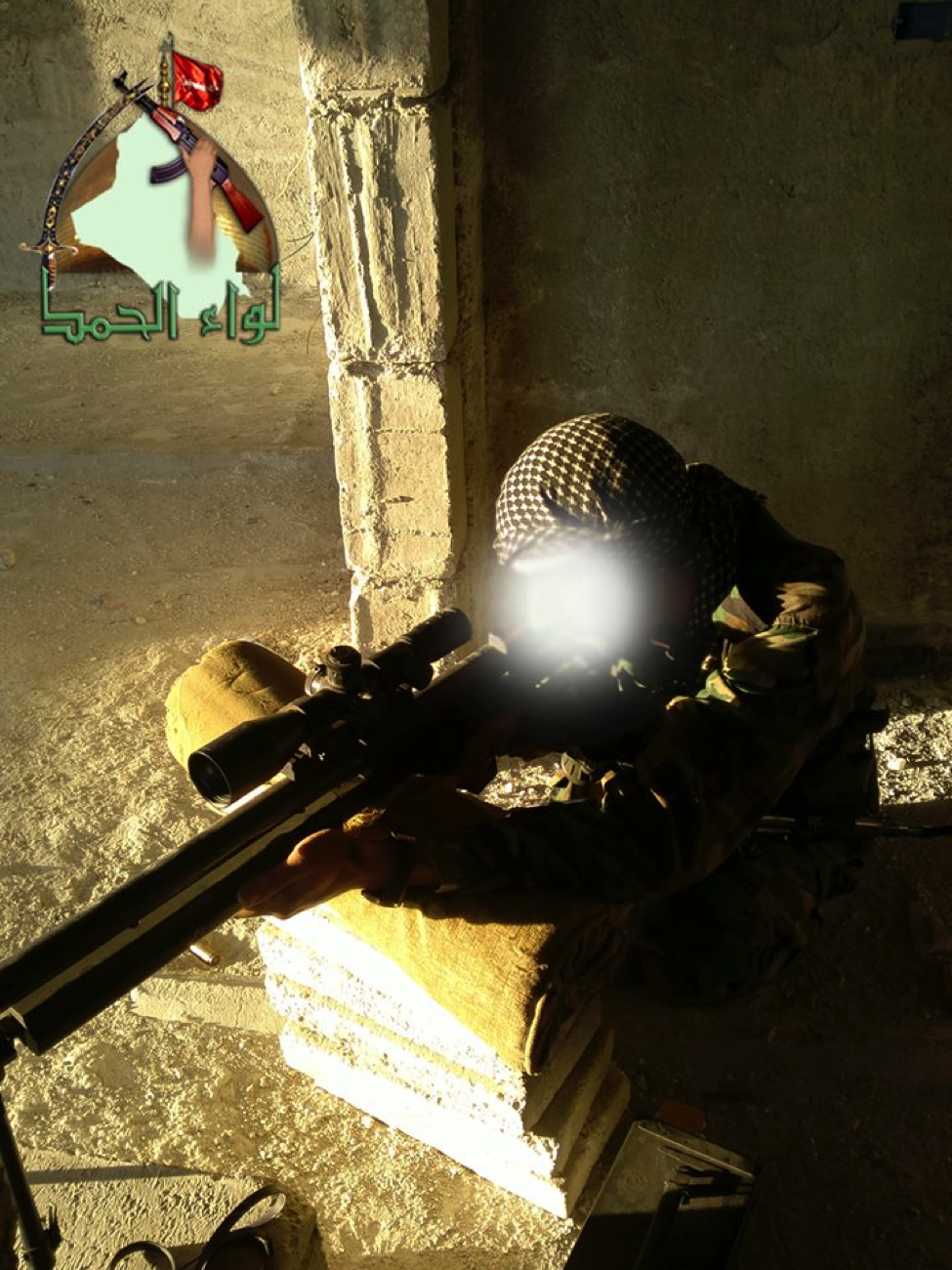

Figure 8: An October photo of a fighter from Liwa’a al-Hamad taking aim with the HS.50-type rifle.
The Badr Organization – Quwet al-Shahid Muhammed Baqir Sadr

Figure 9: Following the announcement that the Badr Organization had created its own expeditionary force for Syria, this was one of the first photos they posted online.
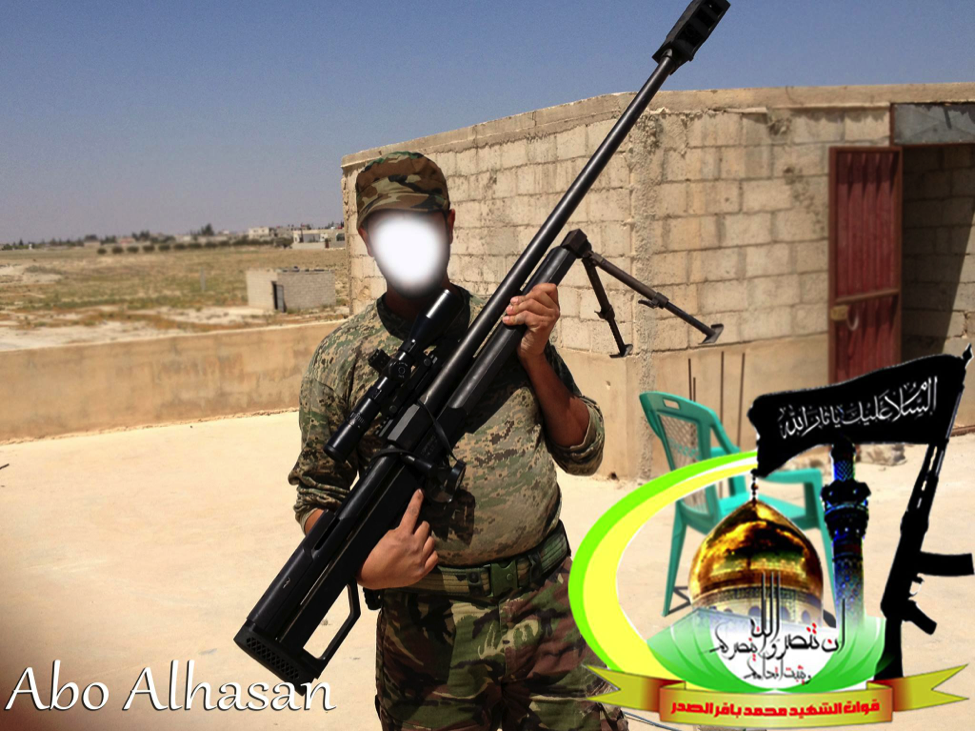

Figure 10: A Badr Organization-Quwet al-Shahid Muhammed Baqir al-Sadr is shown holding the HS. 50 type rifle.
Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir:
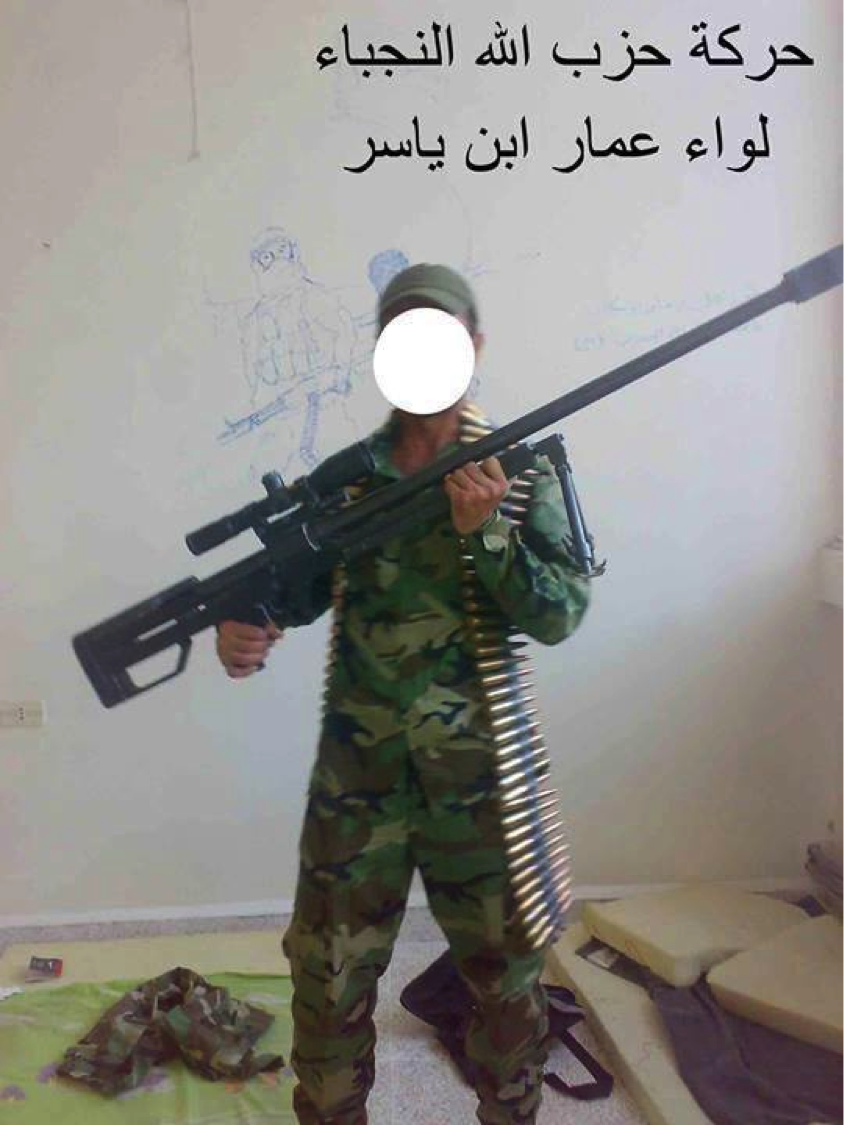
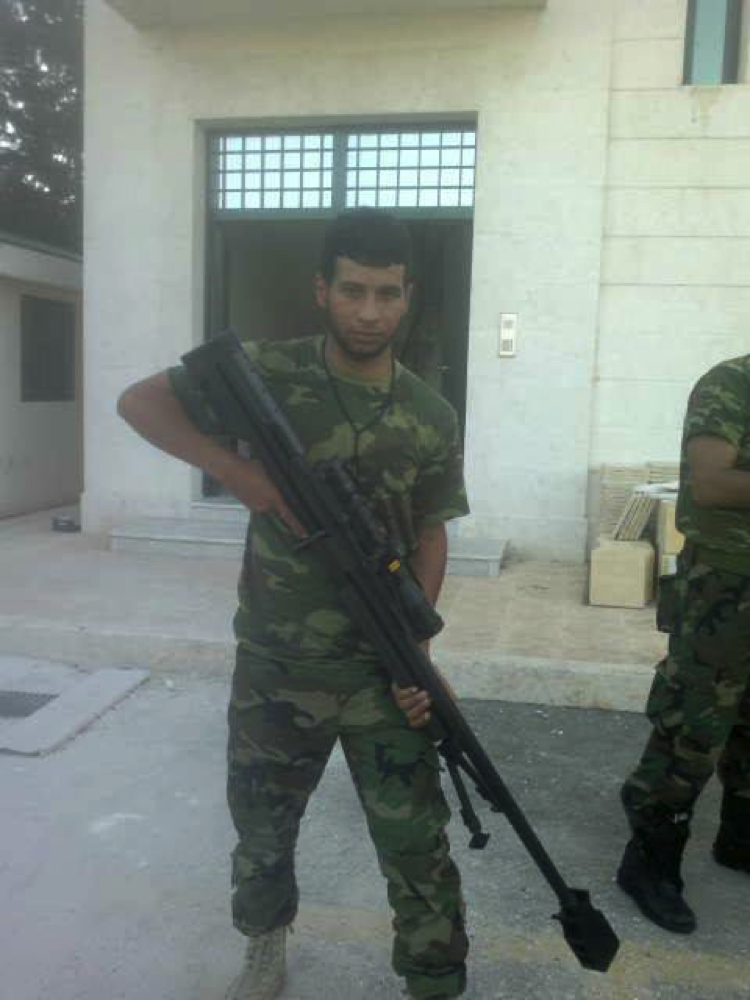


Figure 11: A commander from Liwa’a Ammar Ibn Yasir is seen holding the .50 caliber rifle.
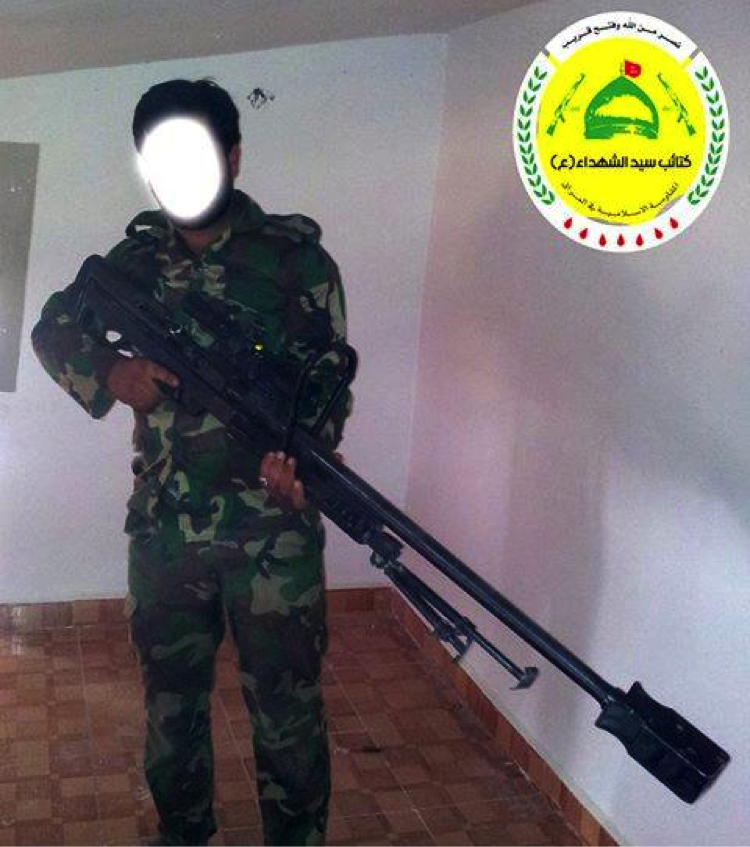
Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada:

Fighters from Other Groups:
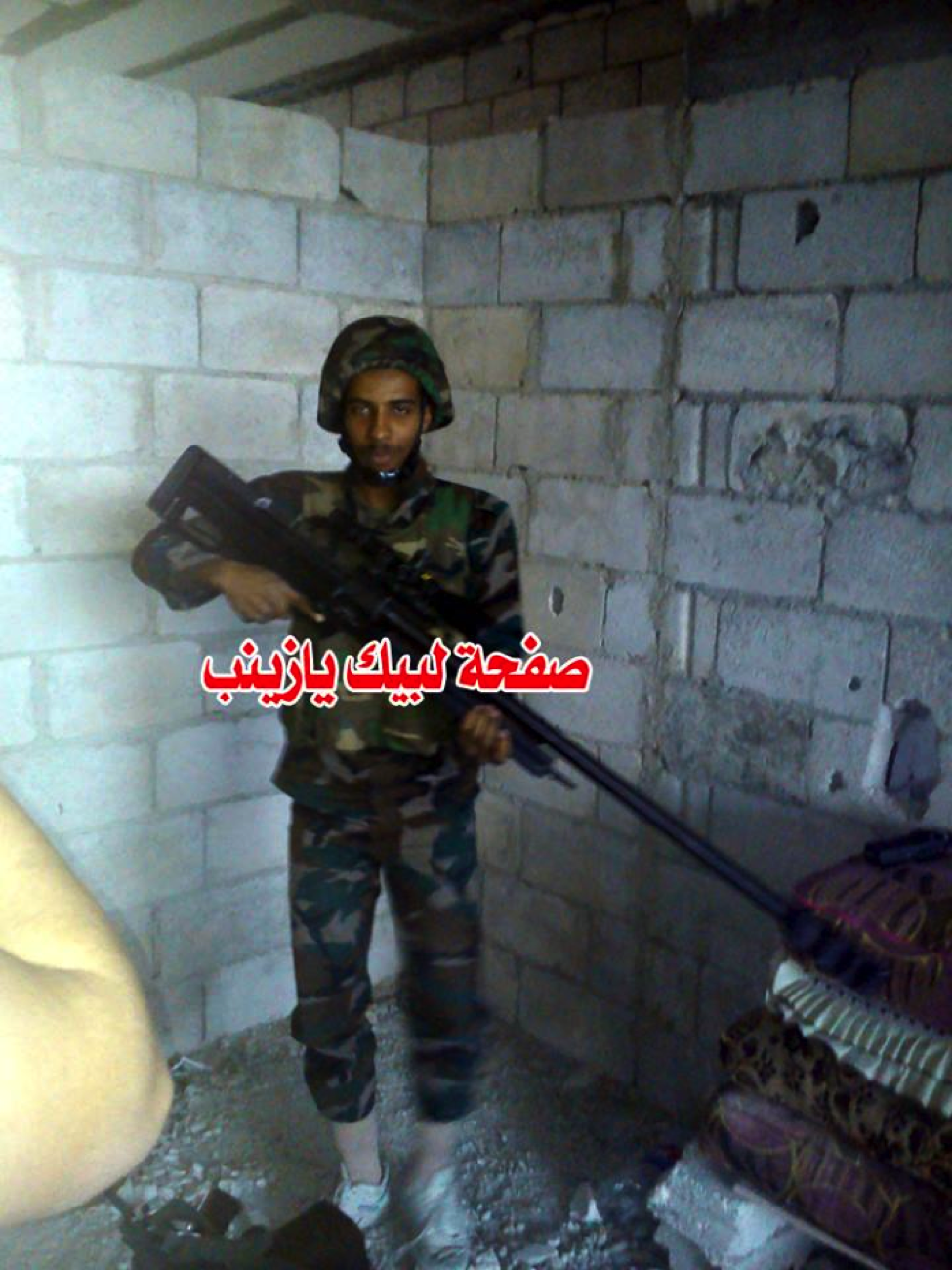

Figure 12: The Shia militia effort’s “first African martyr” (Muhammed Suleiman al-Kuwni) is shown holding the rifle.
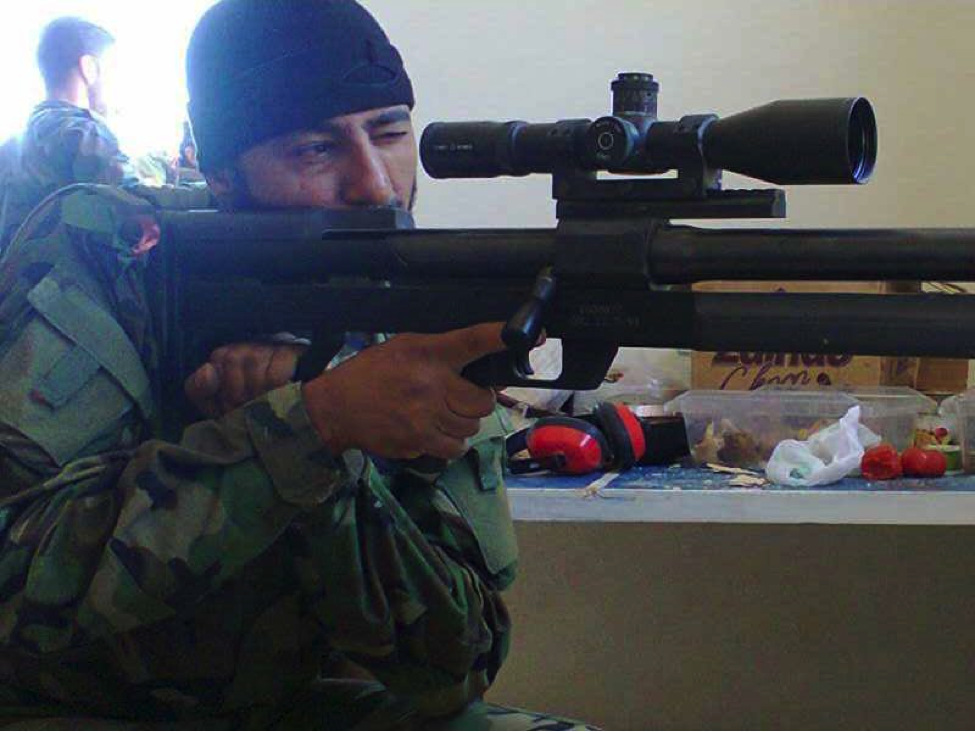

