NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
–
Liwa ‘Abis: A New Active Militant Group in Bahrain
By Phillip Smyth

Figure 1: Liwa ‘Abis’s logo.
Liwa ‘Abis (the ‘Abis Brigade) declared their existence in an announcement dated April 7, 2014 and released it on Facebook and Twitter on April 8. The group’s first announcement declared they were joining those who “preceded” them in “jihad and resistance” against the “oppressors,” meaning the government of Bahrain. As with other radical anti-government organizations, which utilize force, Liwa ‘Abis call their enemies, meaning Bahrain’s internal security forces, “mercenaries.” This terminology is common among Bahraini militant organizations. According to Liwa Abis’s, their attack(s) are representative of the “legitimate jihad” they were waging against the government of Bahrain. Combined with the group’s self-description as “Al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya fi Bahrain” (“The Islamic Resistance in Bahrain”), the group appears to share many themes with other Bahraini militant organizations.

Figure 2: Liwa ‘Abis’s first announcement.
Liwa ‘Abis’s Targets & Their War on the “Occupier’s Economy”
A developing trend among Bahraini militant groups has been to target infrastructure and economic targets. Saraya al-Mukhtar has attacked Automatic Teller Machines (ATMs). Attacks against ATMs occurred in January, February, and March, 2014. These activities led the U.S. Department of State to issue specific travel warning instructions to U.S. citizens in Bahrain, telling them to, “Use caution when approaching ATMs, particularly at night and early morning, by scanning the area for items that are out of place or suspicious to the area in general.”[1]
Liwa ‘Abis appears to have also adopted a strategy of attacking economic targets. These targets have included structures—which the group has argued—assist with the “Saudi occupation” and the Bahraini government.

Figure 3: A Saraya al-Mukhtar edited image showcasing their targeting of economic interests. Bombed-out banks and ATMs are shown on the left. The Bahrain Financial Center—likely a broader warning that other pillars of the Bahraini economy will be targeted—is used as a background on the right.
In late-April, a Liwa ‘Abis operation claimed to attack a factory. Their statement said this plant was flying the flag of the “Saudi occupation” and that the owner of the structure supported the government. The attack on the factory was also claimed to be the first in a campaign the group launched, which coincides with protests of the same name: “Symptoms of the Intifada.” Liwa ‘Abis referred to their operation as “Symptoms of the Intifada 1.”
Interestingly, the statement also claims that the “Rijal Allah” or “Men of God” of “Saraya ‘Abis” (the ‘Abis Brigades) conducted the attack. The term “Rijal Allah” has been adopted by Iranian-backed Shia Islamist militants operating in Syria.

Liwa ‘Abis has also claimed attacks against the Bahraini police. On April 11, 2014 the organization claimed on Facebook that they had attacked a police station in Sitra. The group stated the attack was to gain vengeance for Hasan Mushaima, an exiled anti-government Bahraini Shia leader of the Haq Movement. Attacks by firebomb wielding youths against police stations in Sitra have occurred since 2012.[2] Additionally, Sitra has also been the scene of improvised explosive device-based attacks against Bahraini internal security forces.[3]
Symbolism
Liwa ‘Abis’s name likely refers to ‘Abis bin Abi Shabib, one of Imam Husayn’s loyal, militarily prominent, and powerful companions during the Battle of Karbala.[4]
The group’s logo features two crossed green swords and a red banner with a fist emblazoned on it. The stylized fist, which bears a striking similarity to the fist featured on the logo of Saraya al-Mukhtar. These images are encapsulated in a circular shaped combination of lines and text. As with other Bahraini militant groups, it’s possible the circle may represent the pearl, a symbol of Bahrain.
On the top of the group’s symbol sits a section from Quran 32:22. The entire passage from the Quran reads “And who is more unjust than one who is reminded of the verses of his Lord; then he turns away from them? Indeed we, from the criminals, will take retribution.” This is a clear reference to a number of themes expressed by Bahraini militants, particularly those affiliated with Saraya al-Mukhar. The first is “revenge” for perceived crimes against protesters executed by forces belonging to the Bahraini government. Another theme surrounds how militants consider the ruling Khalifa royals. Using a passage like Quran 33:22 may suggest these groups consider the Khalifas and those who support them to be infidels. Additionally, charges by government media organs which consider militants to be terrorists and vandals are also addressed with the Quranic passage, by flipping the tables and accusing the government of being the true criminals.
___________
[1] See: https://photos.state.gov/libraries/saudi-arabia/323264/riyadh/security_message_for_u_s_citizens-bahrain_situaiton_3-6-2014.pdf
[2] See: https://youtu.be/3mUPS6Eq4Hk. This clip was released in April, 2013.
[3] See: https://www.bbc.co.uk/arabic/middleeast/2013/07/130707_bahrain_bomb_sitra.shtml.
[4] See: https://www.islamquery.com/documents/companions%20of%20Imam%20Husain.pdf.
Category: Hizballah Cavalcade
Hizballah Cavalcade: Singing Hizballah’s Tune in Manama: Why Are Bahrain’s Militants Using the Music of Iran’s Proxies?
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
–
Singing Hizballah’s Tune in Manama: Why Are Bahrain’s Militants Using the Music of Iran’s Proxies?
By Phillip Smyth
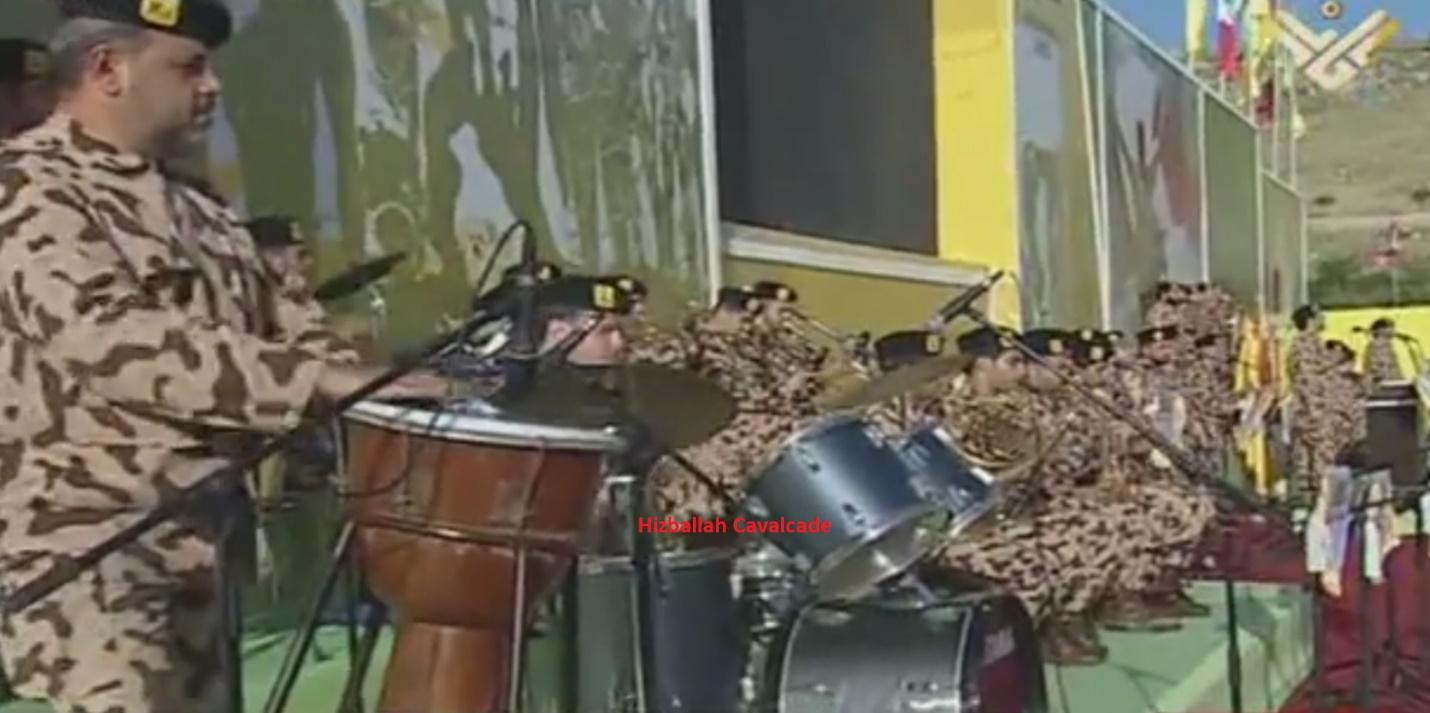

Figure 1: A screenshot of a Hizballah musical band performing at the 2013 “Resistance and Liberation Festival”
Bahraini officials have repeatedly accused anti-government militants and protesters in the country of being supplied, trained, and supported by Iran and its numerous regional proxies. Still, the government of Bahrain has done little to bolster their claims of deep and intrinsic links between Bahraini militants and Tehran. Along with official Iranian denials, the issue of Iran-Bahraini militant links is still quite hazy. Nonetheless, this does not mean that within the material released by Bahraini militant organizations that there are not hints of some level of Iranian influence. One of the more intriguing pieces pointing to influence from Iranian-backed organizations comes from the utilization of specific types of music in the many propaganda videos released by Bahraini militants, their sympathizers, and amplifiers.
Numerous instances of Bahraini militants producing propaganda videos with different varieties of music created and utilized by Iranian-backed proxies could indicate a connection with Iran’s proxies. Nevertheless, this type of overlap should not be viewed as a “smoking gun” affirming Iranian involvement. However, it does assist in piecing together direct and indirect influences.
The pieces of music in question were originally developed and used by Iranian proxy organizations, particularly Lebanese Hizballah, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq (AAH), and Kata’ib Hizballah. In fact, some of the songs that have been promoted fit a long standing media strategy employed by the aforementioned groups and Iran when manufacturing narratives and perceptions for themselves and other armed groups.
The use of music as a transferable propaganda medium follows a very formulaic strategy used by Iran and its “Islamic Resistance” proxy organizations for many years. Often, songs produced for one group are repackaged for newer organizations in other geographic locations. The songs are then altered in a way to make them appeal to the populations and target audience where the new group is located.
Possible Reasons for Using Specific Songs
Why would Bahraini militant groups utilize Hizballah and its Iraqi clones’ music and with such frequency? Some possible answers include:
- Direct Iranian influence or assistance provided to the developing militant groups.
- Video editing/production was offered to Bahraini militants by Iran and/or its proxies as a means to influence and shape militant organizations and to encourage the adoption of a more bellicose strategy to the broader (and more peaceful) protester audience.
- Bahraini militants sympathize with Iranian-proxy groups, their exploits, and with the general concept of “Al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya” (“The Islamic Resistance”). The hope to be as successful, feared, and/or respected as those organizations has led them to adopt the same varieties of music.
- Thumbing their nose at the government: With the government of Bahrain accusing protesters and militants of being Iranian proxies, militant groups may use the material as a way to subtly frighten or encourage speculation among Bahraini government and other observers.
- Narrative Goals: One song by Lebanese Hizballah’s Ali al-Attar called “Wa’ad al-Asra” or “The Prisoner’s Promise” was written to celebrate the release of prisoners Hizballah sought to free during the 2006 Hizballah-Israel War. While the song makes clear references to Lebanese Hizballah and themes related to the 2006 war, the same song was employed by some Bahraini protesters (as background music for their uploaded clips) when they protested the government’s detention of key protest-leaders.
Auto-Tuning the Revolution: Examples of the Musical Overlap
In March 2014, a music video which was claimed to have been produced by “Saraya al-Bahrainiyya al-Muqawama” or the Bahraini Resistance Brigades, (which is likely another name used by The February 14 Youth Coalition’s Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya [Popular Resistance Brigades]) was posted by the popular Revolution Bahrain’s YouTube Channel. The video featured a montage of edited clips, which purported to show Bahraini militants engaged in training. The music video also included a number of videos of bombings orchestrated by militant Bahraini organizations.
Yet, the music used was strikingly familiar in the circles of Iranian-backed Shi’a Islamist groups. In fact, Iranian-backed Iraqi group, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq had released the exact tune back in 2011 to commemorate attacks the group orchestrated against U.S. targets to demonstrate solidarity with Bahrain’s protesters. Later in 2011, when fellow Iranian proxy Kata’ib Hizballah released footage of attacks it had also launched in solidarity with Bahraini protesters, it too used the same song.
However, the song was neither originally Bahraini nor Iraqi, instead its origins were rooted father to the west, in Lebanon. The original song, “Risalat al-Thuwar” (“Message of the Rebels”), was performed by one of Lebanese Hizballah’s official bands, Firqat al-Fajr (The Dawn Band), following the 2006 Hizballah-Israel War. It first appeared on the band’s 2007 “Lahan al-Turab” or “Melody of the Soil” album. Still, the rendition dealing with Bahrain was not the only version of the song. Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq had their own Iraq/Grand Ayatollah Muhammad Muhammad Sadiq Sadr (as opposed to Sayyid Hassan Nasrallah) themed “Risalat Thuwar” produced in 2011.
“Risalat al-Thuwar” is not the only Hizballah song which has been adopted and rebranded by Bahraini militants and their amplifiers. Another song used by Bahraini militants also comes from Firqat al-Fajr. The song, “Ya Wa’ad Allah” (“O Promise of God”) can be found on the group’s 2008 album, “Sharit Wa’ad Allah” (“Take the Promise of God”). The song has been released in different formats, with more recent music video varieties showcasing the assassinated Hizballah terror-mastermind Imad Mughniyeh. The album also included an instrumental version of the song. Both versions have been prominent features on productions done by Hizballah’s Al-Manar TV network.
In Bahrain, “Ya Wa’ad Allah” was used as background for clips released to the popular (particularly with militant groups) Revolution Bahrain’s YouTube account. One of these videos included the firebombing of an armored car used by Bahraini government forces.
It is not just the polished music video-quality material finding its way into Bahraini militant propaganda productions. Bahraini militant group Saraya al-Mukhtar released a video of their April 2014 targeting of Bahraini police with an improvised explosive device. Another bomb attack in Bani Jamra also utilized the same background music.
The musical selection in the background matched with instrumentals used by Iraq’s Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq. This music was first featured on the AAH-affiliated Al-Ahad TV in the late summer/fall of 2013 to commemorate Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq members killed fighting in Syria. Further pointing to some level of Iranian or Iranian proxy influence, is highly unlikely that this particular musical element could find its way into so many pieces of released footage. This may indicate some Bahraini militant footage being sent abroad (possibly to Iraq) where the footage is re-edited and put back together for a later introduction.
Another similar instrumental used by Bahraini militants with Saraya al-Mukhtar and Saraya al-Ashtar was also the same exact tune utilized in a number of Kata’ib Hizballah video releases (see: 00.17-00.40 on “Kata’ib Hizballah Anti-America Video”).
The use of the last two instrumentals create further questions. Why would these groups, which have resorted to using a variety of improvised weapons, and exist under increasing heavy security crackdowns, spend the time to find, edit, and utilize background instrumentals which already have obscure points of origin. Why pick these two exact instrumentals, which have only been found in the repertoire of Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq and Kata’ib Hizballah? Other Bahraini protest organizations have utilized a variety of different musical accompaniments. Thus, the use of these particular musical pieces seem out of place when compared to the rest of what has been released.
Whatever the reasons, closely assessing the propaganda published by these organizations may provide insight into rather opaque organizations. While assessing the musical selections may appear to be a tangential escapade, AAH, Kata’ib Hizballah, and Lebanese Hizballah have all demonstrated their strategy of using this material as another method to push the narrative of the “Islamic Resistance.”
Hizballah Cavalcade: Asa’ib al-Muqawama al-Bahrainia: An Emerging Militant Group in Bahrain?
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Asa’ib al-Muqawama al-Bahrainia: An Emerging Militant Group in Bahrain?
By Phillip Smyth

Figure 1: Asa’ib al-Muqawama al-Bahrainia’s logo.
Asa’ib al-Muqawama al-Bahrainia (The League of Bahraini Resistance or AMB) was first established and marketed as an independent militant organization on February 22, 2014. The group’s founding announcement claimed that the time had become ripe for armed opposition against Bahrain’s ruling monarchy due to the government’s actions. As with other Bahraini militant groups, little is known about AMB’s manpower or armed capabilities.
Regardless, unlike other Bahraini militant organizations, AMB’s founding announcement has found its way onto many different online venues catering to a wide range of readers.[1]
AMB’s statements appear online in bursts. February 22 and February 28, 2014 have been the two dates this organization has placed a series of announcements in public. This pattern is reminiscent of another Bahraini organization, a proto-militant group which went by a similar name, Asa’ib al-Muqawama (The Resistance League). Using Twitter, Asa’ib al-Muqawama released 33 announcements (in both Arabic and English) between April 21 and 22, 2012. Asa’ib al-Muqawama’s threats centered on Bahrain’s controversial Formula One race. One of these statements claimed responsibility for planting three homemade bombs at the race location. At time, there were also instances of Molotov cocktails being thrown at some (from Team India) affiliated with the race.[2] Additionally, on April 9, 2012, seven Bahraini police were wounded due to an improvised bomb planted in the town of Akr.[3] Albeit, neither of these attacks were linked to Asa’ib al-Muqawama.
After their last tweet on April 22, 2012, Asa’ib al-Muqawama went quiet. This is similar to how AMB went silent after their last February 28, 2014 statement. There is a possibility of a link between AMB and Asa’ib al-Muqawama, considering the groups espouse the same militarism, utilized a similar name, and have released announcements in bursts over two-day periods. In fact, AMB’s official Twitter account also describes itself as “Asa’ib al-Muqawama.” It is possible that AMB developed out of the original Asa’ib al-Muqawama. However, beyond these assumptions, there is little substantiating open-source information to assist in confirming any links.

Figure 2: Asa’ib al-Muqawama’s English language Tweet-announcement, declaring they had planted 3 bombs at the Bahrain F1 race.

Figure 3: Asa’ib Muqawama’s logo.

Figure 4: AMB’s first announcement.
On February 28, 2014 AMB announced the launch of their, “Fist of Righteousness” operation to avenge the death of Ja’afar al-Derazi. Derazi, whose burial occurred the day of the announcement, was a 22 year old anti-government activist. According to opposition and pro-Iran sources, Derazi died due to torture and other forms of maltreatment when he was detained within a government jail cell.[4] In revenge for Derazi’s death, on April 11, 2014, Saraya al-Mukhtar claimed responsibility for an attack targeting Bahraini police. Nevertheless, AMB has not yet claimed any other attacks as part of their “Fist of Righteousness” campaign.