Figure 13: A fighter from an unnamed Shia Islamist militia (likely Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir) take aim with his rifle.
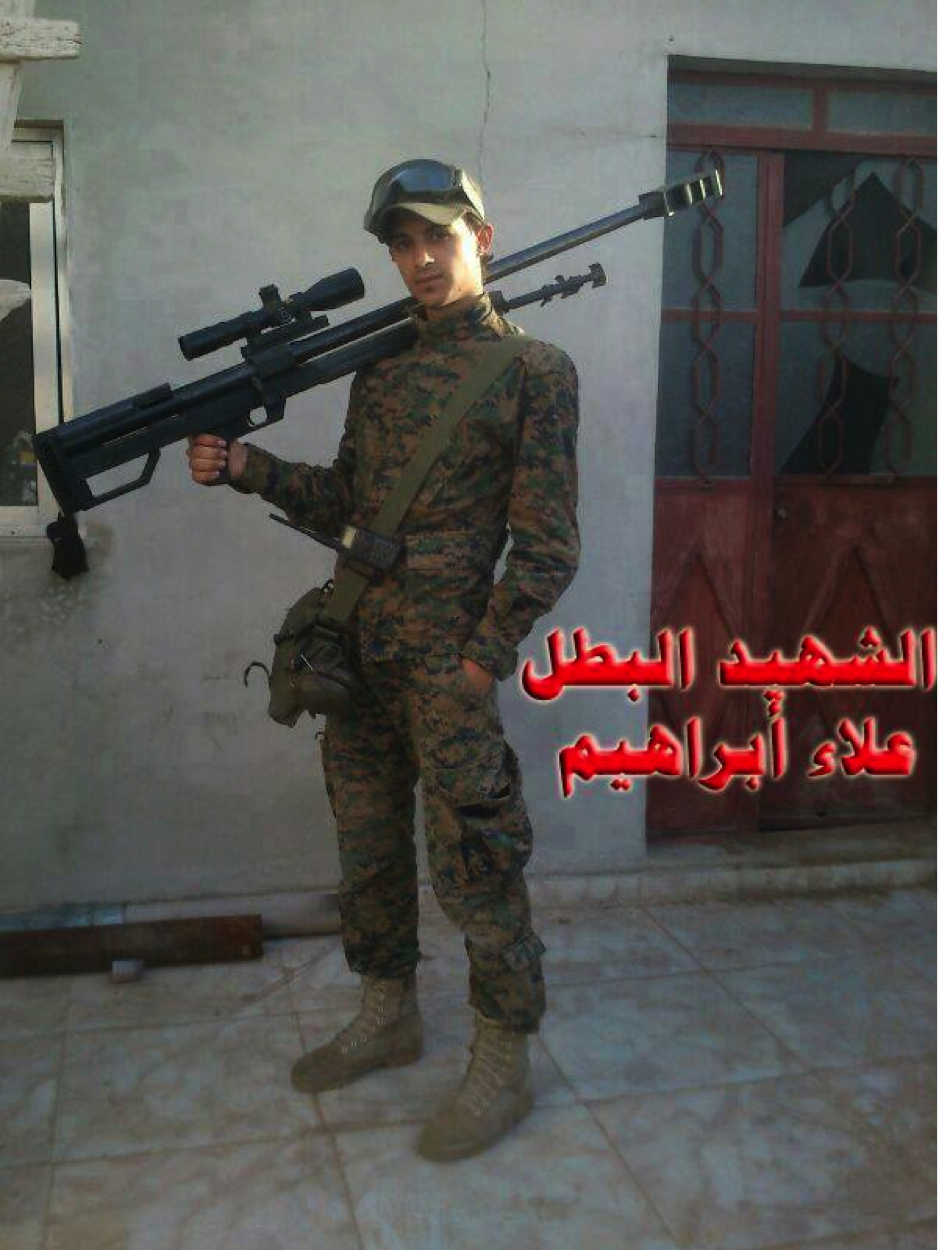

Figure 14: Alla’ Ibrahim (possibly from Liwa’a Zulfiqar), an Iraqi Shi’a fighter buried on November 30, 2013 holds the rifle over his shoulder.

Figure 15: An edited shot of Alla’ Ibrahim shows him posting with the rifle.
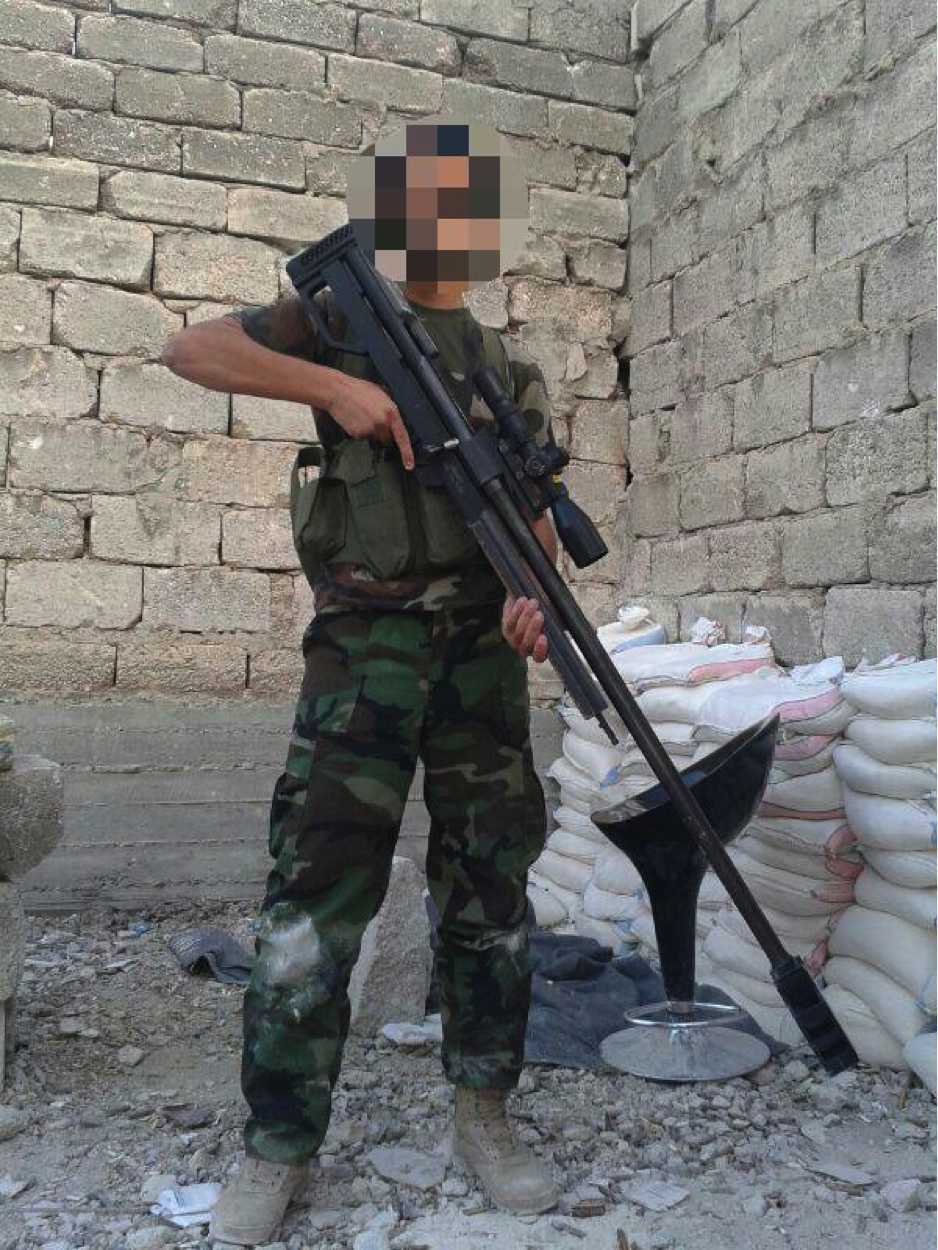

Figure 16: A Shia fighter from an unnamed militia group is shown with the HS. 50-type rifle.
[1] The Oryx Blog has an excellent post on HS. 50-type rifles in Syria: https://spioenkop.blogspot.com/2013/04/syria-and-her-hs50s.html. The post is from April 27, 2013 and pictures of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas members with the rifle.
[2] See: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/1542559/Iraqi-insurgents-using-Austrian-rifles-from-Iran.html
[3] See: https://brown-moses.blogspot.com/2013/04/anti-material-rifles-in-syria.html. See also: https://www.thefirearmblog.com/blog/2012/07/16/mysterious-iranian-50-cals-part-3/. This post by The Firearms Blog should also be read when assessing the rifle in question.
[4] See: https://www.facebook.com/permalink.php?story_fbid=477563188953409&id=174927625878471.
[5] See: https://www.dailytelegraph.com.au/news/opinion/taliban-remain-in-fear-of-lethal-strikes-writes-chris-masters/story-e6frezz0-1226504862496
Hizballah Cavalcade: Sariyya al-Tali’a al-Khurasani: A New Combat-Tested Shia Militia in Syria
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Sariyya al-Tali’a al-Khurasani: A New Combat-Tested Shia Militia in Syria
By Phillip Smyth ([email protected])


Figure 1: The STK’s logo (left) and flag (right). The logo includes Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps’s symbol. A verse from the Quran, Quran 29:69 meaning, “And those who strive for us [in jihad] we will surely guide them to our [Islamic] ways”. Over the rifle the phrase reads, “The Islamic Resistance”.

Figure 2: Another logo used by the STK.
In late September, Sariyya al-Tali’a al-Khurasani (STK or The Vanguards of Khurasani Unit), also referred to as the Khurasani Unit, first made itself known to the world via Facebook. The group may draw their name from Abu Muslim al-Khurasani (A.K.A. Abu Muslim), an 8th century military leader who helped depose the Sunni Umayyad dynasty’s rule over the early Islamic caliphate.[1] The STK also claims to be based out of Arbil, Iraq, the capital of Iraqi Kurdistan. According to the Khurasani Unit’s own releases, it appears to exclusively operate in a military function in rural areas outside of Damascus, Syria.
Technically, the STK was first announced on September 24, 2013 on Facebook. However, it is possible the group’s first page was made “private” and another mirror page was setup in its stead. Thus, the initial announcement of the group’s existence was hidden. The mirror page which first helped formally announce STK’s creation was made on October 8, 2013. Both pages hold unique images from the group and promote the same general messages. As with other Shia militias in Syria, the group claims to defend the Sayyida Zaynab shrine and promotes general pro-Iranian pan-Shia narratives. The promotion of Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and of their own Shia identity through the posting of photos showing Shia clerics in their ranks is a regular theme.
Most of the STK’s imagery was posted in October. In fact, there were days when eight new images were posted on both of their Facebook sites. STK has also released extensive footage showing its fighters in combat inside Syria. This footage has included numerous photos of its fighters, including those of wounded members, and videos of the group engaged in combat. A particular feature of STK propaganda has been images showing the fighters posing with the group’s flag. Only the Badr Organization’s Syria unit, Quwet Shahid Baqir al-Sadr, has also engaged in extensive posting of images featuring their organization’s flag with their fighters in Syria.
While Shia Islamist organizations fighting in and contributing fighters to Syria have done little to hide their connections to Iran, STK went the extra step and actually repackaged Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps’ logo as their own. Their blatant promotion of Iran’s Supreme Leader in many of their posts leaves no illusions to which Shia clerical leader or ideology to which the group swears loyalty.
Unlike other Shia militias (E.G. Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir, Liwa’a al-Imam al-Hasan al-Mujtaba, and Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas) fighting in Syria, the STK has not stated which (if any) Iraqi Shia organizations have contributed fighters to the group.
The number of fighters in STK’s ranks is unknown, though their leadership has been identified. STK, has been reported to be fighting around Damascus’s Sayyida Zaynab Shrine and in the rural area near Damascus called Ghouta. Videos showing engagements featuring their fighters went viral among Syrian rebel supporters and Shia militia supporters online. In part, this has been due to the fact that their videos appear less staged (e.g. Shia militiamen firing a few rounds from a sniper rifle) and are much longer than others produced.
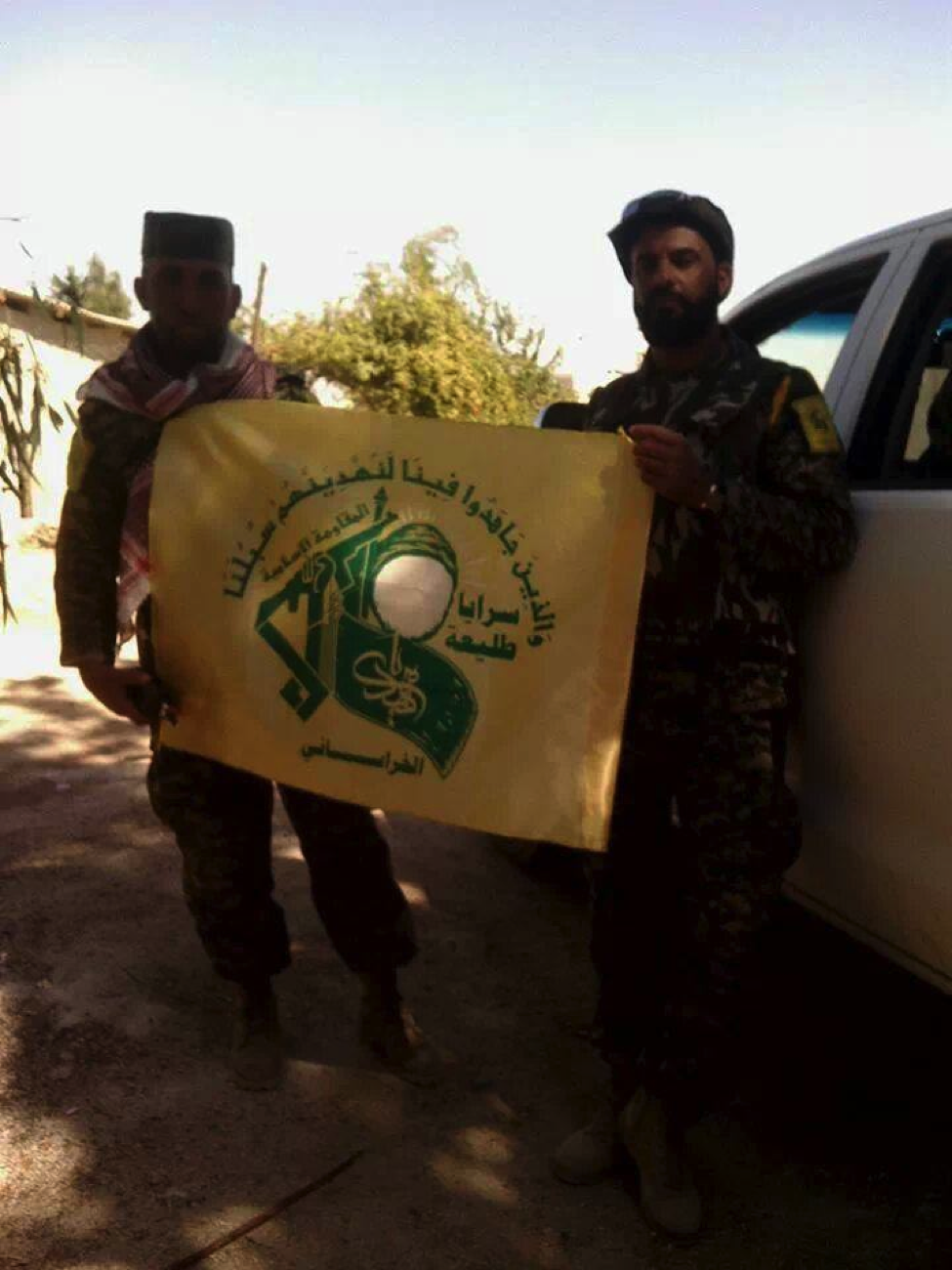