Figure 5: AMB’s second announcement from February 28, 2014.
AMB Joins YouTube
AMB’s official YouTube account claimed to release a video introducing the group on February 21, 2014. However, the first publicly accessible copy of the video was uploaded and released on February 22, 2014. In the video, supposed AMB members are shown marching in formation, extending their arms in a Roman salute. Demonstrating their potential roots as militant offshoots of the larger Bahraini protest movement, young balaclava wearing men hold tires in one of their displays. Tires are a regular feature in some protests; often laid across stretches of road, coated in gasoline, and lit on fire.
Furthering religious themes was also a feature of the film. Young marching militants are seen holding Qurans, wearing white (in addition to other colors) burial shrouds symbolizing a willingness to be martyred, and holding flags with “Ya Husayn” (“O Husayn”) written on them. The “Ya Husayn” flags symbolize a Shia-centric theme, recalling Husayn’s martyrdom via beheading, at the pivotal Battle of Karbala.[5] These flags have also made regular appearances during anti-government protests.
The promotional clip also claims to show AMB launching operations against internal security elements (primarily the Bahraini police). Segments of film featuring Molotov throwing youths are a main theme. However, these clips are usually from earlier films recorded by more violent activists associated with the February 14 Youth Coalition. It is possible this footage demonstrates a further link to the February 14 Youth Coalition or it was simply repackaged by AMB to show a broader theme surrounding the “resistance” against the Bahraini government and their forces.
AMB also appears to have a preoccupation with utilizing weapons which can burn their foes. This may be the result of protester use of Molotov cocktails. Utilizing the limited available tools, some Bahraini protesters, particularly younger male militants, have often thrown Molotov cocktails at Bahraini internal security forces. The theme of the Molotov thrown at Bahraini police, particularly their vehicles, was regularly utilized in AMB’s introductory video. However, the focus on using weapons which can kill and injure using fire does not appear to stop with Molotovs. In one part of their video, AMB shows Bahraini police engulfed in a wall of flame, likely caused by a bomb or another incendiary device.
AMB’s Badge
AMB’s logo may also show links to Saraya al-Ashtar (SaM), one of the first publicly established Bahraini militant organizations. Featuring two crossed M16-style rifles within a circle (which could potentially symbolize a pearl, a recognized emblem of Bahrain), the group’s logo mirrors SaM’s official symbol. This logo also included two crossed rifles (albeit, of the Kalashnikov variety) within a circle representing a pearl.
An Asa’ib of Their Own?
When investigating potential links between AMB, Iran, or Iranian-backed proxies, there was some evidence of overlap between AMB & Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq (AAH). On March 13, 2014, AMB’s founding statement was circulated on AAH’s extensive network of Facebook pages. This often coincided with claims that AMB was representative of AAH’s spreading brand. Claims of this nature may be an Iranian proxy attempt to demonstrate a substantial link to the Bahraini militant group. Both groups utilize similar language, with AMB describing itself as the “Bahraini Resistance” and AAH calling itself the, “Islamic Resistance in Iraq.” Still, there is the possibility that AAH could be jumping on an organically constructed (in Bahrain) group while skillfully playing on AMB’s similar name, all in an effort to claim a connection and demonstrate a broader reach. It is important to note that it took AAH nearly a month before pages associated with the group started to carry AMB’s founding statement.
Another potential link includes religious and ideological themes. The AMB’s founding statement mentioned the group was following their taklif. A taklif, or religiously mandated order, was developed and utilized for political and social events by those embracing Iranian Islamic Revolutionary concepts.[6] The mention of a taklif mirrors a similar statement made by fellow Bahraini militant group, Saraya al-Mukhtar, which also mentioned they were picking-up arms against the government due to a taklif.
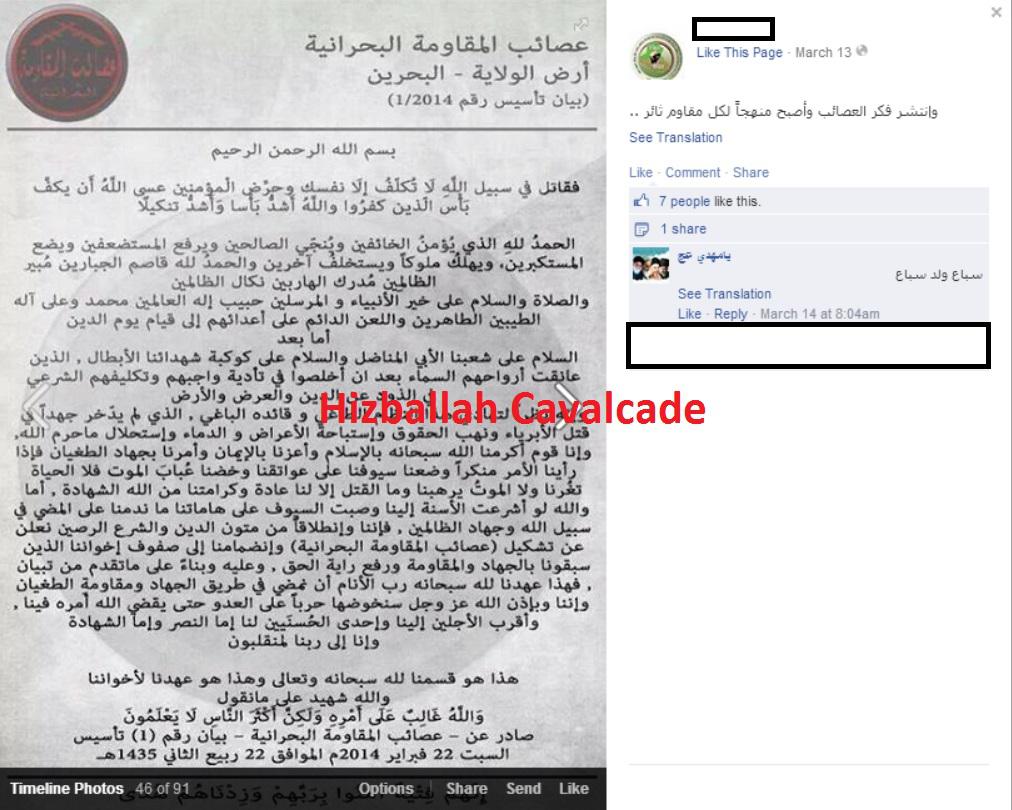
Figure 6: A post promoting the first AMB declaration on an official Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq Facebook page.
Is AMB Dormant?
At the time of this writing, the last statement issued by AMB was released via their Twitter account on February 28. Since that time, AMB has not itself claimed any new attacks, seen related militant groups, protest organizations, or the official Bahraini media, cite any new actions by the group. While little has been heard from this organization since it’s nearly 2 month-long period of silence, AMB’s release of formal statements, broad web-presence (including their YouTube video release), overlap between itself and other Bahraini militant groups, and other attack claims, may indicate AMB is still active.
AMB’s activities may be continuing as members of the organization act as integral elements within other Bahrain militant groups. If there is a true link between the AMB and Asa’ib al-Muqawama, it is possible that following the established model, a new wave of attack-claims could be registered on an entirely new online/social networking apparatus.
Nevertheless, until AMB claims another attack or has an allied organization claim an attack for them, it will be impossible to know what has become of this group
_____________
[1] Note: Numerous Sunni Islamist and Shia Islamist forums, Facebook
Hizballah Cavalcade: Bahrain’s Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya: Militants of the February 14 Youth Coalition
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Bahrain’s Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya: Militants of the February 14 Youth Coalition
By Phillip Smyth

Figure 1: Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya’s logo.
Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya (The Popular Resistance Brigades or SMS), sometimes also called Saraya al-Muqawama (The Resistance Brigades), was listed by the government of Bahrain as a terrorist organization following the deadly March 3, 2014 bombing. The group, along with fellow militant group Saraya al-Ashtar, claimed responsibility for the attack. SMS has been operationally active and publishing its activities online since April 2012. Importantly, Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya does not hide that they are affiliated with one of the main anti-government protest groups, the February 14 Youth Coalition (which was also listed as a terrorist organization by the government of Bahrain). This is hardly a minor connection, since, both the February 14 Youth Coalition and SMS have also distributed images sharing one another’s logos, organized events (such as protests) together, and share a similar narrative. Other militant groups—namely Saraya al-Ashtar and Saraya al-Mukhtar—have only vaguely claimed to represent links to protestors, let alone main protest organizations.
In June 2013, the Bahraini government accused the February 14 Youth Coalition of having a “spiritual leader” based in Karbala, Iraq and of, “frequently travel[ing] between Iran, Iraq and Lebanon to obtain financial and moral support as well as weapons training.” However, Bahraini authorities provided little substantiating evidence dealing with claims of Iranian or Iranian proxy involvement. Nevertheless, according to Iranian reports, February 14 Youth Coalition representatives have thanked Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei for his comments supportive of their activities. Iranian media has also expressed their support for the “revolutionary activities” of the Bahraini group. Despite these pronouncements, the actual relationship between Iran and the February 14 Youth Coalition, particularly dealing with any attempts at training or equipping militant elements attached to the organization, is still unknown.

Figure 2: Both the February 14 Youth Coalition and Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya’s logos on a promotional image released onto multiple February 14 Youth Coalition pages.
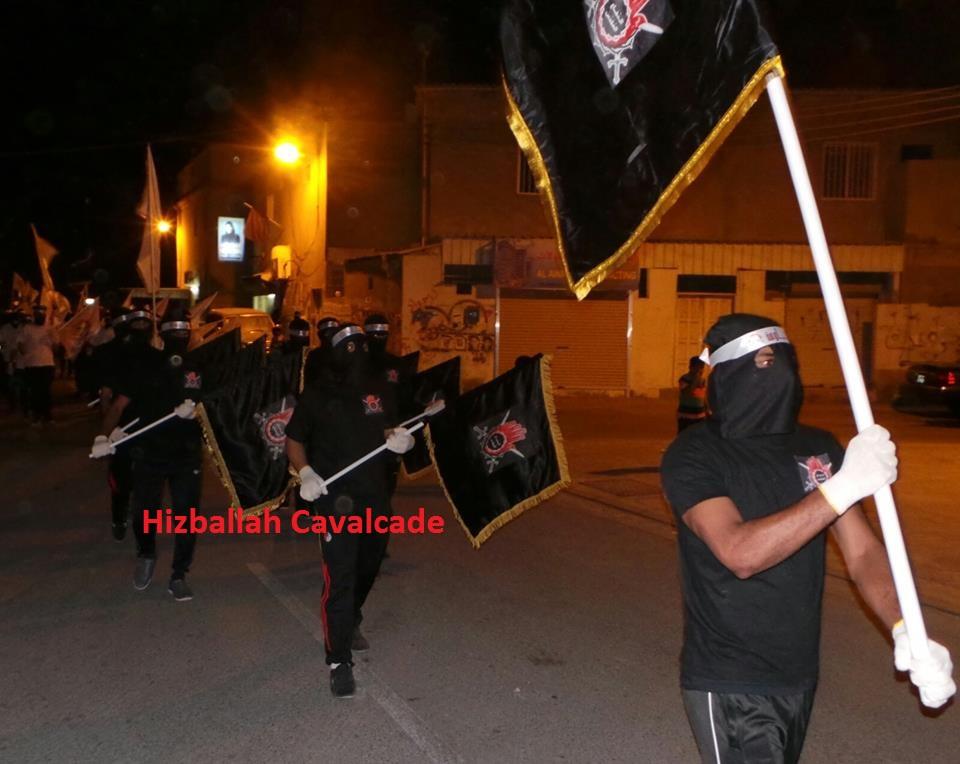

Figure 3: SMS supporters carry the group’s flag during a march.
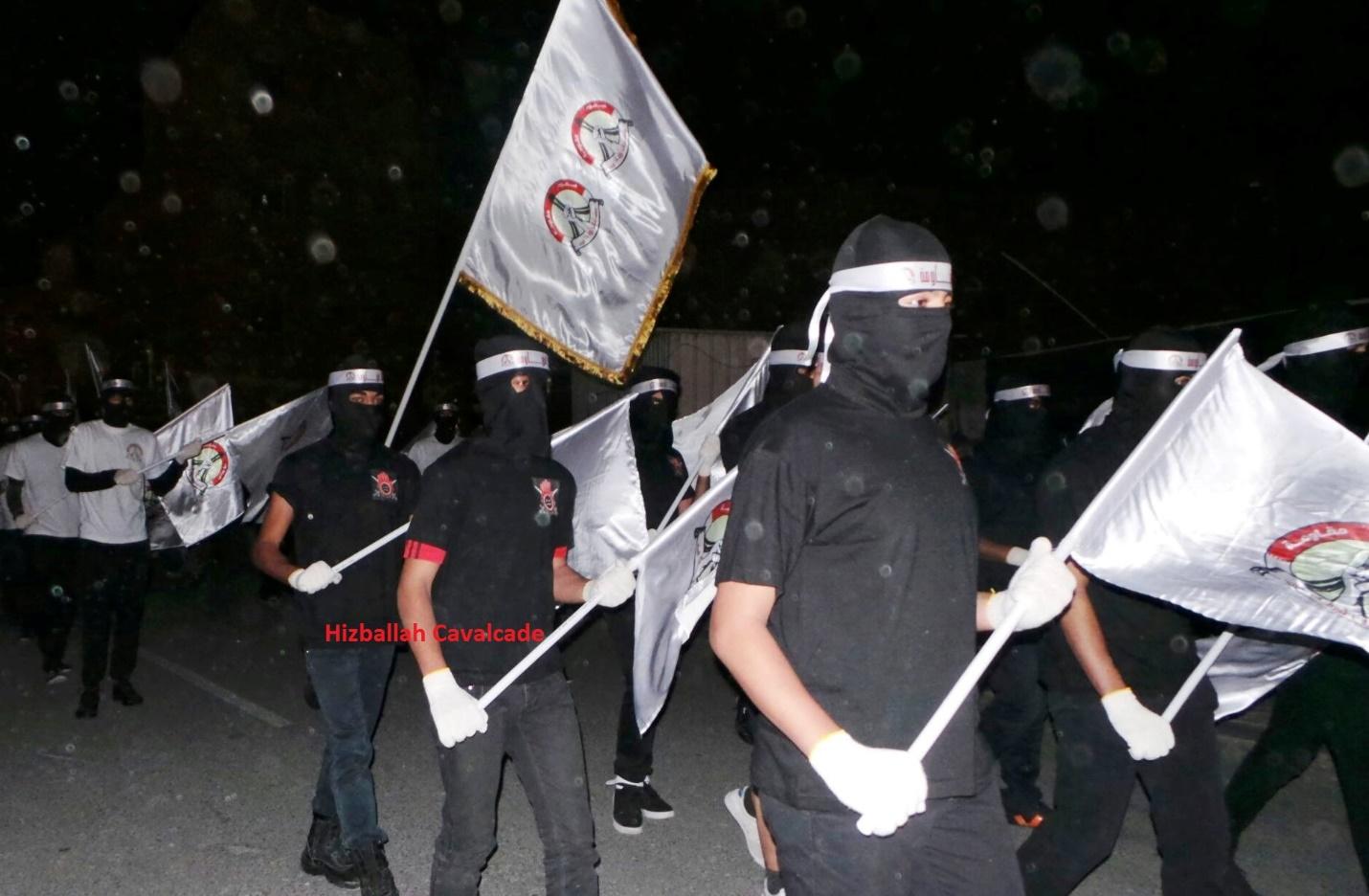

Figure 4: SMS and February 14 Youth Coalition supporters march together and carry February 14 Youth Coalition flags.
Initially, the February 14 Youth Coalition did not embrace violence. However, after publishing a series of “warnings” to the Bahraini government, Gulf Arab states (namely, Saudi Arabia and the UAE) which have deployed forces to Bahrain, and foreigners recruited into the Bahrain’s internal security forces (often referred to by the group and other Bahraini militants as, “mercenaries”), the coalition issued communiques demonstrating they would choose a more militant path of “resistance.” In a January 27, 2012 English-language statement made by a February 14 Youth Coalition affiliated page, the group issued a statement reading:
“We have so far preserved our right to use force for self-defense, hoping that would make you hesitant from attacking peaceful protestors, women and children. However, common sense and human logic do not seem to work on you…Our people have decided to bring an end to the illegitimate regime…We shall take no responsibility for whatever might happen to the mercenaries after this final warning.”

Three months after this announcement, SMS pushed for a response to the holding of the controversial 2012 Bahrain Grand Prix Formula 1 race. The group released images urging protestors to throw the gas (the group claimed it was poisonous) used by Bahraini police at the race cars. However, no armed action was taken against the race by SMS. It is likely that in such an early stage of development and combined with Bahraini government crackdowns, the group was unable to act.

Figure 5: One of SMS’s English language posters calling for action against the 2012 Grand Prix race.
Narrative Structure
SMS considers its fighters to be “jihadists,” refer to their attacks as “jihadist operations,” and believe they are fighting a “jihad against the infidel Khalifas [Bahrain’s ruling royal family].” While the message of jihad is repeated in many SMS statements, these statements do not share the same level of more complicated religious and ideological messaging found with other non-Bahraini Shia jihadist elements.
SMS also lacks a specific goal for what type of government will rule in Bahrain following a theoretical collapse of the currently ruling Khalifa royal family. Still, this has not stopped the group from constructing complex narratives via militant activity for their enemies.
Following Saraya al-Ashtar’s and SMS’s claim of responsibility for the March 3, 2014 bombing (which killed two Bahraini police officers and a police officer sent by the United Arab Emirates [UAE] to Bahrain), SMS used the opportunity to criticize government claims that forces of the Peninsula Shield Force were being used in conjunction with local Bahraini police forces to counter protests and riots.
Sent to Bahrain in 2011, the Peninsula Shield Force included hundreds from the Saudi military and the UAE’s police force. Officially, these units claimed they were not involved in internal matters in Bahrain and were only interested in securing strategic bases and locations from “external influence.” Regardless, the death of a UAE police officer attached to Bahraini police served as a propaganda coup for SMS.
The timing of the SMS’s bombing claim and messages which proceeded it also fit into a broader message dealing with the Peninsula Shield Force and particularly Saudi Arabia. SMS has demonstrated a specific ire for the Saudis. The organization’s communiques have called Saudi Arabia the “usurper of land,” “occupiers,” and have stated their operations are to “purge the land of its Saudi and Khalifa occupiers.”
In part, this may tie back to February 14 Youth Coalition links to Saudi Shia activists. Researcher Fredric M. Wehrey noted that an “important attribute of the February 14 Youth Coalition is its strong affinity with Shi’a activists in neighboring Saudi Arabia.” Wehrey went on to explain how coordinated protests were conducted by Bahraini and Saudi groups out of solidarity. The February 14 Youth Coalition’s and SMS’s links to the Saudi Shia is also important when viewed in context with announcements by fellow militant organization, Saraya al-Mukhtar. Saraya al-Mukhtar has issued a number of announcements saying they share the cause of the “people of the [Saudi] Eastern Region” –an area heavily populated by Saudi Shia. The shared narrative may demonstrate deeper links between Saraya al-Mukhtar, SMS, and the February 14 Youth Coalition.