Figure 3: Two STK fighters pose in front of a truck holding the organization’s flag.
Ali al-Yasiri: The STK’s Commander
The immediate announcement of commanders for specific Shia fighting units in Syria is usually not a common theme. Less than two weeks after the first Facebook post made by the STK, it was announced by the group that their commander was named Ali al-Yasiri. Yasiri is shown in many photographs posted by the organization on its Facebook pages. Yasiri was also shown in photographs featuring Sayyid Muhammed Jawad al-Madrasi, a Shia cleric.[2]
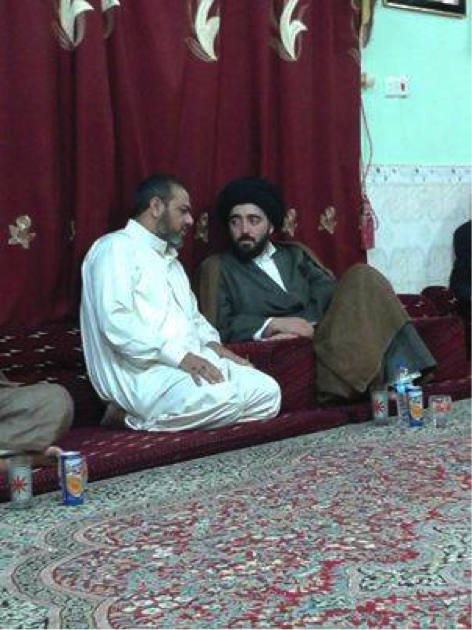

Figure 4: Ali Yasiri is shown with Sayyid Jawad al-Madrasi. On Facebook, the group identified the cleric as, “Ajwad Madrasi”.
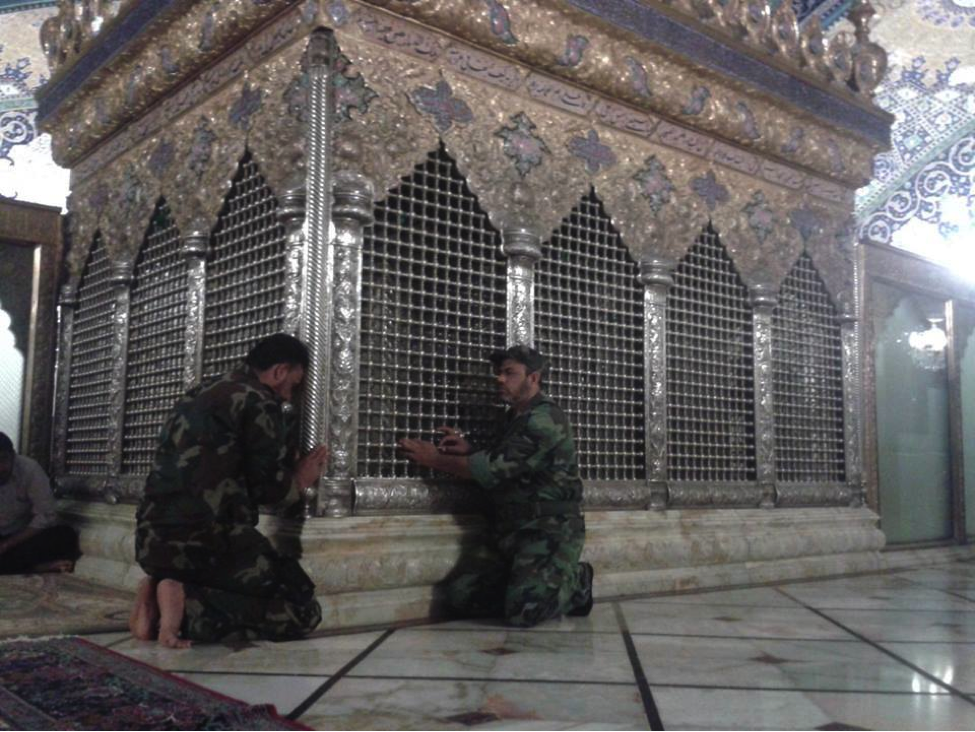

Figure 5: Yasiri and another unnamed STK fighter pose at Zaynab’s tomb.
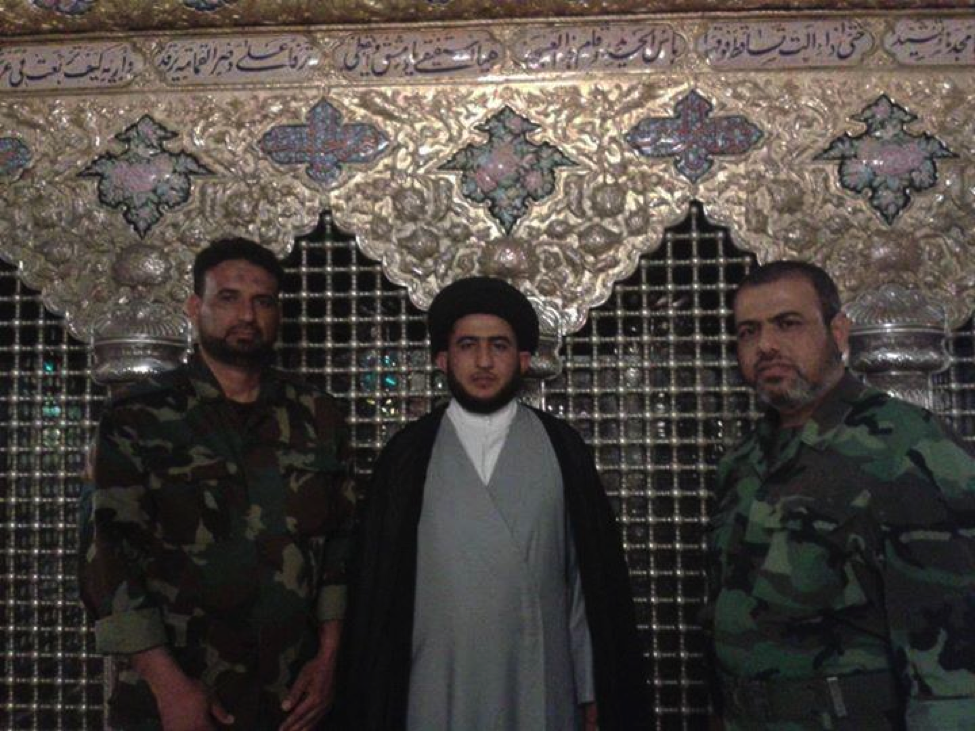

Figure 6: Yasiri and an unnamed fighter pose with an unnamed cleric at Zaynab’s tomb. All three figures have been featured in other photos released by STK.

Figure 7: Yasiri (left) and the same unnamed fighter pose together for a photo. The fighter on the right holds an SVD type sniper rifle.
STK’s Fighters & Equipment
Little information is available on the numbers of fighters STK has operating in the field. Judging from their photographs, the group has over twenty members. The arms the group uses mimic the varieties used by other Shia militias. Most of these weapons are Kalashnikov-type rifles, SVD-type sniper rifles, RPG-7s, and the PKM-type machine guns. The group has also been recorded using light mortars in clashes in rural areas outside of Damascus.
In addition to their small-arms, the militia’s uniforms appear to include types of U.S.-style digitized camouflage. Some of the group’s uniforms include M81-type woodland camouflage and Desert Camouflage Uniform-type patterns. Also, other unidentified types of camouflage patterns have been seen on the STK’s fighters.
Interestingly, many of the same faces are featured in photographs of STK fighters. In fact, one in particular, that of a Shia Islamic cleric wearing a black turban, can be spotted in many photos of STK militiamen. His inclusion may be a way the group demonstrates their Shia Islamic identity. The Badr Organization has also included clerics in their militia photos in a similar effort.
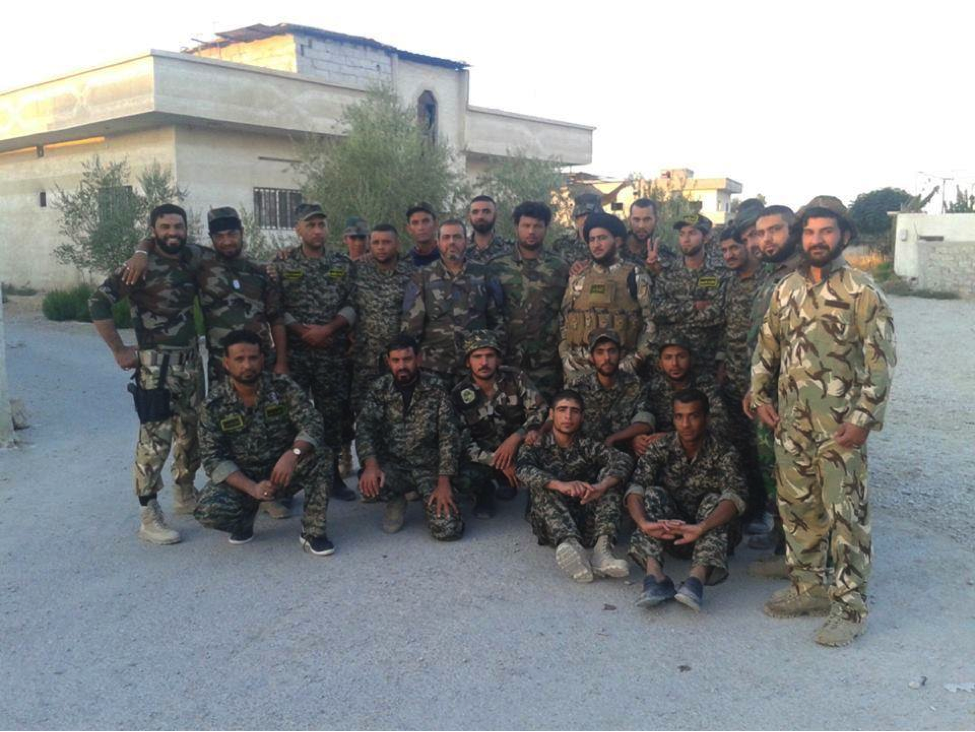

Figure 8: STK fighters pose for a photo in East Ghouta, Syria.
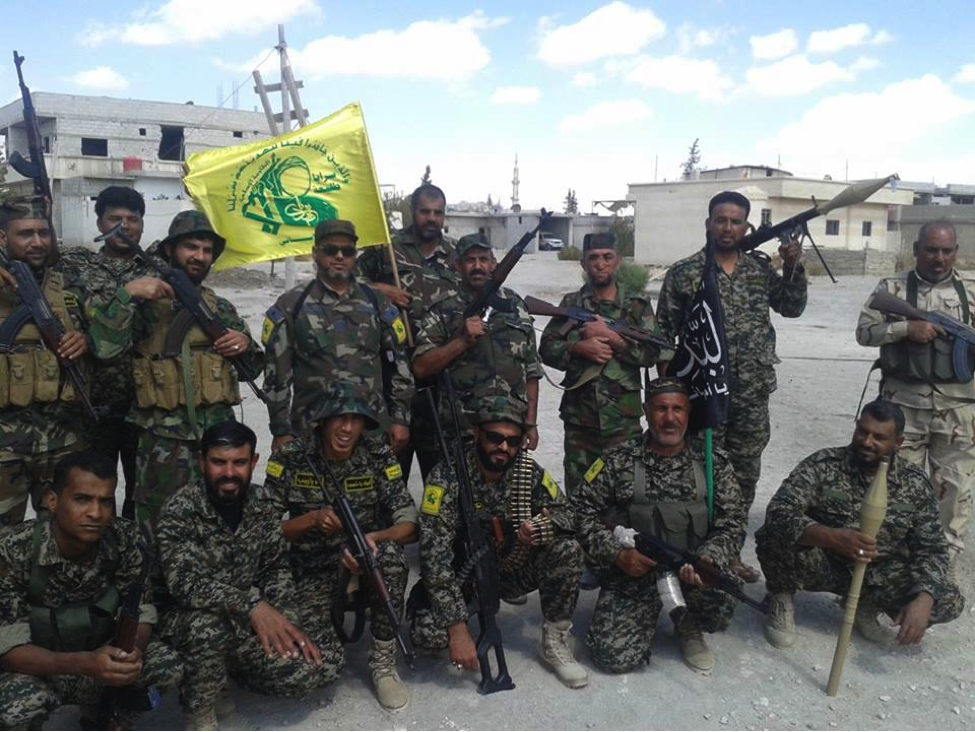

Figure 9: STK fighters pose with the group’s flag and light weapons.
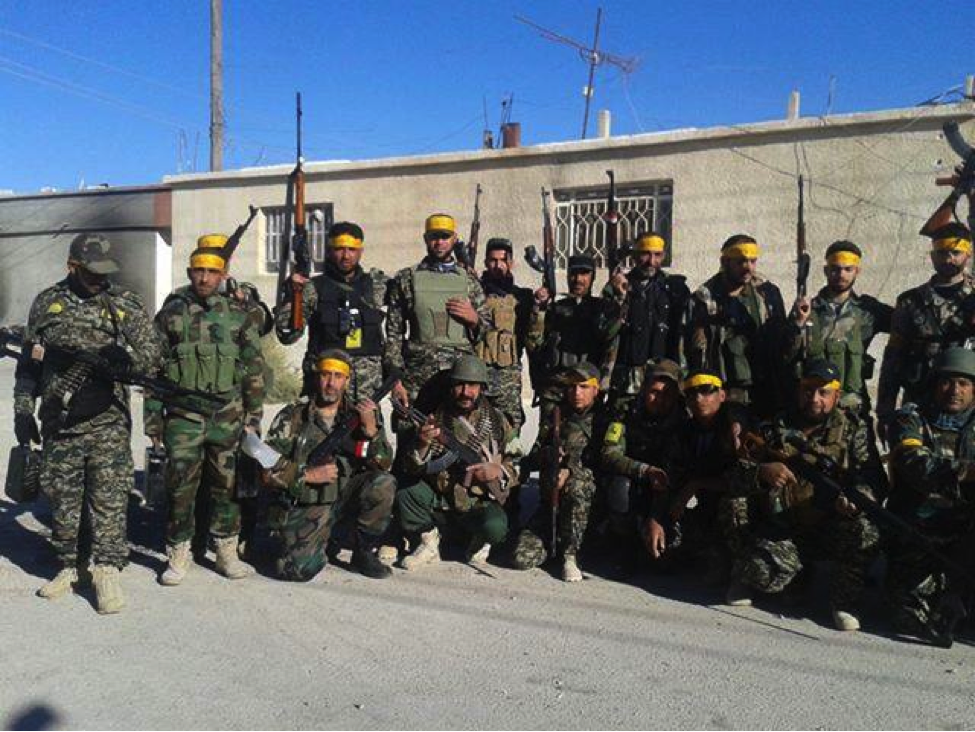

Figure 10: STK fighters pose in their uniforms and headbands.
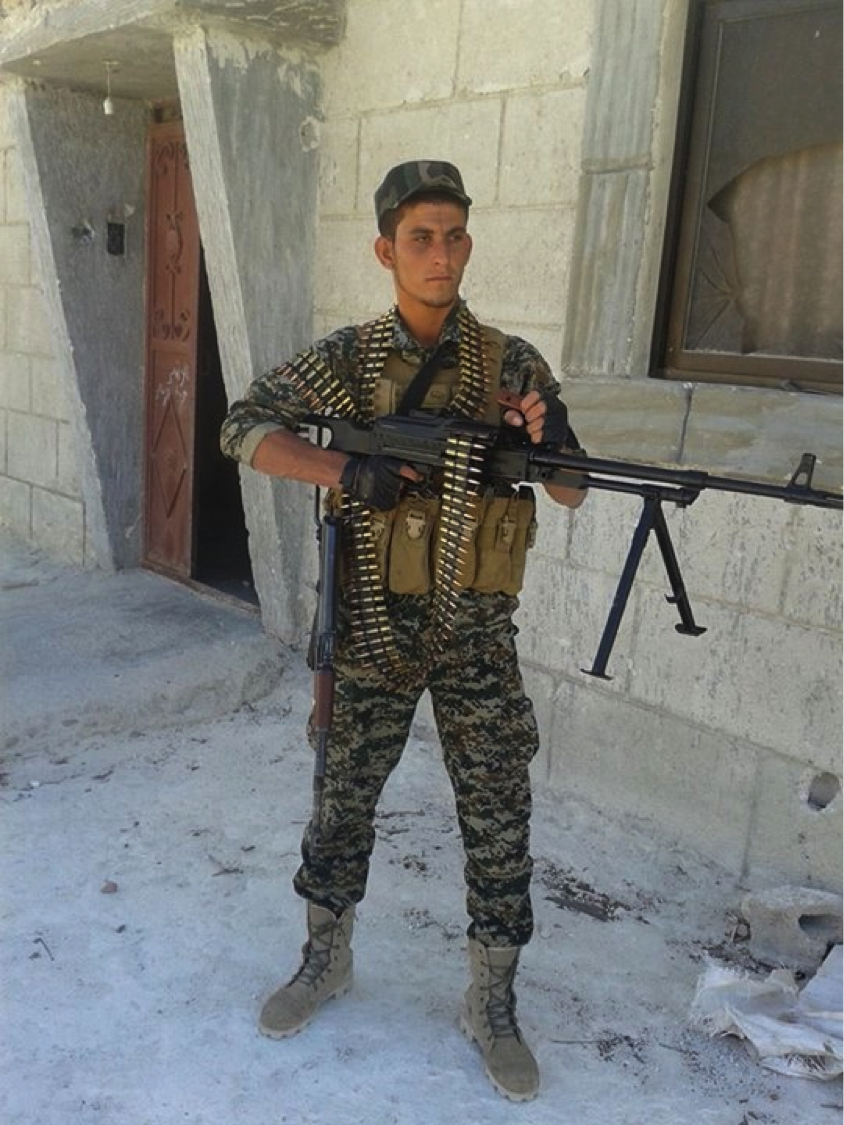