Figure 6: A poster released by the February 14 Youth Coalition asking, “Who are the terrorists?” The photo shows Saudi forces crossing the King Fahd Causeway which links Bahrain to Saudi Arabia.
As part of the view casting the Saudis as foreign occupiers, activists from SMS and the February 14 Youth Coalition have drawn parallels between Israel and Saudi Arabia; accusing both counties of using the same techniques of occupation. Prior to a series of March 2014 protests against “Saudi occupation”, the February 14 Youth Coalition and SMS circulated images attempting to link Saudi Arabia and Israel as fellow occupying states. This also extended into the realm of February 14 Youth Coalition partisans attempting to directly link the causes of Palestinian and Bahraini demonstrators.

Figure 7: The Israeli flag flies behind Jerusalem’s Dome of the Rock (left) while a bulldozer is shown destroying the 400 year old Amir Mohammed Braighi Mosque with a Saudi flag behind it (right). The latter incident occurred in 2011 along with the Bahraini government destruction of other Shia mosques. This picture was used as a tool to organize activists for protests and events against the “Saudi occupation.”

Figure 8: A poster showing a Bahraini protester (with February 14 Youth Coalition) and a Palestinian activist. The former looks to the now demolished Pearl Roundabout statue, the latter looks to the Dome of the Rock. The picture attempts to show a unity of purpose and cause between Palestinian and Bahraini demonstrators.
Symbols of the “Popular Resistance”
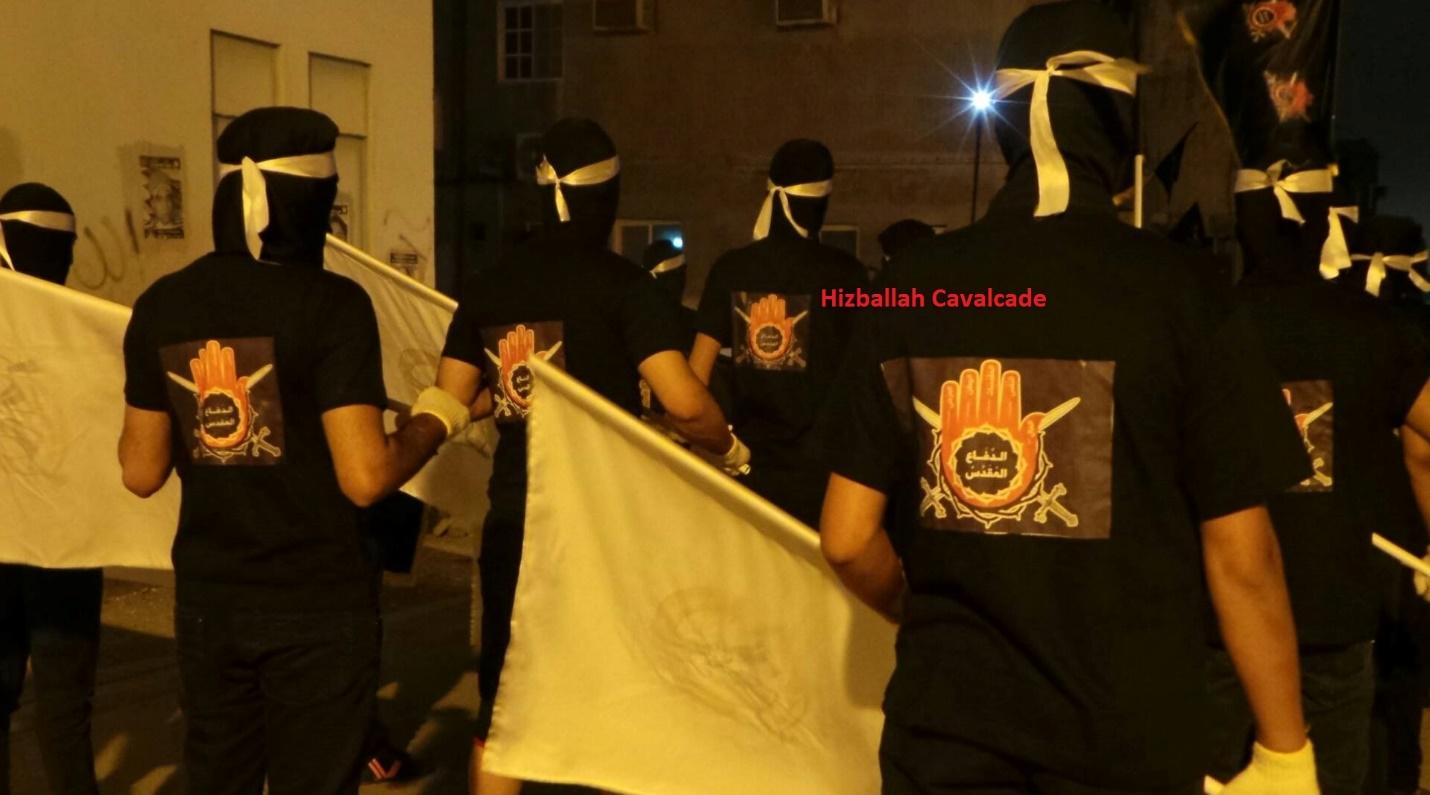

Figure 9: SMS protesters at a February 14 Youth Coalition event demonstrating against “The Saudi Occupation.”
Shia symbolism is heavily featured in the group’s logo. The most prominent image is the symbolic hand of Shia leader Abbas Ibn Ali; son of the first Shia imam and loyal aid and military leader for the third Shia imam, Husayn ibn Ali. Serving as Husayn’s flag bearer during the historic Battle of Karbala, Abbas’s hand was cut off by one of the forces of Yazid, the reviled leader of the Umayyads, as Abbas went alone to collect water for Husayn’s dehydrated camp. Abbas went on to fight singlehandedly until his other arm was cut off by sword strikes from Yazid’s forces and was then killed. Abbas’s loyalty and steadfastness until being cut down remains an important message for many Shia Muslims.
Another unique feature from the logo is that “The Sacred Defense” is written within the symbolic hand of Abbas. This helps convey that the group’s conflict with the government is viewed as both a defensive and religiously justified action. Intriguingly, the Shia jihad in Syria and the Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988) have (by Shia actors) both been described as “The Sacred Defense.”
Behind the
Hizballah Cavalcade: Saraya al-Mukhtar: A Bahraini Militant Group with Regional Goals
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Saraya al-Mukhtar: A Bahraini Militant Group with Regional Goals

Figure 1: Saraya al-Mukhtar’s newest logo. The group’s name is on the bottom, a black zulfiqar style sword combines in with a a black roundel featuring a green fist and black barrel and forearm of a Kalashnikov-type rifle. On the left is a red map of Bahrain.

Figure 2: Saraya al-Mukhtar’s first logo. The symbol appears to show two crossed bifurcated Zufiqar-type swords resting on a book (most likely the Quran). The organization’s name appears at the bottom of the logo.
First announcing itself to larger audiences online in a September 26, 2013 statement on Facebook (albeit, the statement itself was dated September 27), Saraya al-Mukhtar (The Mukhtar Brigade or SaM) has claimed numerous attacks on Bahraini security forces and has developed a sophisticated messaging strategy. At the time, the then new group promised to strike at the ruling Khalifa royal family and their security forces with, “operations of quality”. Despite the group’s September online appearance, it still claimed attacks since the summer of 2013. These operations have primarily included the use of crudely produced improvised explosive devices (IEDs) and types of arson attacks. SaM also has the unique distinction among Bahraini militant groups for claiming their first fallen member, or “martyr”, Ali al-Sayyid Ahmed al-Musawi. The group’s narrative on both a regional and potential religious-ideological level have also set it aside from other Bahraini armed organizations.

Figure 3: Saraya al-Mukhtar’s martyrdom poster for Ali Sayyid Ahmed al-Musawi.
Save for the occasional mentions state-run Bahraini press organs and opposition reports on the situation in Bahrain, for the most part, the group has not received as much media scrutiny as militant groups such as Saraya al-Ashtar. Additionally, SaM appears to have escaped specific mention on Bahrain’s terror group list.[1]
The group calls their foes; The Khalifa royal family, Bahraini security forces, and Saudi Arabia, “a mafia/the Khalifa mafia”, “mercenaries/criminals”, and “occupiers”, respectively. In a November 3, 2013 announcement, SaM vowed to “crush the fascistic regime.” This type of discourse generally fits with most rhetoric issued by Bahraini militant groups. Though, SaM appears to be a bit more colorful when describing their enemies.

Figure 4: SaM’s November 3, 2013 statement.
In terms of promoting the group’s goals, narrative, and attacks, Saraya al-Mukhtar has exhibited the most advanced strategy and online presence when compared to other Bahraini militant organizations. The group has Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram accounts, among other modes of digital communication with supporters. On March 5, 2014, the group’s main Facebook was taken offline. Another page was quickly made in its place where the group claimed “the tyrant’s mercenaries” took the last page down. On YouTube, the group (or possibly loosely-linked supporters) started separate accounts which would upload one clip of an attack the group claimed and then become inactive. It is unclear whether this is done as an operational security method or for some other purpose. As with Saraya al-Ashtar, the group has also sent footage of its attacks to popular pro-revolution YouTube stations for broader dissemination.
Shia religiously-based rhetoric is a more established common feature in SaM’s releases, rhetoric and even the group’s name. The organization also calls itself, “Al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya al-Bahrania” or the “Bahraini Islamic Resistance.” Most Iranian-backed militant organizations also use this term as a self-descriptor.[2] However, it is possible this could be an example of mimicry, demonstrating the group respects the strength of those organizations and is attempting to adopt their rhetoric to appear more powerful.
Saraya al-Mukhtar’s moniker is likely a reference to Mukhtar al-Thaqafi. Mukhtar al-Thaqafi was a figure who launched a failed rebellion against the Umayyad’s in the 7th century. The rebellion was initiated in southern Iraq and executed in order to get revenge for the death of the third Shia imam, Husayn ibn Ali, who was killed by the Umayyads during the Battle of Karbala.[3]
Interestingly, the name of the group and its background history plays into the style of media campaigns and announcements made by SaM. Often, the group brands their attacks and those launched by other groups against internal security elements as “revenge.” On January 27, 2014 SaM launched the “Vengeance Has Been Achieved Media Campaign.” Until the time of this writing, the slogan, “Vengeance has been achieved” is still stamped onto the photos of injured (often in hospital) Bahraini police.
The recruitment and naturalization of foreigners (particularly from Sunni Muslim religious backgrounds) into Bahrain’s internal security forces has been a main objection for peaceful protesters and militants alike. This is a main reason why SaM, other Bahraini militants, and peaceful protesters have referred to these internal security elements as “mercenaries.” Tapping into this grievance, SaM regularly posts images of police officers with foreign backgrounds that the group has targeted.
Additionally, the motive of “revenge” may be another attempt to appeal to some younger portions of the protest movement. Due to numerous bloody crackdowns by the government, these elements have become fed-up with more traditional groups leading peaceful protests.[4] Thus, SaM likely sees them as a component which can be brought into to give some level of support (even passive) to the organization’s activities.
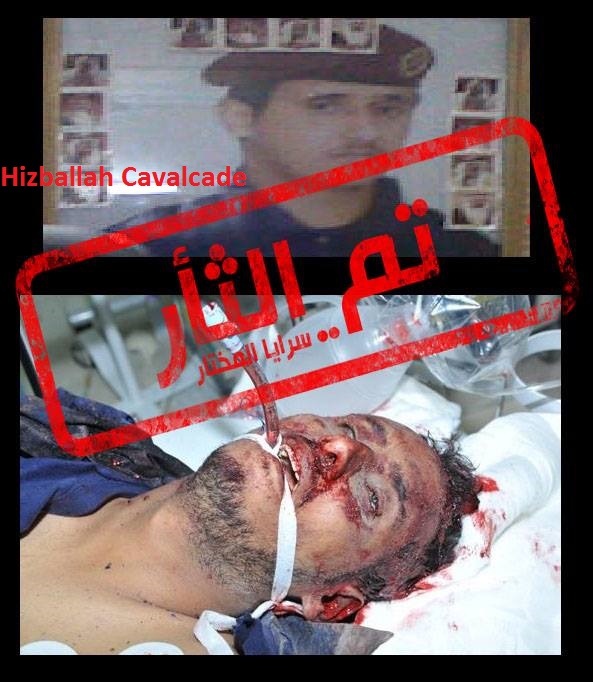
Figure 5: On February 9, 2014, SaM claimed to kill Ahmed Rashid al-Moraysi, a Syrian working for the Bahraini police. “Vengence has been achieved” was stamped on the photo.
Claimed Militant Activities
Saraya al-Mukhtar has been quite prolific in the production of videos and the release of photographs to show off its attacks. In one November, 2013 attack on what the group claimed was a communications network station, photos and a video of the target being attacked (with what appears to be a crude incendiary device) were posted online.

Following Saraya al-Ashtar’s claimed March 3 bomb attack against Bahraini police, Saraya al-Mukhtar praised the, “Bahraini Resistance.” On March 5 SaM released an edited photo showing the aftermath of the bombing and praising the action.

Figure 6: Saraya al-Mukhtar’s image praising the bomb attack on March 3, 2014.
The group also claims to be in possession of a special sniper weapon they call the “Mukhtar 1”. It is unclear if the weapon is a firearm or some other improvised device. However, SaM has released video on March 4, 2014 of the Mukhtar 1 in use against Bahraini police forces. Like Saraya al-Ashtar, SaM’s videos were released through a combination of the group’s own YouTube pages.
Another uploaded Saraya al-Mukhtar video claimed to show a January IED attack against a Bahraini police checkpoint. This video was also sent into other YouTube stations in a possible effort to increase viewership.
Figure 7: A Saraya al-Mukhtar released photo claiming a January attack against “mercenaries”.
Regional Outlook & Ideology
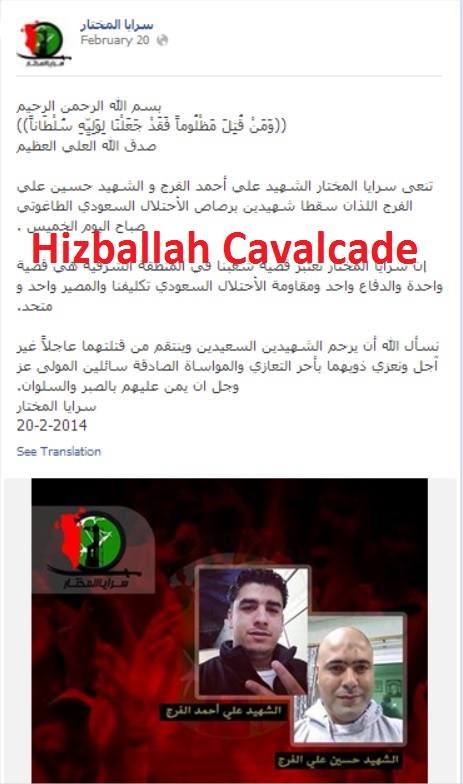
Figure 8: Saraya al-Mukhtar’s February 20, 2014 post.
Saraya al-Mukhtar’s potential links with radical Shia Islamist ideology and the group’s regional aspirations were showcased in a small post made on their official Facebook page on February 20, 2014. The group appears to view the conflict in Bahrain as part of a larger regional conflagration involving Saudi Arabia. Their post read, “The cause of the people in the Eastern Region [of Saudi Arabia] and our defense is one…Resistance against Saudi occupation, our taklif, and our fate are united.”
The statement about Saudi Arabia’s “Eastern Region” is a direct reference to an area which not only borders Bahrain, but is main zone where much of the Saudi Shia Islamic community, 15 percent of the Saudi population, call home.[5] Saudi Shia have faced exclusion from politics, government positions, and many economic opportunities, not to mention suffering religious discrimination. Throughout 2013, Saudi Shia groups organized numerous protests—particularly in Qatif,
Hizballah Cavalcade: Saraya al-Ashtar: Bahrain’s Illusive Bomb Throwers
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here. For the first part in the subseries on Bahraini militant groups: “The Pearl and the Molotov.”
—
Saraya al-Ashtar: Bahrain’s Illusive Bomb Throwers
by Phillip Smyth

Figure 1: Saraya al-Ashtar’s main logo. The symbol shows two Kalashnikov-type rifles crossed over a roundel which resembles a pearl. The base includes the group’s name.
“The operation comes in revenge for our martyrs”, read the March 3, 2014 “Statement No. 9”, issued by Saraya al-Ashtar (The Ashtar Brigades or SaA) on Facebook and Twitter. This declaration directly referred to a bomb which was detonated during a Bahraini police operation in the town of Daih. Three were killed, including an Emirati officer who was deployed to Bahrain as part of the “Gulf Waves Force”.[1] Reportedly, the police were attempting to disperse what was claimed in an official statement as a “riot.” The protests occurred following funeral demos for another Bahraini protester.[2] However, the group claiming responsibly for the bombing received little attention in Western media and passing mention in Arabic language news. Regardless, the Saraya al-Ashtar group is quickly making a name for itself via it bombing campaign.
Since the summer of 2013, the group claimed almost twenty attacks against security personnel in Bahrain. The March 3 blast appears to be another attack in a long and developing list of bombings carried out by the group. This will probably not be the group’s last. On March 4, the Bahraini government listed Saraya al-Ashtar as a terrorist group.[3] Still, the organization is quite shadowy and despite Bahraini government arrests, appears to be active.