Figure 11: An STK machine gunner.
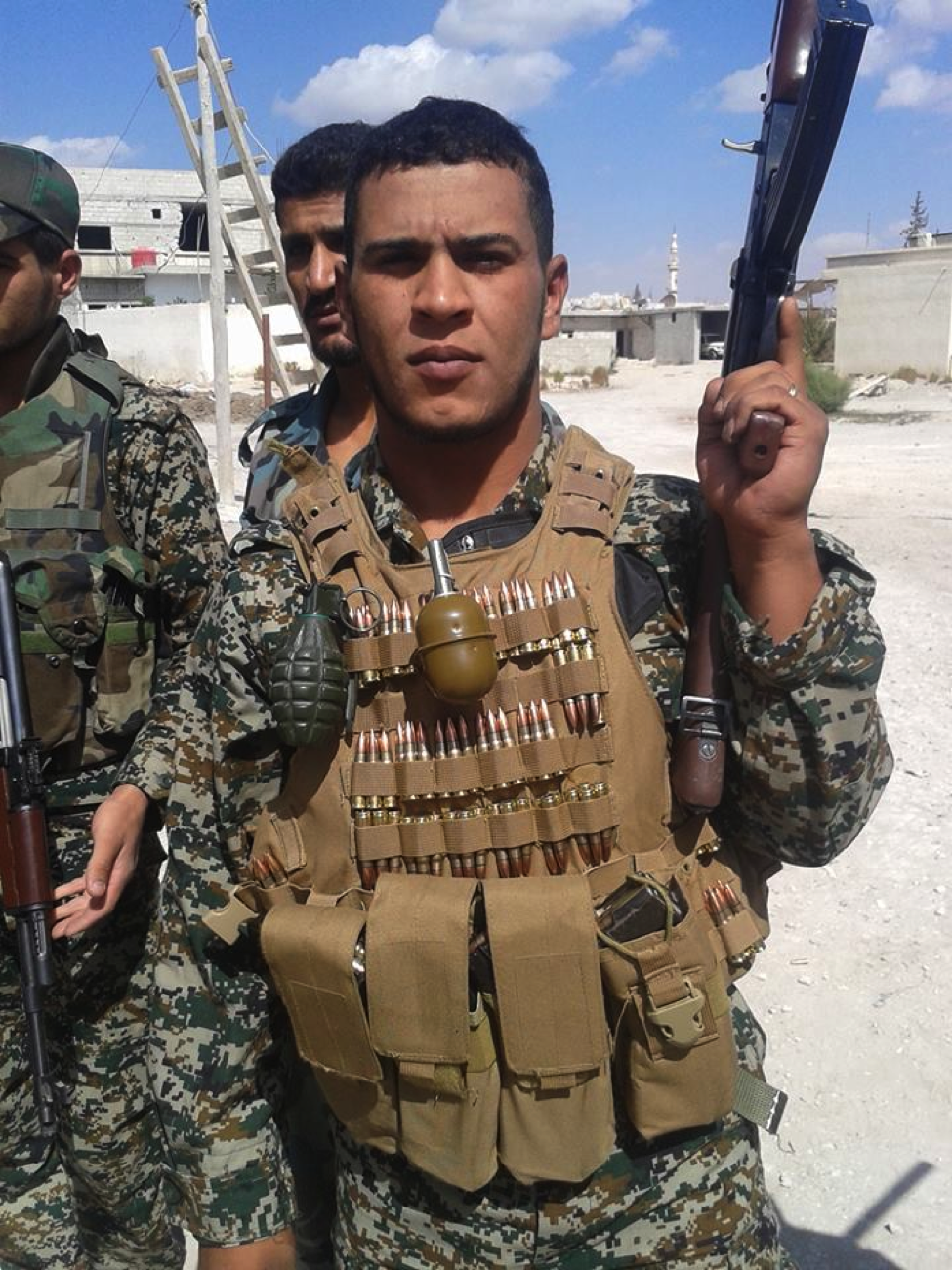

Figure 12: An STK fighter holds his rifle as he stands with other members of his organization.
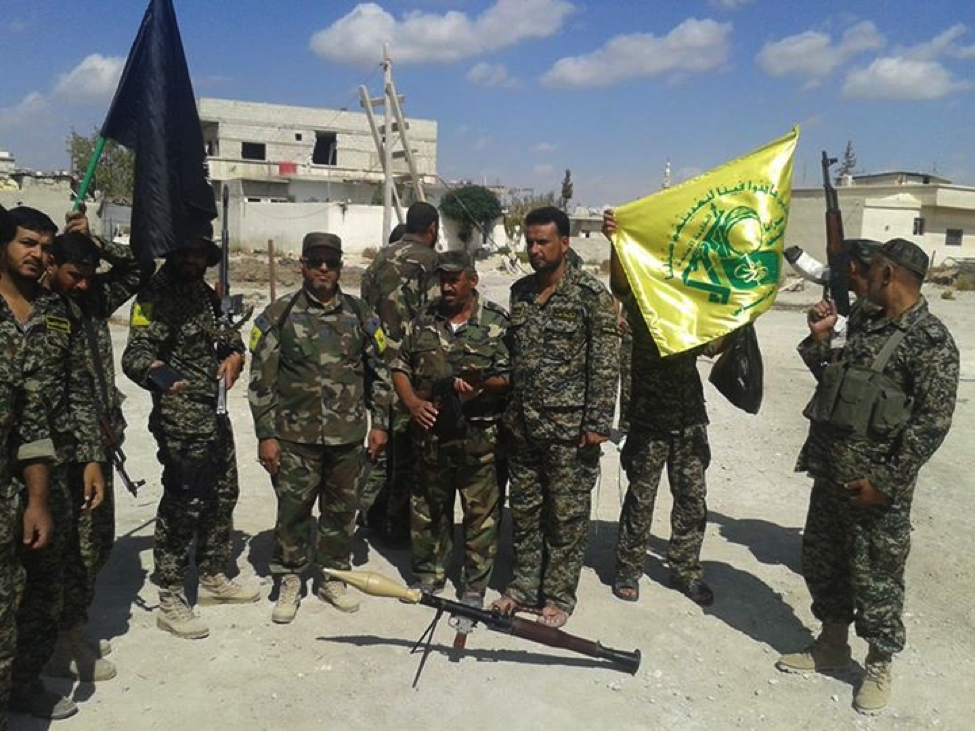

Figure 13: STK fighters pose around an RPG-7 and the group’s banner.
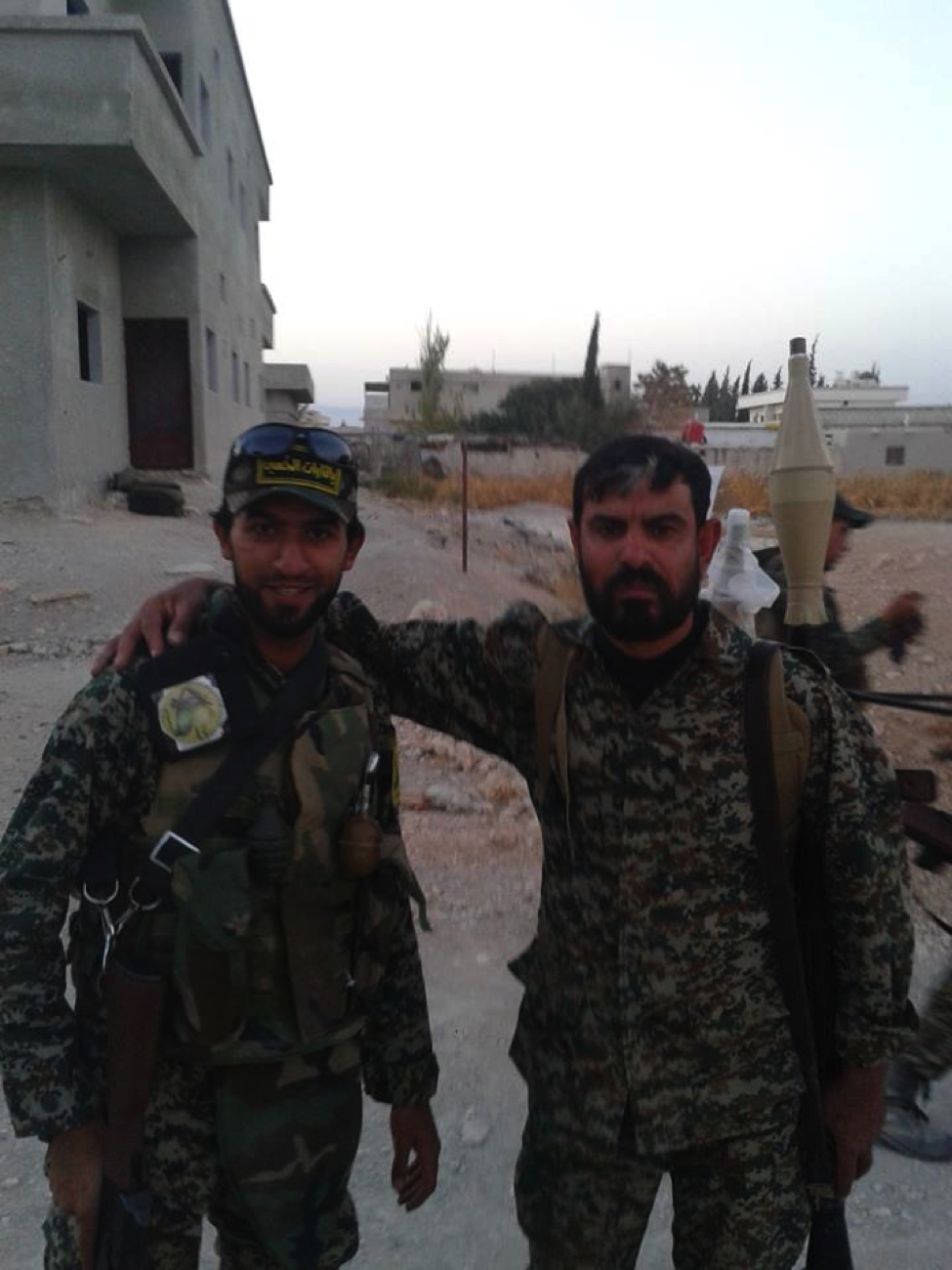

Figure 14: STK militiamen pose for the camera. The fighter on the right holds an RPG-7.
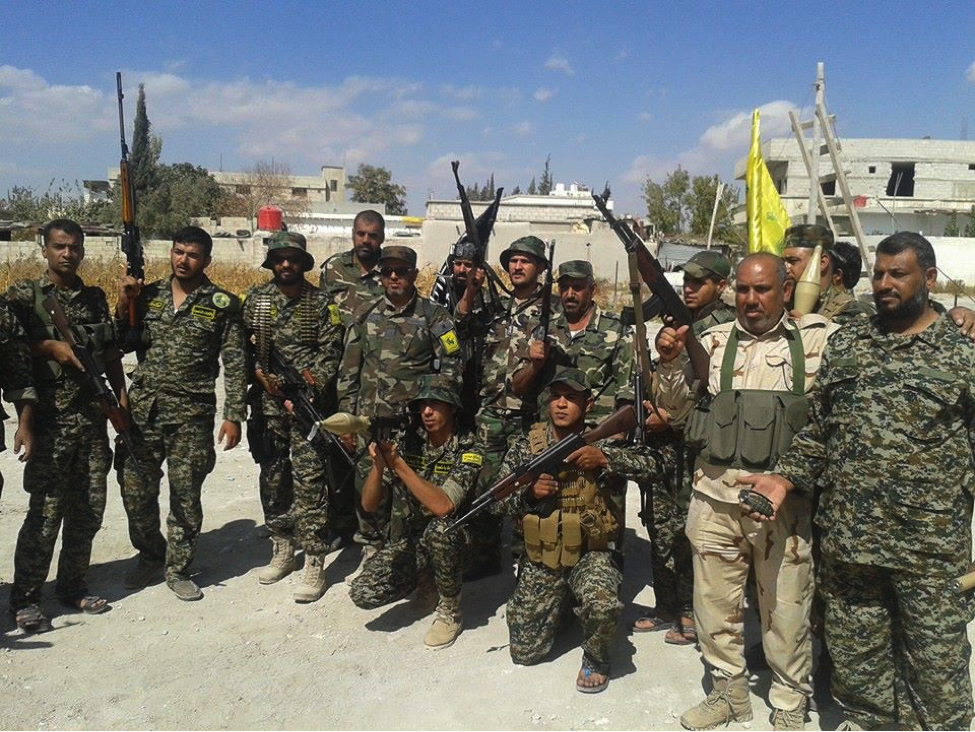

Figure 15: STK fighters stand and kneel together with their weapons as they pose for photographs.
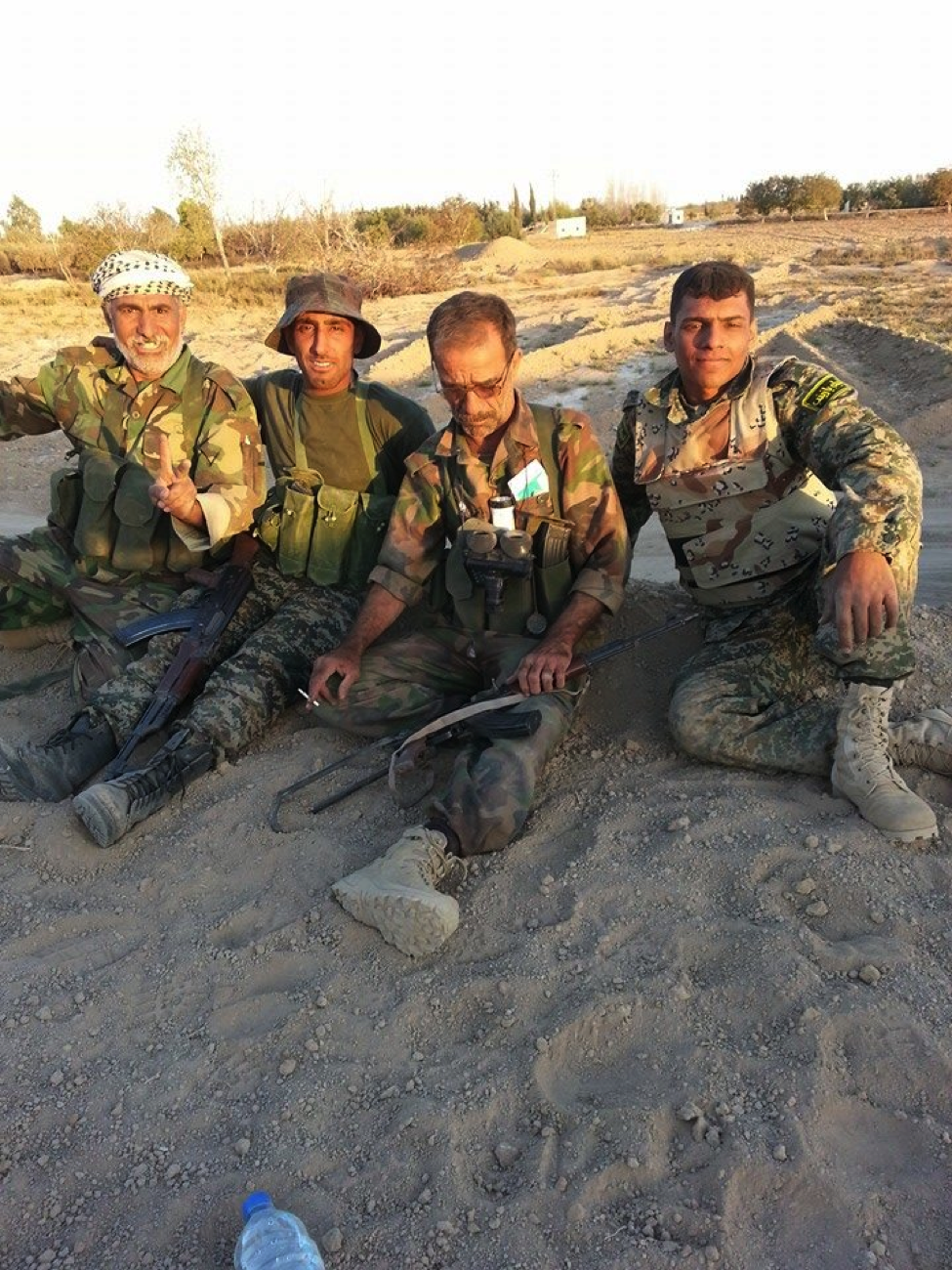

Figure 16: Older and younger fighters sitting together in Rif Dimashq.