Figure 2: Saraya al-Ashtar’s Statement 9, which claimed responsibility for the bombing of Bahraini police officers.
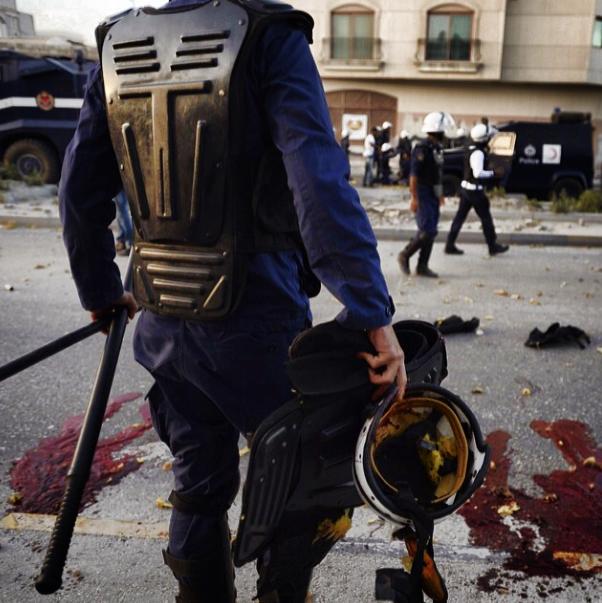

Figure 3: A member of the Bahraini internal security forces looks at blood-stained concrete following the March 3rd blast. (Source: Facebook)
Saraya al-Ashtar released its first statement via their Facebook page on April 27, 2013 (albeit, the written statement was dated April 28, 2013). In part, it stated, “Enough is enough” in regard to the actions of, “the rabid dogs of al-Khalifa [Bahrain’s ruling royal family].” The group promised to strike their enemies the next day. Keeping to their word, on April 29 SaA claimed in another post that they had, “Targeted a collection of mercenaries [the term most Bahraini militants use to describe Bahraini internal security forces] at the Adra roundabout”.[4]
Attacks such as these have demonstrated SaA’s preferred method of operation: Building and detonating improvised explosive devices and their direct targeting of Bahraini government security personnel.
SaA has an extensive social media presence with Facebook and Twitter accounts. These platforms are used to promote the group, broadcast threats, and to claim responsibility for attacks. Nevertheless, the group has not posted any photographs of their operations, membership, or weapons systems.
In fact, SaA has not released any photographs save for their logos. With the logos come further questions. SaA’s first displayed symbol was clearly modeled off of Iranian-backed groups, most likely Kata’ib Hizballah’s logo. Their second, showing crossed Kalashnikovs over what appears to be a pearl (a national symbol for Bahrain) continues the militant theme.

Figure 4: SaA’s first logo.

Figure 5: Kata’ib Hizballah’s logo. Note the similarities between the fist-clenching-Kalashnikov images.
While photographs have been lacking, there have been a number of videos released onto the internet showing SaA’s attacks. Since the summer of 2013 the group has also posted video footage of some of the attacks it has carried out against Bahraini security personnel. One of the videos claimed to show an attack the group made in Bani Jamra, a town in northwestern Bahrain.[5] In another video from October, the group wrote, “This is just the beginning.”
Designed to coincide with the major February 14 protests (which commemorate the start of the 2011 Bahraini Uprising), SaA carried out another nighttime attack against Bahraini internal security forces and also released a film of their action. Albeit, instead of using their own accounts, this time the group sent the video to the popular “Revolution Bahrain” YouTube station. This style of release was repeated following the March 3 bombing when the group released footage it claims to have taken showing the aftermath of the bomb. In all cases, films of their attacks are regularly edited in order to give the group a level of operational security.
Following the March 3 blast, supporters of the group published clips which reportedly showed protests in support of the “holy warriors of Saraya al-Ashtar.” During the protest, candy was handed out to show support for the attack.[6]
The Rhetoric of Saraya al-Ashtar
Demonstrating a direct link to the adoption of Shia-centric forms of messaging, Saraya al-Ashtar’s name was likely no coincidence. It’s possible the group draws the roots of its name from Malik al-Ashtar, one of Imam Ali Ibn Abi Talib’s most loyal aids and colleagues. Malik al-Ashtar was also known to be a brave warrior and took part in a number of major battles at the behest of Ali. Ali Ibn Abi Talib, was the Islamic Prophet Muhammad’s relative and viewed by Shia as the Prophet’s successor and the first Imam.
The organization also refers to its combatants as “Rijal Allah” or the “Men of God.” The utilization of the phrase sets the underpinning for a religiously focused message: These fighters are doing the work of God. This immediately casts their foes as agents of a notably less than holy origin. The term finds regular use as a descriptor for Lebanese Hizballah and Iraqi Shia Islamist fighters among the supporters and members from Iranian-backed proxy organizations currently fighting in Syria.
Nevertheless, it is still essential to acknowledge that despite the organization’s clear Shia-centric messaging, it has attempted to argue that it is not a sectarian entity. In Saraya al-Ashtar’s July “Statement No.4”, the group accused the government of “igniting sectarian strife between the communities.” SaA also claimed that, “all of [Saraya al-Ashtar’s] operations are directed at the pillars of the corrupt regime and its mercenaries.”
There are a few ways to measure such a statement. When compared to the bulk of Iranian-backed Shia Islamist group rhetoric, those organizations also claim to be non-sectarian while simultaneously promoting an undercurrent of heavy Shia-centric sectarian messaging. There is also the possibility the group is honestly conveying its “revolutionary” beliefs. Arguing that its enemy is not Sunni Muslims, just the government under the Khalifa royal family and their supporting elements, is given more weight considering the group has only directly targeted security personnel.
As with other Bahraini militant groups, Bahrain’s security personnel are regularly referred to as “mercenaries.” The charge that Bahraini security forces are “mercenaries” stems from Bahraini recruitment of outsiders, primarily Sunnis from Pakistan and other Arab states. Additionally, while the organization has not specifically called-out Saudi Arabia or other Gulf states which sent forces to Bahrain in 2011, it does make passing references to their presence as, “the occupation.” In an effort to demonstrate the weakness of the Khalifa royal family, the SaA regularly refers to the Bahraini royals as a “collapsing regime”.
Saraya al-Ashtar’s Messaging & Links to Iran

Figure 6: Saraya al-Ashtar’s Statement No. 4.
At the time this post was written the group had released nine statements dealing primarily with their militant activity. Besides claiming responsibility for bomb attacks, another main focal point for SaA’s releases have dealt with the fate of political prisoners and to show support for main figures involved with the protests The condition of Abdulwahab Husayn Ali Ahmed Isma’il (A.K.A. Abdulwahab Husayn), a major ideologue, politician, and protest leader since the uprisings in Bahrain in the 1990s, was a core concern in SaA’s 2nd (May 17, 2013) and 8th (November 10, 2013) released statements. At the start of the 2011 Bahrain protests, Husayn was arrested by Bahraini authorities,
Hizballah Cavalcade: The Pearl & the Molotov: Bahrain’s Growing Militant Groups
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
The Pearl & the Molotov: Bahrain’s Growing Militant Groups
By Phillip Smyth
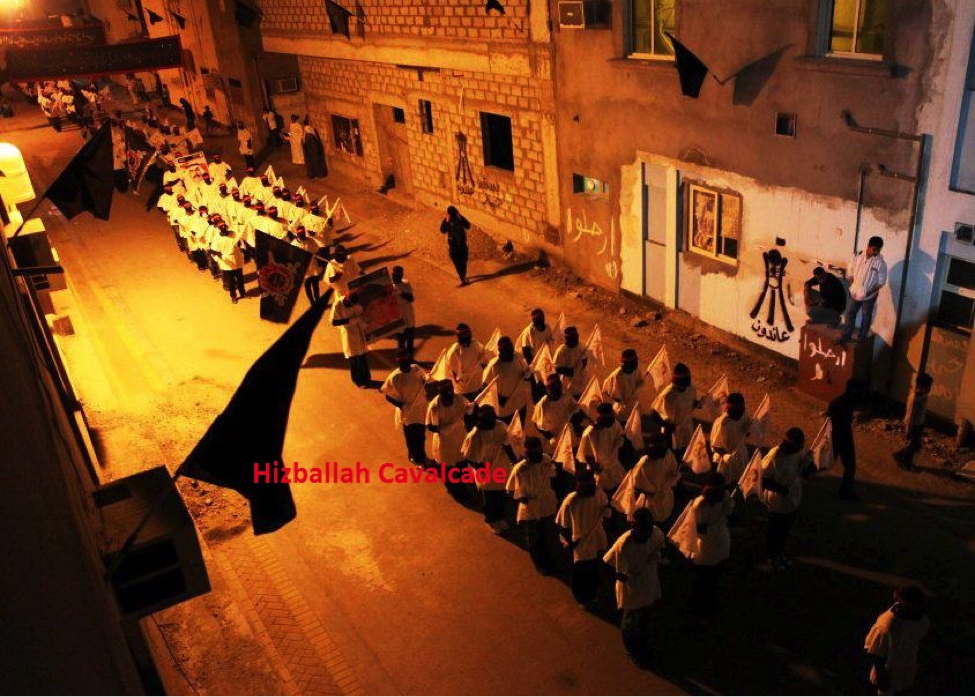