Figure 17: STK fighters take a break during fighting. The photo appears to be taken in the same area where some videos of STK combat engagements occurred.
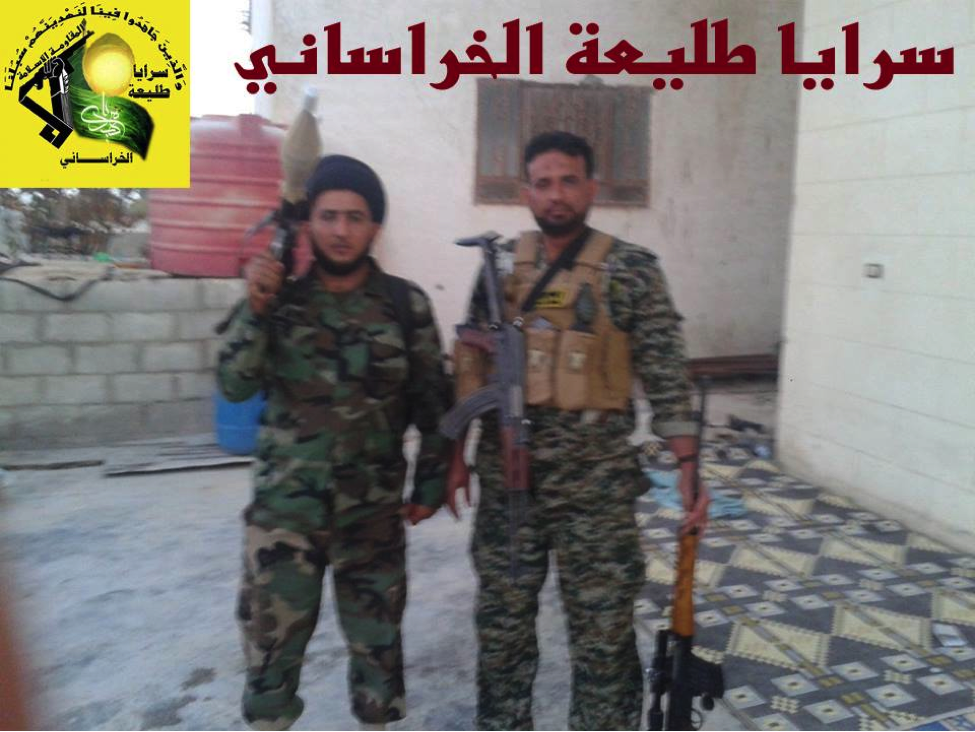

Figure 18: STK fighters, one appearing to be a Shia cleric, hold a mixture of small-arms.
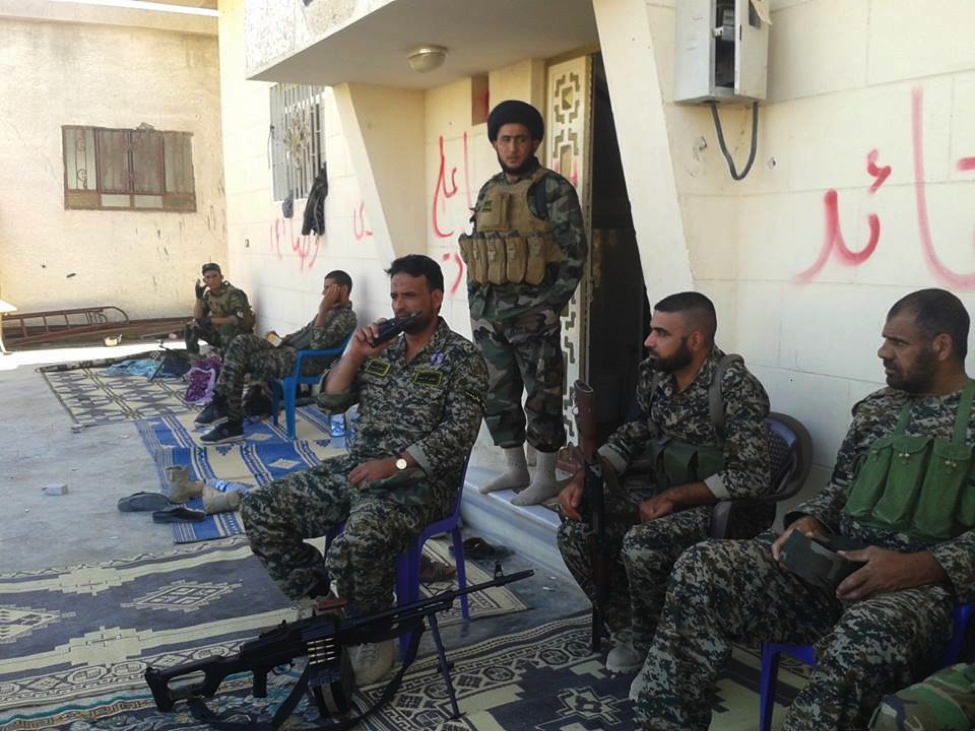

Figure 19: STK militiamen and a fighter in a black turban (signifying clerical status and descent from the Islamic Prophet Muhammed) relax in Rif Dimashq.
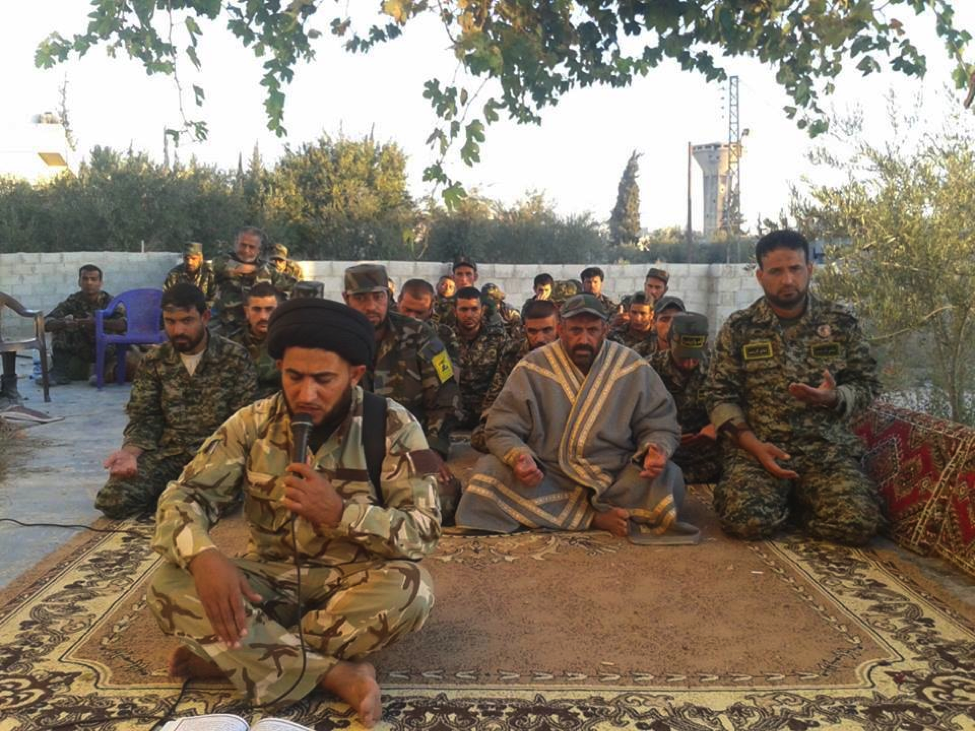

Figure 20: STK fighters at prayer time.
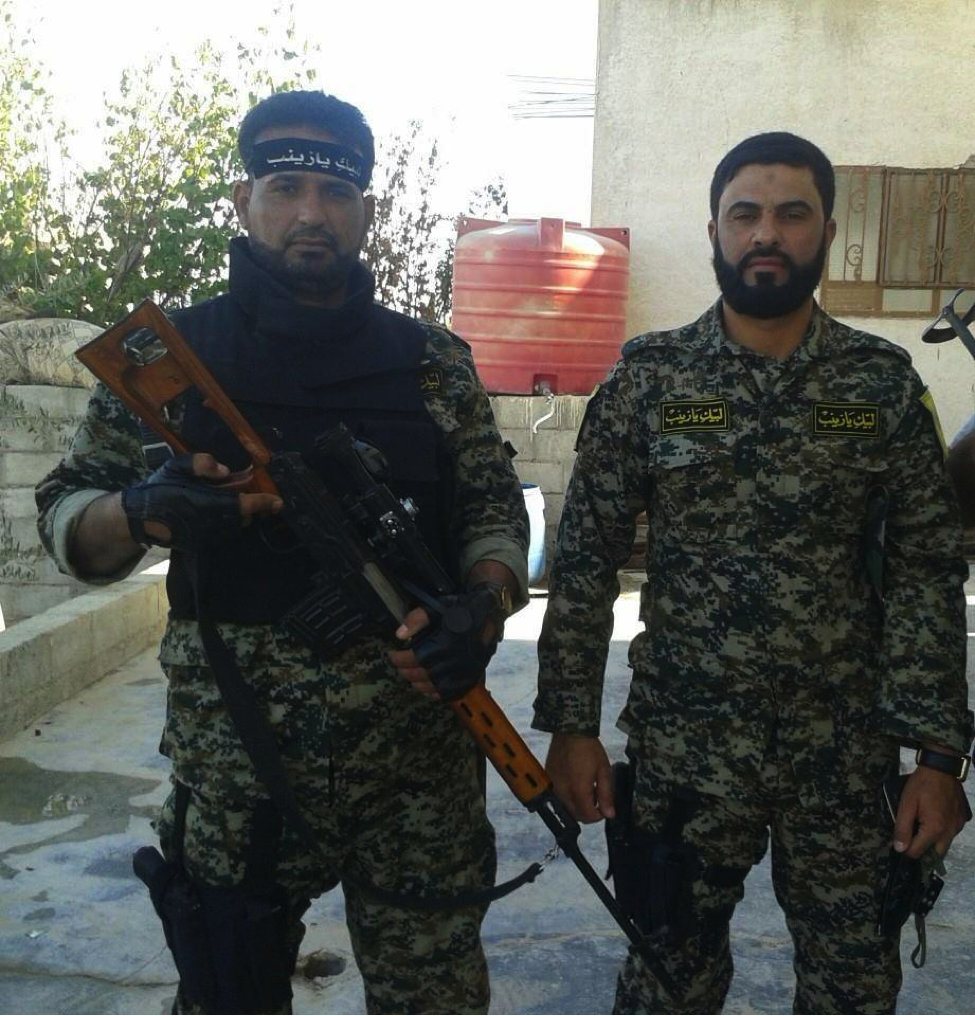

Figure 21: STK fighters. The fighter on the left has an SVD-type sniper rifle.
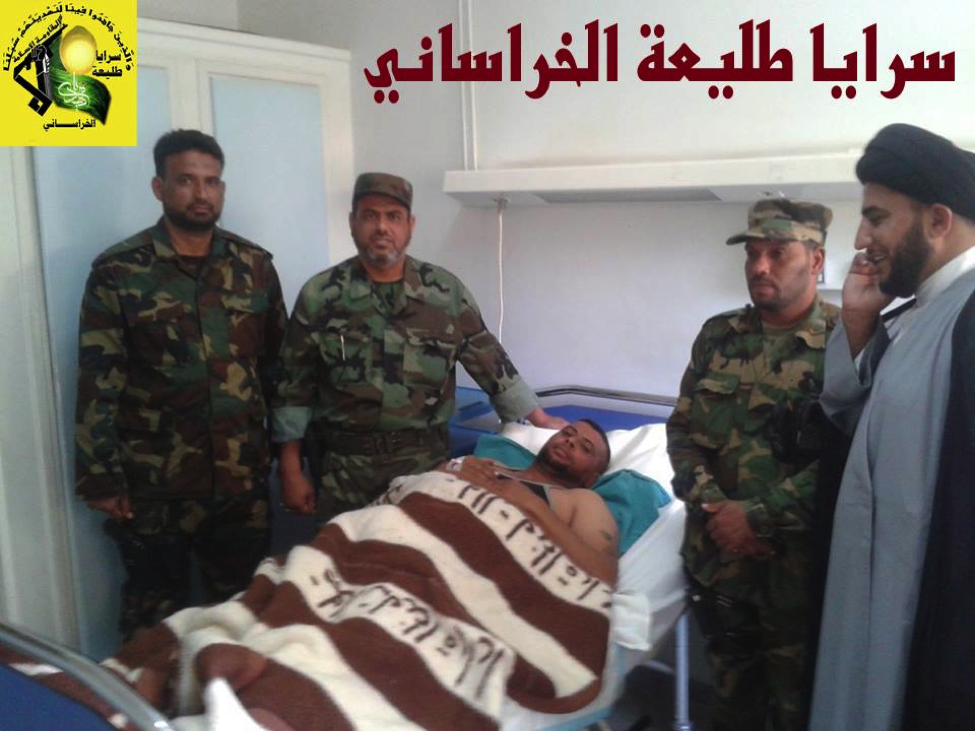
Figure 22: An injured fighter is shown with his compatriots and a Shia cleric.
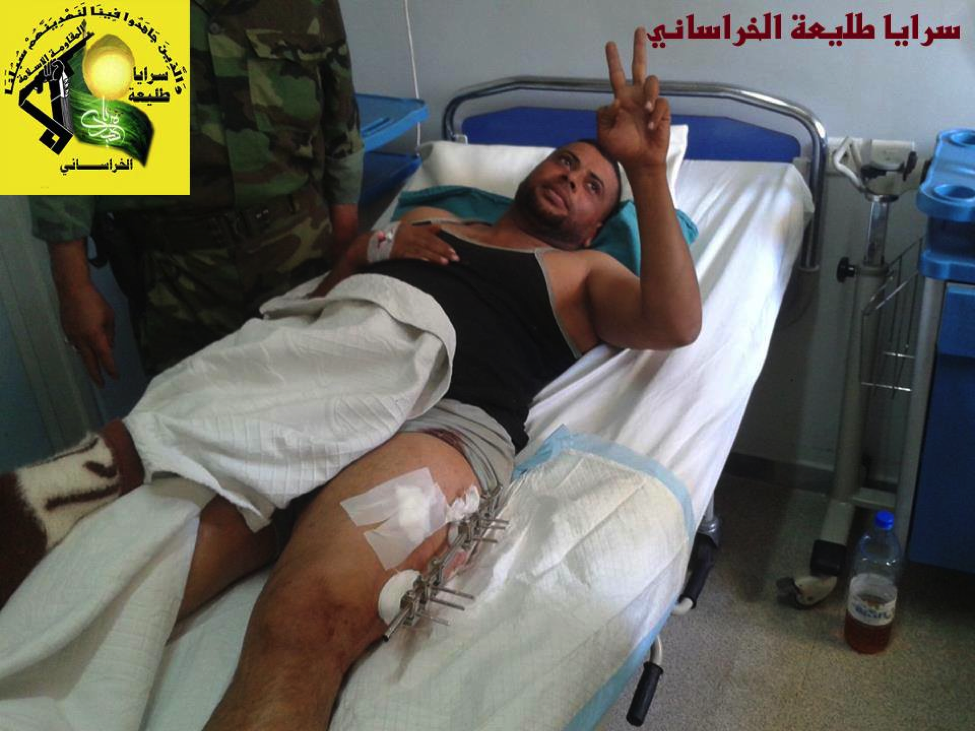
Figure 23: The same injured fighter flashes a “V for victory” symbol from his bed.
STK on Film
STK’s combat videos were first released in October and were quickly disseminated on Shia militia social media. When Syrian rebels came across the films in the weeks after their release, often the fighters were incorrectly branded as members of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas.
The first of the videos STK released shows the group fighting from a structure in Rif Dimashq. Save for the caption and titles on the videos posted, there was nothing which identified the fighters in the film as members of STK. In two other combat videos it show STK militiamen operating in East Ghouta section of Rif Dimashq, firing mortars, RPGs, rifles, and other weapons.
[1] Matthew S. Gordon, The Rise of Islam, (Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, 2005), Pp. 47-48. [2] See al-Madrasi’s Facebook page: https://www.facebook.com/pages/%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B3%D9%8A%D8%AF-%D9%85%D8%AD%D9%85%D8%AF-%D8%AC%D9%88%D8%A7%D8%AF-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D8%AF%D8%B1%D8%B3%D9%8A/178591738857323 The page has not been updated since 2012 and little information is available about the cleric online.
Hizballah Cavalcade: The Badr Organization’s Syrian Expeditionary Force: Quwet al-Shahid Muhammed Baqir al-Sadr
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
–
The Badr Organization’s Syrian Expeditionary Force: Quwet al-Shahid Muhammed Baqir al-Sadr
By Phillip Smyth ([email protected])
Click here for a PDF version of this post

Figure 1: The official logo for the Badr Organization’s Quwet al-Shahid Muhammed Baqir al-Sadr.
On July 13, 2013, Iraq’s Iranian-backed Badr Organization announced they had forces operating in Syria. Their announcement, made on a caption on the group’s “Military Wing” official Facebook page, noted that 1,500 Badr Organization fighters had been sent to Syria. Later, on July 21st, the Badr Organization announced their first casualty, Abu Dhar al-Sa’wdi. Seven days later, it was announced another Badr Organization fighter, Abu Sajad al-Hawli, was killed in Syria and that his funeral was held in Iraq (see below).
With the official July 28th declaration of Hawli’s death came the proclamation he was a member of Quwet al-Shahid Muhammed Baqir al-Sadr (BO-QSMBS). Though, at the time, the organization was simply referred to as, Quwet al-Shahid al-Sadr. The announcement of this Badr Organization sub-grouping followed the lead of their ally, the Iranian-backed Iraqi Shia Islamist organization, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq (AAH) and their Liwa’a Kafeel Zaynab. Liwa’a Kafeel Zaynab was setup specifically to fight in Syria as a type of AAH expeditionary force. In effect, the BO-QSMBS serves a similar role.
BO-QSMBS’s Facebook page was started on August 19, 2013 while their official YouTube station was established on February 28, 2013. In both cases the admin name of “Abo Alhassan” was used and regularly finds a mention on photos and YouTube clips posted by the group. The first original photos which were not simultaneously or previously posted on other official, semi-official, or mirror Badr Organization Facebook pages began to appear on August 25, 2013. However, most of BO-QSMBS’s causalities have been posted on the official Badr Organization Military Wing’s Facebook page, as opposed to the BO-QSMBS Facebook site.
BO-QSMBS is named after the late Grand Ayatollah Muhammed Baqir al-Sadr, the former leader of the Da’wa Movement in Iraq. Sadr, a Najaf, Iraq-based cleric, was instrumental in assisting with the creation of the Islamist ideology which would later be put into place in post-1979 revolutionary Iran by the late-Grand Ayatollah Khomeini. Sadr’s radical politics led him to be known by the name, “Khomeini of Iraq”.[1] In 1980, Sadr and his sister were both executed by the regime of Saddam Hussein.
BO-QSMBS has yet to post details about where they are fighting in Syria. However, based on their posted photographs, it is clear they are stationed in Damascus. As with other Shia Islamist organizations fighting in Syria, it is likely they have been deployed to fight on the East Ghouta front.
BO-QSMBS’s Weapons Systems
BO-QSMBS fighters utilize similar weapons systems as other Iraqi Shia organizations contributing fighters to Syria and Lebanese Hizballah. RPG-7s, PKM machine guns, SVD-style sniper rifles, Kalashnikov-pattern assault rifles, and M16-style assault rifles are the primary small-arms types featured by BO-QSMBS. M16-pattern rifles, particularly the M4 carbine model, appear to be fitted with optics, which may mean they are used in a designated marksman role. Additionally, the M16-type rifles are featured in BO-QSMBS’s posts about combat units more often than they are with other Shia militias operating in Syria.
It is possible that the group is using the Iranian-copy of the Austrian Steyr HS.50, a .50 caliber, long-range anti-material sniper rifle.[2] This rifle has been shown in the hands of many different Iraqi Shia organizations operating in Syria and Lebanese Hizballah.
As with Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq’s Liwa’a Kafeel Zaynab, the Badr Organization’s fighters in Syria are shown using pickup trucks (possibly the same pickup trucks as AAH’s men. See the videos on the Hizballah Cavalcade post Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq’s Liwa’a Kafeel Zaynab).

Figure 2: A BO-QSMBS fighter with an HS.50 type rifle.
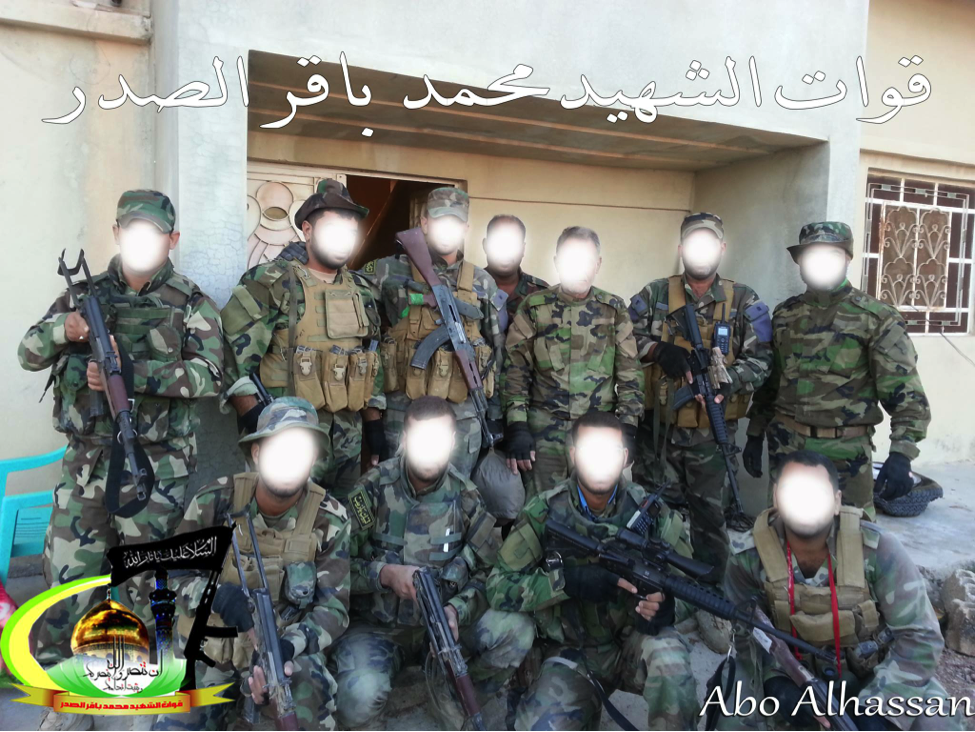

Figure 3: A combat unit of BO-QSMBS fighters. Note the 2 optics-mounted M4-style rifles.
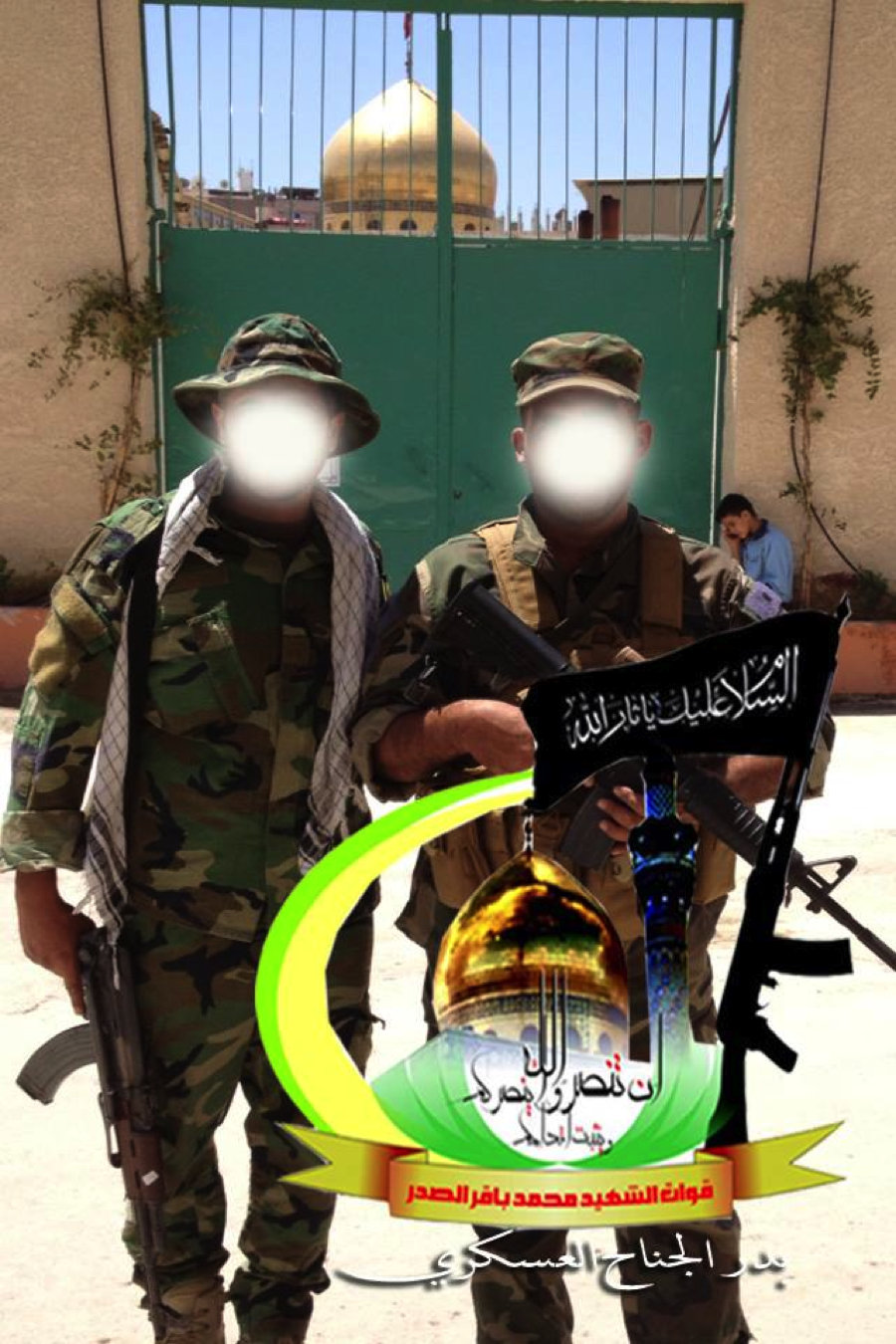

Figure 4: Two Badr fighters pose in front of the Sayyida Zaynab shrine in Damascus. The fighter on the right is holding an M4-type carbine (the same pictured in the photo above).
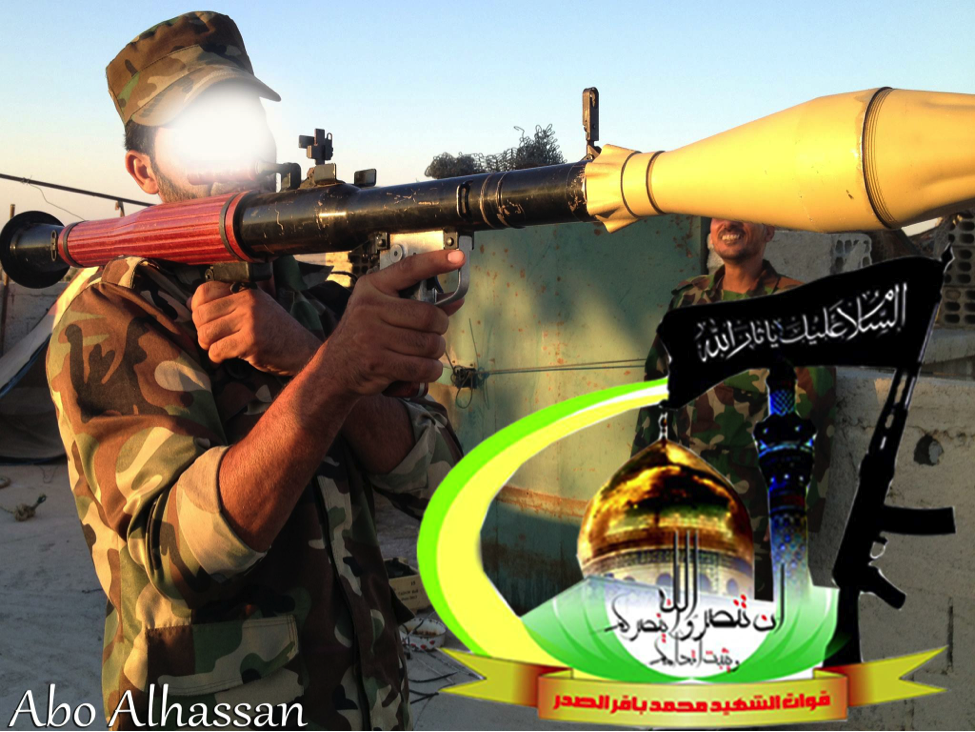

Figure 5: A BO-QSMBS fighter with an RPG-7.

Figure 6: A BO-QSMBS fighter holds a PKM machine gun in aloft as the late Grand Ayatollah Muhammed Baqir al-Sadr looks down upon him.
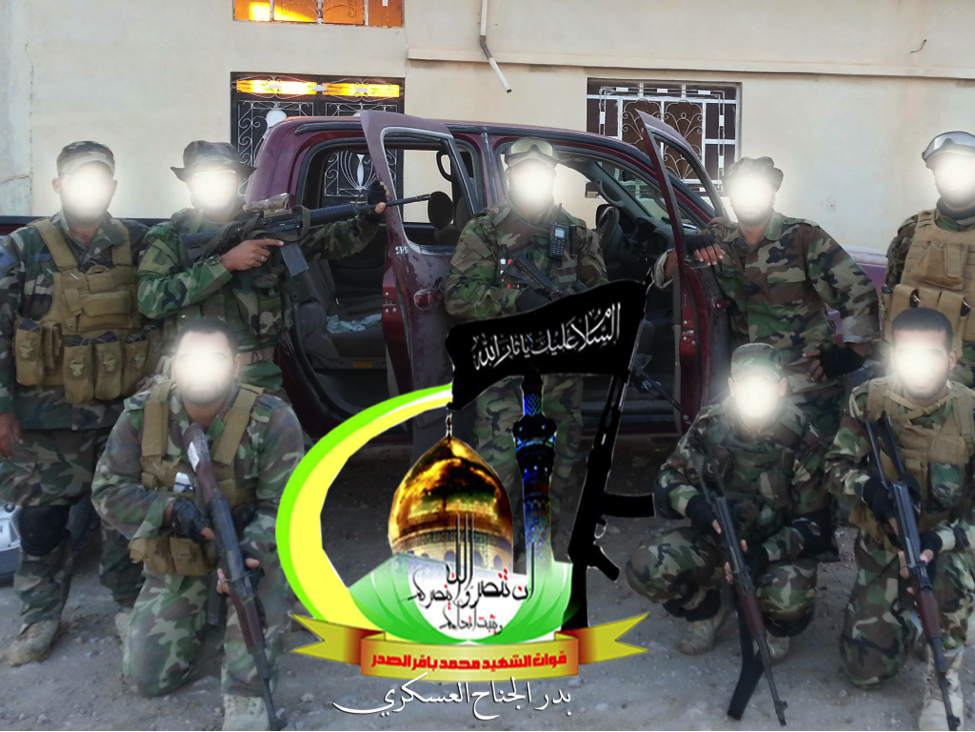

Figure 7: Badr fighters pose in front of a red pickup truck.
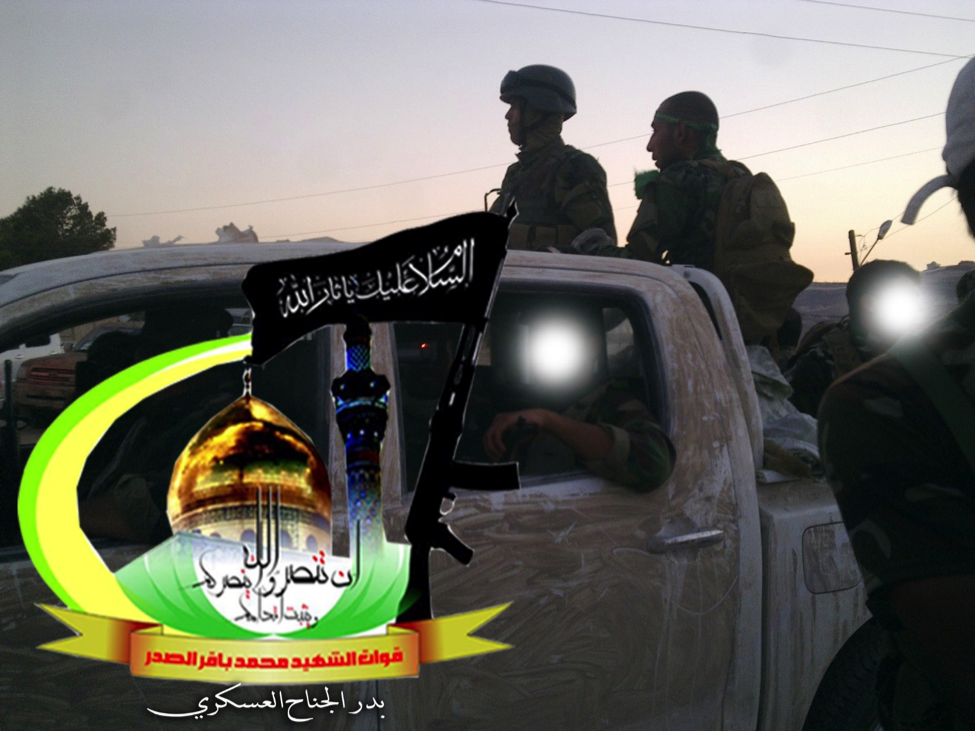

Figure 8: Badr fighters ride into battle in a mud coated white pickup truck.
BO-QSMBS’s Messaging to the Shia
BO-QSMBS has posted photographs attempting to show that Shia Islamic clerics have joined them in their fight inside Syria. The effect of these images may be to show the broader Shia community that there is broad religious support for the group’s actions in Syria.
The interconnectedness between the Badr Organization, Shia Islamist Iran and Lebanese Hizballah is also a regular feature on their social media webpages. One BO-QSMBS photo claimed to show Lebanese Hizballah fighter, Mahdi Yaghi and a fighter from the BO-QSMBS. Photos of Iranian Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei and of Iranian Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps commander, Qassem Suleimani are regular features on BO-QSMBS’s Facebook page.
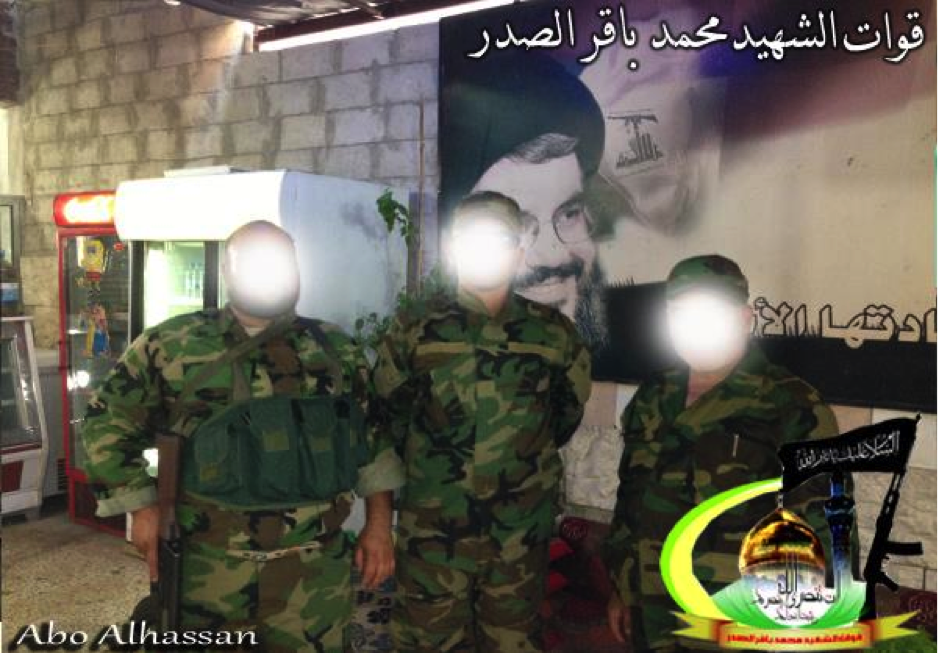

Figure 9: BO-QSMBS fighters stand in front of soda machines and a poster featuring Lebanese Hizballah leader, Sayyid Hassan Nasrallah.
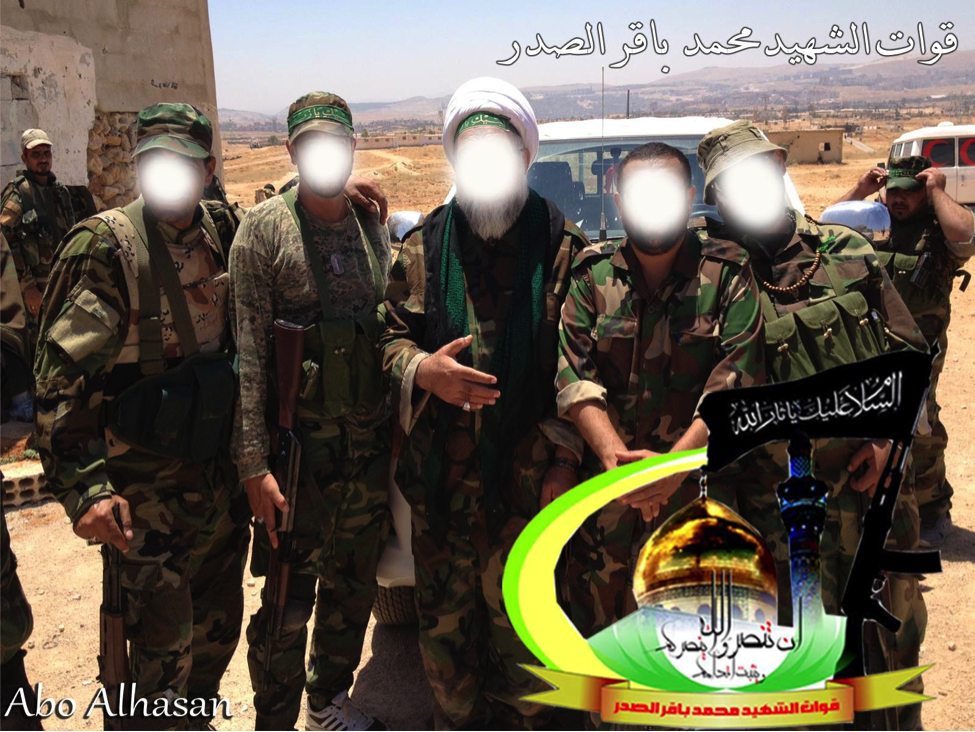