Figure 1: In a nighttime demonstration, members of Sariyya al-Muqawama al-Sha’bia (The Brigades of Popular Resistance) march wearing balaclavas and white burial shrouds. The shrouds exhibit their willingness to be martyred.
While a Shia jihad is being fought in Syria, Bahrain stands as another central conflict which continues to influence discourse, regional policies, and exacerbate sectarian tensions. For many Shia Islamists, particularly militant groups backed by Iran, Bahrain is a major political sore spot and focal point. Over the course of three years, the development of new militant groups within Bahrain has demonstrated that there is an increasing utilization of violent tactics. Since these militant groups are in the more rudimentary stages of development, there is the further possibility that they are increasingly viewing the conflict in Bahrain along regional and sectarian lines.
Main Goals of Hizballah Cavalcade’s Bahrain Posts
Since violent Bahraini organizations have not received adequate profiling, it is the goal of Hizballah Cavalcade to clarify their positions using primary open source material. Thus main goals include, but are not limited to:
- Describing the established organizations, their claims, goals, and ideological orientations.
- Analyzing claims made by the groups.
- Attempting to establish whether the organizations in question may have a connection to external actors.
A Little Background
Since 2011, Shia-majority Bahrain, which is led by the Sunni Khalifa royal family, has been gripped by protests calling for (among other demands) the Khalifas to abdicate, democratic reforms, and greater access for Shia to government positions.[1] For the most part, protests have been peaceful and have at times included both Sunni and Shia Muslims. These protesters have been faced with a number of often violent government crackdowns and accusations of the use torture by authorities.[2]
Yet, the protests, deaths, and growing polarization in Bahrain has regularly been considered a sort of sideshow when compared to other major protests and civil wars in the Middle East. The BBC even referred to the protests as the, “Forgotten Spring.”[3] Still, it would appear that some within the protest movement and possibly external organizations, are bent on forming groups to achieve their ends via violence.
On February 14, 2014—to commemorate the first “Day of Rage” held by Bahraini protesters on the same day in 2011—massive protests, which included main opposition parties and independent groups were held throughout the country. For the most part, these protests were peaceful. Around this time Bahraini authorities also reported a “terror blast.”[4] While this was hardly the first act of violence by a group within Bahrain, the blast underlined a number of more violent actions carried out by new organizations, since 2012.
In December of that year, Reese Erlich of the Global Post noted that younger elements of the protest movement were increasingly turning to violence and were making it difficult for local traditional leaders to control their activities.[5] By the end of 2013, new armed organizations calling for the overthrow of the Bahraini government were announced and continue to claim new attacks within Bahrain. In a period stretching from September 2013-January 2014, most of these new groups adopted higher profiles and attempted to brand their narratives, claimed attacks, and group identities within their online communities and pages.
Understanding Bahraini Militant Rhetoric
Bahraini militant organizations utilize rhetorical phrases and terms found with other Shia Islamist militant groups operating in Syria and Iraq. Often, their enemies are referred to as, “the Khalifa mafia”, “mercenaries” or “Saudi agents”. Nevertheless, this type of rhetoric also draws heavily upon local issues.
There were reports as early as 2011 that Bahrain was recruiting Sunni foreigners to man the internal security apparatus.[6] This issue of naturalizing foreign Sunnis, particularly from Pakistan, is viewed by protest leaders and militants alike as a major sectarian, economic, and social issue.[7] As future posts will show, the utilization of foreign-born police and security personnel is showcased in Bahraini militant propaganda.
Additionally, Saudi Arabia and other Persian Gulf Arab states sent forces as part of the Peninsula Shield which sent troops to Bahrain in March 2011. In April 2013, Peninsula Shield established a further headquarters in Bahrain in order to better coordinate their forces in the country.[8] Bahraini outlets have also reported that as of January 2014 these military forces were still defending “key instillations” and claimed they were not involved in Bahrain’s “internal issues.”[9] The presence of Saudi forces has added to the charge by protesters and militants that the Khalifas are simply propped-up by outside forces. An underlying message, which combines both national and religious identity, is that outside Sunnis (namely those who subscribe to Wahhabism; A religious movement which at times has demonstrated a violent hatred for Shi’ism) are continuing to control what should be Bahraini Shia affairs.
At the time of this writing, none of the groups have overtly stated that their goals are directly related to Shi’ism. However, many of the organizations use Shia-centric imagery, and have almost exclusively Shia members. Moreover, a number of the organizations in question have adopted the moniker, “Al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya” (“The Islamic Resistance”), a term heavily utilized and favored by Iranian-backed organizations, particularly Lebanese Hizballah and Iraq’s Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq.
What About Iran?
Bahraini authorities have regularly accused Iran of being a main driver behind the protests and in violent acts executed against security forces in the country.[10] As documented in other Hizballah Cavalcade posts, Iran makes no secret about its support for Shia jihadis in Iraq, Lebanon, and Syria. In fact, Iran has been a vocal supporter of the Bahraini protesters. In commemoration of 120 protesters killed in Bahrain, Iran opened a memorial for the “martyrs of the Islamic Revolution” in Tehran.[11]
In May 2013 Bahraini authorities banned political organizations within the country from contacting Lebanese Hizballah.[12] Later in December, Lebanese Hizballah’s Al-Manar TV station apologized for their coverage of events in Bahrain.[13] Shia Islamists in Iraq have also launched protests and issued very public criticisms of the situation in Bahrain. Iraq’s Muqtada al-Sadr has also been active in voicing his concern and support for Bahraini Shia protesters.[14]
Of course, Bahrain is not Syria and any claimed “jihad” would be hamstrung by the fact that Bahrain has strict gun control laws.[15] Smuggling of arms is also complicated by the presence of the US Navy’s Fifth Fleet (which is based in Bahrain) and by Bahraini units. As a result, many attacks have not used firearms, but instead utilize Molotov cocktails, hand grenades, homemade bombs, and other improvised weapons. In December 2013, Bahraini authorities claimed to intercept a shipment of “Iranian-made” explosives and other arms.[16]
Despite the many claims of Iranian involvement, there have been strong denials regarding the “Iranian hand” since the start of the protests.[17] Available information on armed organizations and their links to Iran is sparse and still developing. Additionally, some sympathetic to the protest movement have claimed these organizations are little more than fabrications by the Bahraini authorities. Regardless, this does not necessitate that Iran is not attempting to co-opt some of the more violent elements belonging to the anti-government ranks, create new militant organizations in Bahrain, or extend a more covert hand to those engaged in violence. Forthcoming posts will delve into these specifics in more detail.
Hizballah Cavalcade: Selling Sectarianism: Shia Islamist Groups & Maliki’s Anbar Offensive
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
–
Selling Sectarianism: Shia Islamist Groups & Maliki’s Anbar Offensive
By Phillip Smyth
As the Iraqi government offensive in Anbar continues to engage Sunni groups which are protesting the government (some have now taken up arms against the government) and the Islamic State of Iraq and al-Sham (ISIS), sectarian messaging by Shia Islamist groups which support the government and its offensive has also increased.
Coming after the operation against jihadi militants on December 23, 2013 and following protests by Sunni groups (including a number of tribes), on December 25 Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki announced an offensive against ISIS and “armed groups” in Iraq’s Anbar province. The offensive has been controversial regionally and within Iraq, with some accusing Maliki of engaging in sectarian politics.[1] Analyst Charles Lister even called the coordinated offensive, “one move too far”.[2]
Sectarian language explaining the Iraqi government onslaught has been utilized by all sides. Even Nouri al-Maliki called the operations, “a fierce confrontation between the supporters of Hussain and the supporters of Yazid”.[3] Shia Islamist groups, including Iranian-backed and possibly those claiming to back Iraqi Shia cleric and political leader Muqtada al-Sadr, have taken the opportunity to issue statements, upload photos, and produce music in support for the Iraqi government’s operations.[4] For these groups, the offensive was viewed as a golden opportunity to demonstrate their importance to the Iraqi Shia community and to demonstrate they were assisting the fight against jihadi-type organizations. These groups also played upon sectarian sentiments to promote the Iraqi government’s operations and suggest that the Iraqi Army is a pro-Shia sectarian entity. There were also claims that some Iraqi Shia Islamist forces which had fought in Syria, returned to fight ISIS and other Sunni groups in Iraq.
Statements of Support
On December 28, Ahmed al-Alwani, a Sunni parliamentarian and protest leader, was arrested by Iraqi security forces. The raid against him resulted in the death of Alwani’s brother and a number of guards from his security profile.[5] Alwani was well-known for vitriolic anti-Shi’ite statements.[6] His arrest by Iraqi security forces was immediately praised by some Shia Islamist groups, particularly Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq, which praised the raid (see photos below). The day also saw a near simultaneous release of statements by Iranian-backed Shia Islamist organizations which are also fielding armed units in Syria.
Liwa’a Zulfiqar, a Syria-based Shia Islamist armed group, also announced its support for the Iraqi Army in its operations against ISIS and announced they would stand by them against, “racist Zionist terrorism”. This represents a continuance of the narrative that armed Shia Islamist groups (primarily backed by Iran) consider al-Qa’ida and its allied organizations as merely agents of Israel. On the same day, Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada, released its second publicly available official communique. The statement stressed their support for the Iraqi Army’s fight in Anbar. Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq also issued their own messages of support for the offensive against ISIS.
Figure 1: An announcement of support for the Iraqi Army’s efforts in Anbar from the official Liwa’a al-Zulfiqar Facebook page.

Figure 2: Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada’s release in support of the Iraqi government’s offensive into Anbar.

Figure 3: Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq’s statement about their support for the Iraqi government and military against ISIS and armed groups in the country.
Main Messaging Themes:
- National Institutions: Shia Islamist groups have claimed to fully support the Iraqi Army and present themselves as integral elements to the Iraqi military and police operations in Anbar. This theme coincides with other Iranian-backed organizations messaging, namely the narrative presented by Lebanese Hizballah and their claims of fully backing the Lebanese Armed Forces.[7]
- One Army, One Sect: Photos and statements implying the Iraqi military and police are engaging in the fight against ISIS to defend Shi’ism. These themes are also combined with photos claiming to show members of the military and/or police showing support for certain Shia political leaders and clerics. This sort of rhetoric had gone on since the spring of 2013 during the initial announcements of foreign Shia fighter involvement in Syria. In one May 2013 photo, a soldier reportedly from the Iraqi Army is shown holding a Shia religious banner on top of what is claimed to be an Iraqi military armored vehicle (see below).
- Two Fronts, One War: Tying the war in Syria to the fighting in Iraq involves extending the “Defense of the Sayyida Zaynab” (the defense of the Sayyida Zaynab shrine in southern Damascus is held as the reason for Shia Islamist fighters are in Syria) narrative which claims Shia Islamist armed groups are present in Syria to protect holy shrines/Shi’ism and stop jihadi-linked fighters. As a result, the engagements within Iraq which claim to also target ISIS and other organizations are grouped together as part of a unified effort to protect Shi’ism.