Figure 10: A white turban wearing Shia cleric wearing combat fatigues stands in the center of BO-QSMBS fighters.
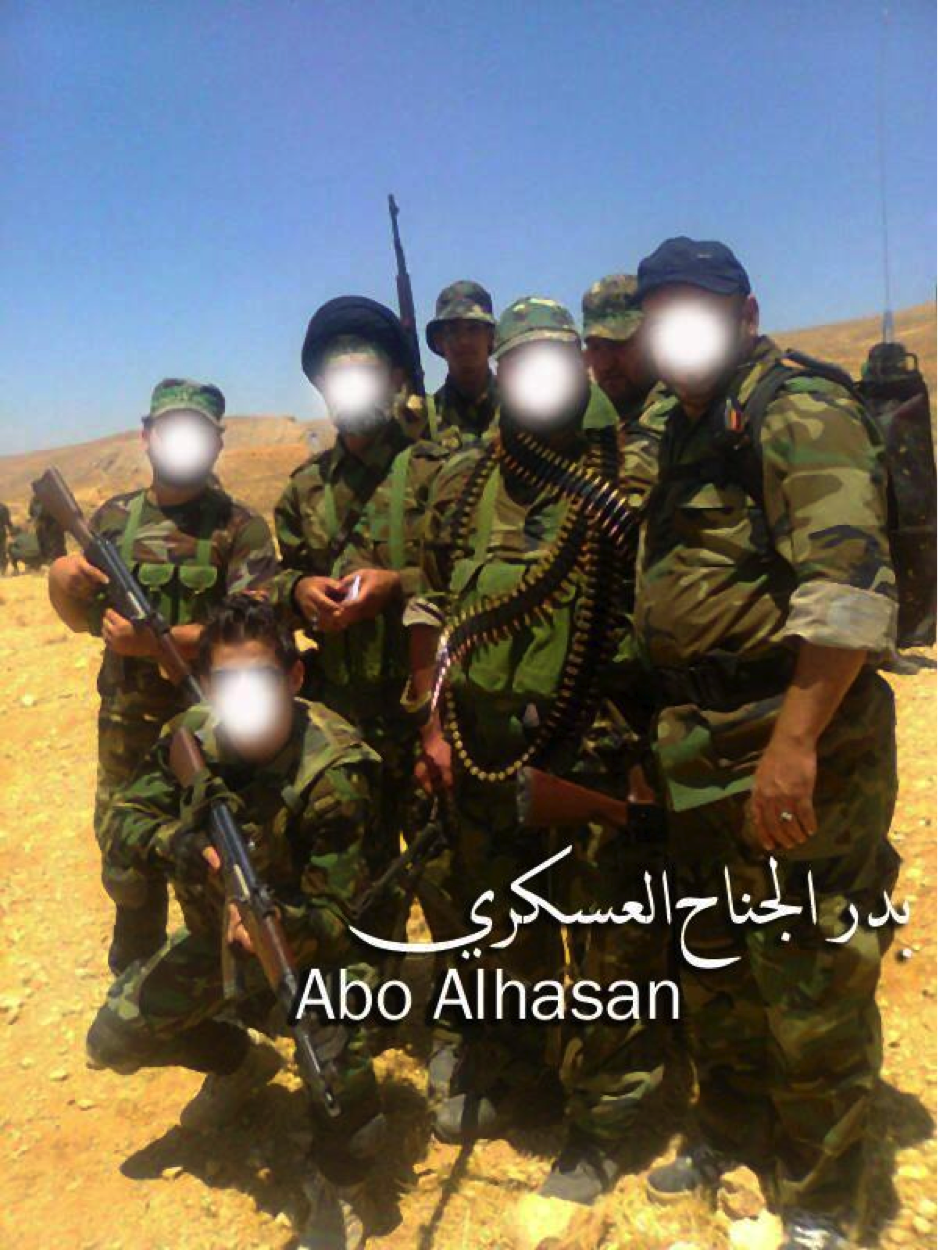

Figure 11: A black turbaned (denoting that he is descended from the Islamic Prophet Muhammed) Shia Islamic cleric stands in combat fatigues with Badr fighters.

Figure 12: BO-QSMBS claims this photo shows one of their fighters and Lebanese Hizballah’s Mahdi Yaghi. Yaghi was announced killed in Syria in October, 2013.

Figure 13: Lebanese Hizballah leader Sayyid Hassan Nasrallah and Iranian Surpreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei are pictured behind the Sayyida Zaynab shrine in Damascus.
Videos Released by the Group
A number of videos have been released by the BO-QSMBS. However, most of them are of poor quality and follow an established pattern seen with other Shia Islamist militias (all Iranian-backed) in Syria. Most of these videos utilize older footage previously released by other groups. In October, the footage of Abu Sajad al-Hawli was released by the Badr Organization. The video was placed on YouTube, Facebook, and official Badr websites.
[1] Patrick Cockburn, Muqtada Al-Sadr and the Battle for the Future of Iraq, (New York: Scribner, 2008), Pp. 27-35. [2] See: https://www.thefirearmblog.com/blog/2012/07/13/steyr-hs-50-in-iran-counterfeit/
Hizballah Cavalcade: Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada Emerges: Updates on the New Iraqi Shia Militia Supplying Fighters to Syria
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada Emerges: Updates on the New Iraqi Shia Militia Supplying Fighters to Syria
By Phillip Smyth ([email protected])
Click here for a PDF version of this post

Figure 1: A KSS member salutes the group’s flag.
When Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada (KSS) first announced their presence to the world, little was known about the organization, its leadership, or its force size. Funerals the group held for three of its fallen fighters in May not only announced the group’s existence, but also pointed to a strong link with Iran. However, following these funerals, little was heard from the group. Nevertheless, it would appear that starting in August the organization has fully redeveloped its messaging and online propaganda. This campaign has included well-organized and professional group funerals for members killed fighting in Syria, brand new and far-less amateurish imagery, and the introduction of some more unique features in KSS’s propaganda. Even the group’s uniforms have undergone a type of remake, featuring the KSS’s logo and patches showing their fighter’s commitments to “Defending Sayydiah Zaynab”.
The group has also been more open when it came to the numbers of its fighters deployed to Syria. In an Al-Sharqiya interview held with KSS’s information office, the group claimed to have sent 500 members to Syria.[1] Public announcements by the group have also established that since July, KSS has deployed a number of combat units to more rural zones around Damascus, particularly the frontlines in East Ghouta.
Additionally, via official websites belonging to the Badr Organization Military Wing, it is possible that a closer relationship exists between KSS and the Badr Organization. Since Badr did not announce its involvement in Syria until July, 2013, this may be a signal that KSS was used as a front group to send Badr fighters to Syria.
In terms of a social media presence, KSS has tried to reinvent itself. When the group’s more private group page was removed from Facebook, the organization simultaneously established a new Facebook page and more private profiles to disseminate photos and other information about the group. Since August, KSS has posted 1-4 unique new photographs of their activities in Syria. Additionally, other pro-Shia militia-in-Syria Facebook pages have re-posted their photographs.
Social media stature aside, the group’s rapid public growth, increased professionalism, combat deployments, and growing presence in Iraq—beyond its original base in Basra, demonstrates KSS as a rapidly growing Shia militia force. It is likely KSS will continue to announce its militant activities in Syria.
The Fighters
The fighters of Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada appear to be uniformed with clear identifiable insignia. The combatants carry arms which are familiar to other Shia militia groups, particularly the PKM machine gun, RPG-7s, Kalashnikov-type assault rifles, and the popular SVD-style sniper rifle. KSS fighters have also been photographed with anti-material sniper rifles.

Figure 2: A KSS fighter with a customized Kalashnikov-type rifle and an SVD style sniper rifle.
Figure 3: A KSS fighter poses with a mortar.
Figure 4: A KSS fighter poses on rubble with an SVD style sniper rifle. Note the KSS logo patch.
Figure 5: A KSS fighter holds an RPG-7.
Figure 6: KSS fighters pose with a PKM machine gun.
Figure 7: A small unit of KSS fighters holding a mixture of Kalashnikov type rifles, an SVD style sniper rifle, and a PKM machine gun
Figure 8: This KSS fighter appears to be holding a Steyr HS .50 style, .50 caliber bolt action anti-material sniper rifle. The rifle could also be an Iranian copy of the HS .50.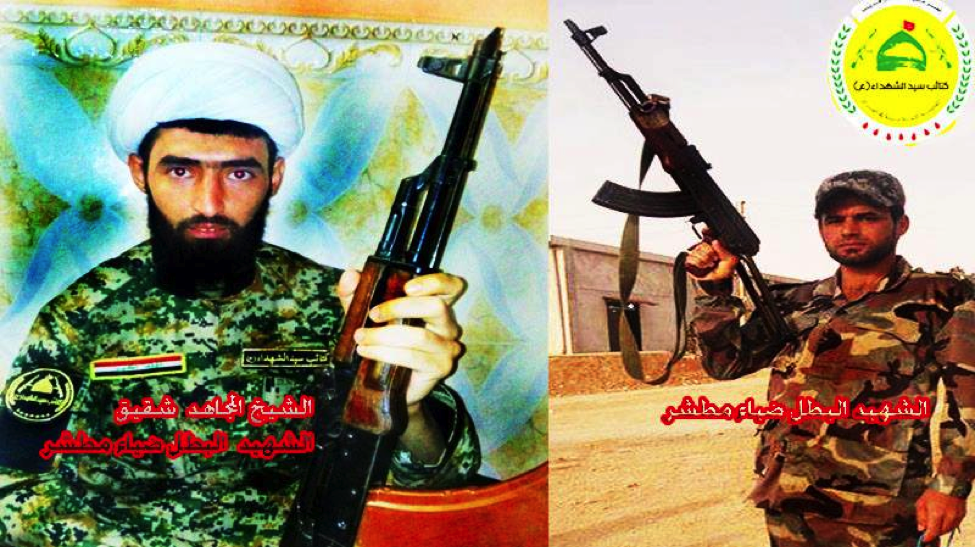
Figure 9: Diya Issawi’s brother (left), pictured in a white turban of commonly found with Shia clerics. He was listed by KSS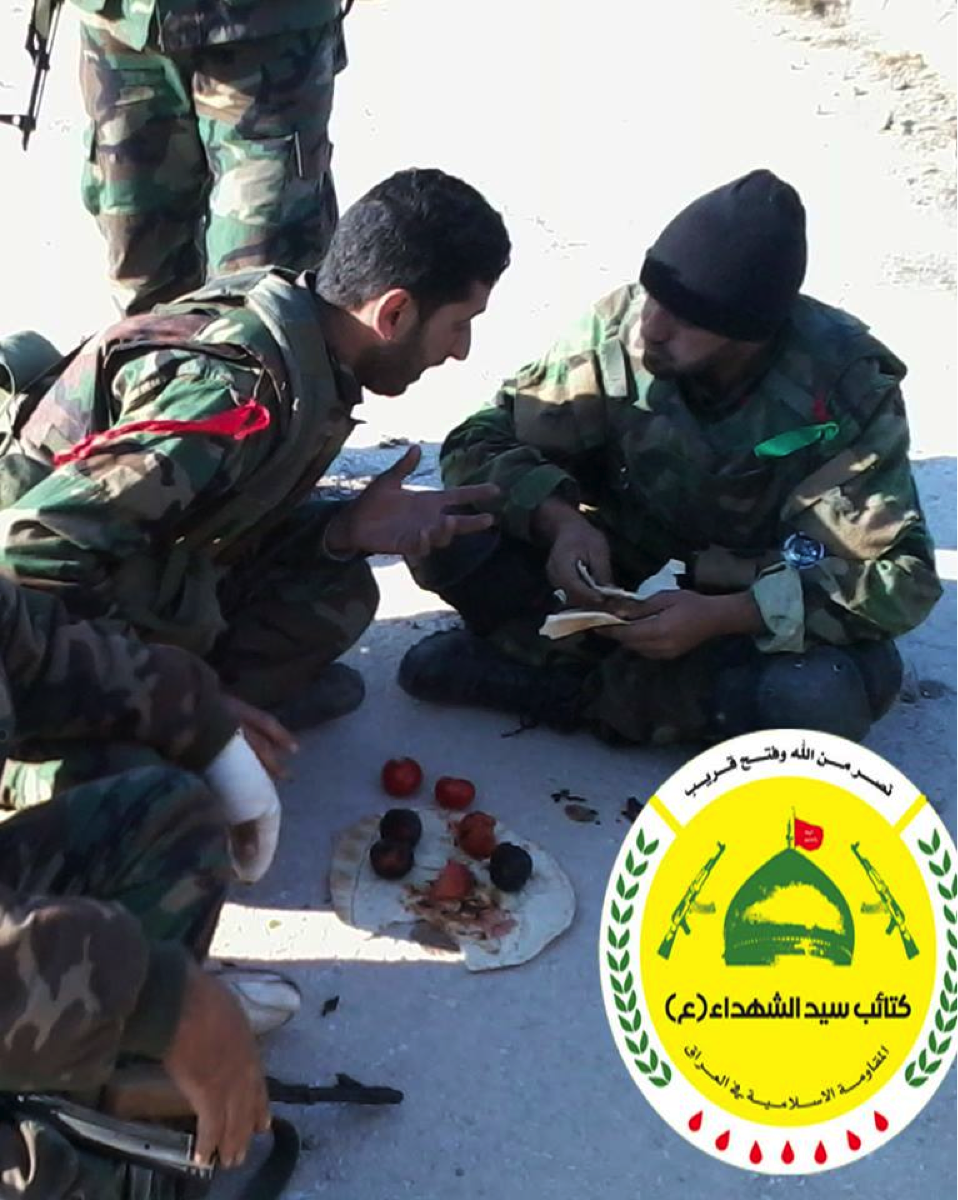
Figure 10: KSS members “Enjoy a simple modest lunch”. This photo was issued by the group to demonstrate the humility of their fighters.
The KSS’s New Martyrs
On August 20, a main Facebook page which publishes information about Shia militia operations and deaths in Syria, claimed that Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada was operating in East Ghouta. During their operations in the area, the page reported three fighters as killed-in-action, with another five missing (listed in the post as, “Fate unknown”).
On August 24, KSS released eight martyrdom announcements in the form of more professionally designed graphics. The photographs were first released on the KSS and then the Badr Organization Military Wing’s official Facebook page. The posted images presumably show the eight fighters who were killed or who were missing in East Ghouta, in Rif Dimashq. It is important to note that on August 21, East Ghouta was also the reported as the scene of the deadliest chemical weapons attack within Syria.[2] According to American Military University’s In Homeland Security Blog chief correspondent and chemical weapons expert, William Tucker, it is possible these KSS fighters were, “bracketing the kill box”.[3] Meaning, they had generally surrounded the area where the chemical weapons were used and then attacked any Syrian rebel elements which may have tried to breakout.
However, a video emerged on September 1st showing some of the KSS fighters being killed in an assault by rebel forces. A longer video of the engagement was released on September 7th. The KSS fighters were reportedly stationed in what rebels referred to as a train station in East Ghouta. This would suggest that some of the KSS fighters may have been guarding transportation links in the area.
** Warning: Graphic Imagery **
In the video, it is clear to see that KSS fighters openly wear the insignia for their organization during combat operations. Some KSS and possibly Hizballah fighters are shown with Shia Islamic paraphernalia. One card removed from the pocket of a dead fighter featured a stylized photo of the assassinated Hizballah terror-leader, Imad Mughniyeh.[4]
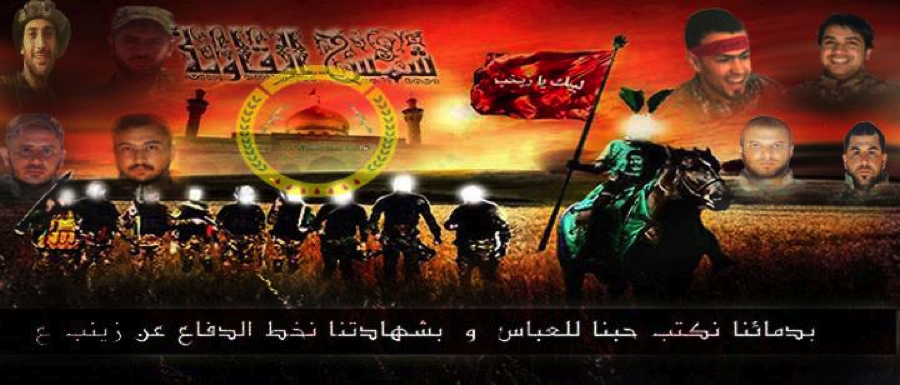
Figure 11: Eight of the dead KSS members are featured on this poster.
Name: Amir al-Badlawi
Death Announced: September 5, 2013

Name: Muhammed Radi al-Shumaylawi
Death Announced: August 24, 2013. Funeral held on August 27, 2013.

Name: Al-Said Hasan ‘Ali Farhoud al-Furaydawi
Death Announced: August 11, 2013

Name: Sejjad al-Shibani
Death Announced: August 23, 2013, reportedly killed on August 20, 2013, funeral reportedly held on August 27, 2013.

Name: Walid al-‘Abudi
Death Announced: August 23, 2013, reportedly killed on August 20, 2013.

Name: ‘Ali Hamza al-Deraghi al-Sadiqi
Death Announced: August 23, 2013, reportedly killed on August 20, 2013, funeral reportedly held on August 27, 2013.


Figure 12: Sadiqi is shown in a car with what may be another KSS member and a Kalashnikov style rifle.

Figure 13: An official KSS release of Sadiqi with other KSS fighters.
Name: Zulfiqar al-Raseetmawi
Death Announced: August 25, 2013, reportedly killed on August 20, 2013, funeral reportedly held on August 27, 2013.

Name: Muhammed ‘Abd al-Husayn al-Faridawi
Death Announced: August 25, 2013, reportedly killed on August 20, 2013, funeral reportedly held on August 27, 2013.

Name: Ala al-Ka’bi
Death Announced: August 23, 2013, reportedly killed on August 20, 2013, funeral reportedly held on August 27, 2013.

Name: Watheq Hashem al-‘Anzi
Death Announced: August 23, 2013, reportedly killed on August 20, 2013, funeral reportedly held on August 27, 2013.


Figure 14: An officially produced martyrdom post
Name: ‘Ali Sami al-Zubaydi
Death Announced: August 23, 2013, reportedly killed on August 20, 2013, funeral reportedly held on August 27, 2013.
Notes: Zubaydi was one of the few KSS dead who had other photos of him in Syria uploaded to a number of pro-Shia militia
Hizballah Cavalcade: Breaking Badr, The New Season: Confirmation of the Badr Organization’s Involvement in Syria
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Breaking Badr, The New Season: Confirmation of the Badr Organization’s Involvement in Syria
By Phillip Smyth ([email protected])
From May-June, 2013, the Iranian-backed, Iraqi Shia, Badr Organization upped their rhetoric regarding the group’s potential involvement in the Syrian Civil War. This rhetoric resulted in a Hizballah Cavalcade post which attempted to assess whether the group was in fact sending fighters to Syria. Despite their threats, only a few propaganda photos and the death of a possible Badr Organization fighter were available. Thus, the results were inconclusive. Nevertheless, it was still established the group may become more involved in the fighting or that they were preparing a phased approach to publicize Badr’s participation in the fighting.
On July 13th, the group announced via Facebook that it had sent “Over 1,500” militiamen to Syria. By late-July, 2013, the Badr Organization’s Military Wing openly announced it had lost members in Syria and held public funerals for them. According to the Badr Organization Military Wing’s Facebook page, one of these funerals was held in Baghdad. The Badr Organization Military Wing also released one photo which supposedly shows some of their members in Syria.
With the death announcement for one of the Badr Organization’s men came the claim he belonged to “Quwet Shahid al-Sadr” (Forces of the Martyr Sadr). The Forces of the Martyr Sadr is not a separate or new militia operating in Syria. Instead, it is simply the name the Badr Organization has given to the group of its fighters operating in Syria.
Regardless, unlike other Iranian-backed organizations which have increased the amount of photos, videos, and social media announcements since the beginning of July, the Badr Organization has only released limited amounts of information about its forces and operations inside Syria.

Figure 1: On July 13, 2013, the Badr Organization’s Military Wing posted this photograph with the announcement that over 1500 of its fighters had been sent to Syria.

Figure 2: The Badr Organization’s Military Wing claimed this photo showed members of the group operating in “Defense of Saydah Zaynab”. Some of the fighters are familiar faces and can be seen in propaganda for Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas.
The Badr Organization’s Losses In Syria
Name: Abu Dhar al-Sa’wdi
Death Announced: July 21, 2013
Notes: Unlike other martyrdom posters which, have only announced the dead as having “Defended Zaynab”, this poster clearly mentions that al-Sa’wdi was killed “in Syria”.

Name: Abu Sajad al-Hawli
Death Announced: July 28, 2013
Notes: Only one photograph has been released on social media of Abu Sajad al-Hawli’s funeral. His death was first announced on the Badr Organization Military Wing’s official Facebook page.

Figure 3: Abu Sajad al-Hawli’s martyrdom poster features the golden dome of the Saydah Zaynab Shrine in the background.
Hizballah Cavalcade: Breaking Badr: Is Iraq’s Badr Organization Operating In Syria?
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Breaking Badr: Is Iraq’s Badr Organization Operating In Syria?
By Phillip Smyth ([email protected])
Click here for a PDF version of this post
Due to many public funerals, a number of Iranian-backed Iraqi organizations (Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq, Kata’ib Hizballah, and Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada stand as prime examples) have been identified as supplying combatants to fight in support of the regime of Bashar al-Assad in Syria. However, the Badr Organization, an Iraqi group which has pledged its loyalty to Tehran, was absent from announcements involving Iraqis killed in Syria and has been rather murky on whether it is fighting in Syria.

Figure 1: The Badr Organization Military Wing’s logo. Note its similarity to Lebanese Hizballah’s, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq’s, Kata’ib Hizballah’s and the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps’ logos
In February, 2013, Hadi al-Amiri, leader of Iraq’s Badr Organization, said Turkey and Qatar were supplying Al Qa’ida and that this was a declaration of war against Iraq.[1] During a June 21, 2013 interview with Reuters, Amiri said the group was contemplating intervening in Syria and could not, “sit idle while the Shi’ites are being attacked”. [2] Regardless, after assessing posted material issued by the Badr Organization’s social media webpages, it is becoming clear the group may actually be involved in the fighting in Syria.
Beginning life as the Badr Brigade, the militia for the Supreme Council for the Islamic Revolution in Iraq (SCIRI), the Badr Organization split from SCIRI and became its own political group.[3] In 2006, the Council on Foreign Relations reported the Badr Organization had upwards of 10,000 militiamen.[4]
Before and after the split with SCIRI, the Badr Organization received heavy funding, training, and equipment from Iran.[5] The group is also unabashed about its close links with Iran, especially Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, and Iranian proxy groups.
Despite material which affirms the group supports the actions of Lebanese Hizballah in Syria, the official Facebook page for the Badr Organization makes no mention that its militiamen may be also operating in Syria. Nevertheless, there are hints of involvement on the group’s page for the Badr Organization Military Wing, the Badr Organization’s militia. Throughout the Spring of 2013, the Badr Organization increased the level of supportive rhetoric for Lebanese Hizballah, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq, Kata’ib Hizballah, and Iran’s efforts in Syria. A June 21, 2013 photo’s caption said the, “Badr Military Wing will defend Zaynab to the last mujahid”.
Figure 2: Photo from the Badr Organization Military Wing’s Facebook saying the group will “Defend the Zaynab Shrine to the last holy warrior [mujahid]”.
Earlier, on April 22, 2013, The Badr Organization Military Wing produced and uploaded a song to YouTube. The song’s discription said it was, “A message from Badr to the unjust”and included the lyrics, “We will issue a death sentence against the Free Syrian Army (Jaysh al-Hurr) and no one will be able to defeat us.” The only images present during the music were those of a fighter armed with an RPG-7 in front of the Saydah Zaynab Shrine, the logo for the Badr Organization Military Wing, and the logo for the Badr Organization.
From May 5-9, 2013, a few photographs depicting Badr Organization fighters showing their “Soliderity” with members of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas (LAFA) appeared on various pro-LAFA, Badr Organization, and pro-Lebanese Hizballah websites. LAFA has acted as the main front for pro-Iranian fighters inside Syria.
Nevertheless, Badr’s symbols are not a pervasive presence on LAFA or Liwa’a Zulfiqar’s social media websites. Since the group reportedly did not suffer any killed in Syria before June, coverage of the organization’s possible involvement with LAFA or Liwa’a Zulfiqar was muted. The group’s social media posts appeared to do little more than offer visible support for the actions of other pro-Iranian Iraqi groups operating in Syria.

Figure 3: The photo was first posted on the Badr Organization Military Wing’s official and mirror Facebook pages. The photo shows Badr militiamen armed with Heckler and Koch MP5 submachine guns (though, it’s possible these are Iranian copies) and AK-47 style rifles.
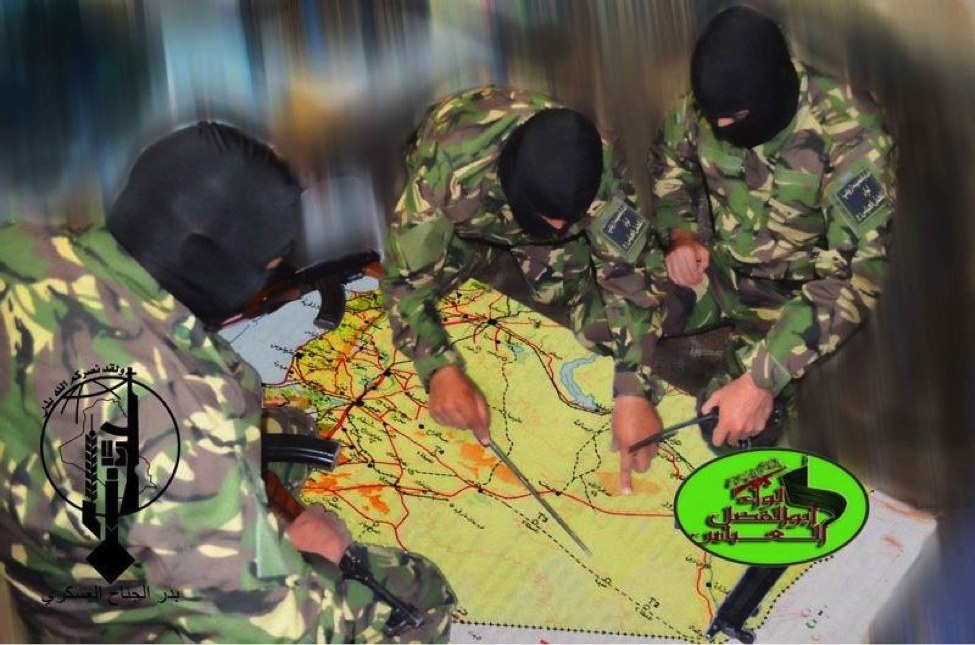

Figure 4: A photo first posted on Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas’s Facebook page claims to show Badr Organization militiamen studying a map of Syria. Most captions to go along with this photo claimed it was a photo to express solidarity with the defenders of the Zaynab Shrine.
However, the Badr Organization’s public statements regarding Syria grew louder after May 20, 2013. Immediately following attacks on buses carrying Iranian pilgrims near the Iraqi city of Tikrit, the Badr Organization Military Wing announced they would adopt a more threatening posture. [6] The statement said the “Plotters” of the attacks were the United States, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and “The Zionist Entity” (Israel), and that they would face a swift retaliation. It is important to note that the same compendium of enemies is blamed by Iran and its proxies operating in Syria for being behind forces opposing the regime of Bashar al-Assad. Interestingly, notwithstanding the other, often more horrific bombings Iraqi Shia suffered, and other attacks launched by Sunni Islamists against Shia in Iraq, the Badr Organization appeared to draw a redline with the attack on the Iranians. It is also possible the targeted bus was not carrying Iranian pilgrims as reported, but Iranian advisors or fighters, which would further inflame a pro-Iranian proxy group like Badr.[7]
Based on the fact that other smaller Iranian-backed Iraqi Shia groups have sent fighters into Syria, it is possible the Badr Organization has also sent members. This possibility gained added credence on June 17, 2013 when the Badr Organization Military Wing announced a member had been killed “Defending the Saydah Zaynab Shrine”. Despite this announcement, it is still unclear whether the Badr Organization has committed sizable amounts of fighting men to the war in Syria.

Figure 5: May 20, 2013 Badr statement threatening Saudi Arabia, Qatar, “The Zionist entity”, and the U.S.
The Badr Organization’s First Martyr In Syria?
Name: Yasin Muhammed al-Zayn (A.K.A. Hadi)
Death Announced: June 17, 2013. (He was declared killed on June 17, 2013). The Badr Organization Military Wing’s Facebook declared his death on June 18, 2013.
Notes: Only on the Badr Organization Military Wing’s official page was al-Zayn claimed as a member of the Badr Organization. On his martyrdom poster, it was claimed al-Zayn was killed in the Zayn al-‘Abideen neighborhood of Damascus while “Defending the Saydah Zaynab Shrine”. Other pro-Assad/pro-Iranian backed Shia organization Facebook pages did not mention his affiliation with the Badr Organization. Additionally, no footage of al-Zayn’s funeral could be located. A personal martyrdom page was also created (on June 18, 2013) for al-Zayn.[8] On the page, no mention of any Badr affiliations was made. Interestingly, his death was not claimed by Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas or Liwa’a Zulfiqar, the two groups Iraqi Shia have fought for in Syria.
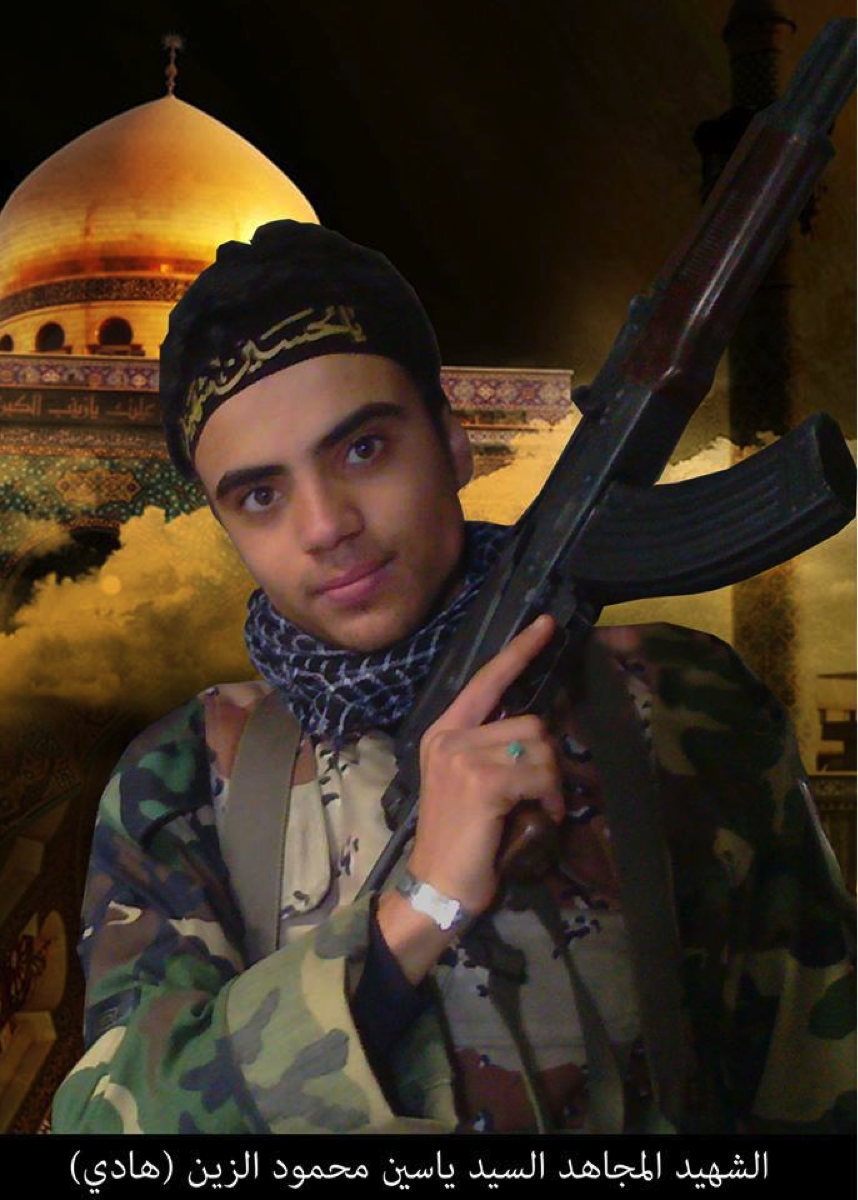


Figure 6: The Saydah Zanab Shrine’s golden dome features prominently in the background. No logos for the Badr Organization Military Wing were present on the martyrdom poster.



The Badr Organization’s Imagry For Syria
The Badr Organization Military Wing has created a number of provocative online photos dealing with events in Syria. When compared to other Iranian proxies, they have exhibited the most blatant links to Iran’s Supreme Leader. It is possible the group may be setting-up a religious pretext for their [future] involvement in Syria by continually showing pictures of Khamenei. Khamenei had already given religious sanction for Shia fighters to engage in battle in Syria.[9]

Figure 7: “Min Baghdad – al-Jadriat Labayk ya Zaynab” (“From Baghdad – al-Jadriya [a Baghdad neighborhood] We are here for you, O Zaynab”).

Figure 8: A photo published by the Badr Organization Military Wing showing members of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas. The image is attempting to convey that the Badr Organization has members within LAFA.
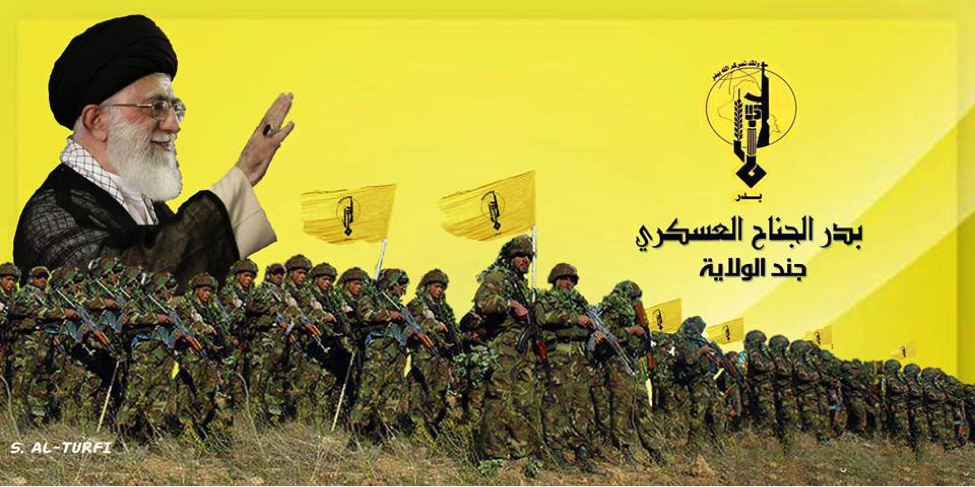

Figure 9: Iran’s Supreme Leader waves and smiles as Badr Organization militiamen stand below him.

Figure 10: This photo appeared on two pro-Badr Organization Military Wing pages on Facebook. Intriguingly, the photo is extremely blatant about the connection (logos from left to right) Asaib Ahl al-Haq, Lebanese Hizballah, the Badr Organization, the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps, and Kata’ib Hizballah share. Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei looks out from the globe.

Figure 11: Another online poster featuring the Badr Organization Military Wing and Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei. The background is a photo of Lebanese Hizballah marching with an added golden hue. [1] Michael Knights, “Syrian and Iraqi Conflicts Show Signs of Merging”, March 7, 2013, Policywatch 2042, Washington Institute For Near East Policy, https://www.washingtoninstitute.org/policy-analysis/view/syrian-and-iraqi-conflicts-show-signs-of-merging. [2] See: https://www.trust.org/item/20130621144421-omxch. [3] See: https://en.aswataliraq.info/(S(clhorg45ylfsgrrhg3vbwlmb))/Default1.aspx?page=article_page&id=147369&l=1. [4] See: https://www.cfr.org/iraq/iraqs-militia-groups/p11824#p6. [5] See: https://www.mcclatchydc.com/2005/12/12/v-print/13157/iran-gaining-influence-power-in.html. [6] See: https://now.mmedia.me/lb/en/mena/8-dead-in-iraq-bomb-attack-on-iran-pilgrims-officials-say. [7] Personal conversation with Michael Knights, June 24, 2013. [8] See: https://www.facebook.com/KlnaAlshhydAlmjahdYasynMhmwdAlzyn. [9] See:
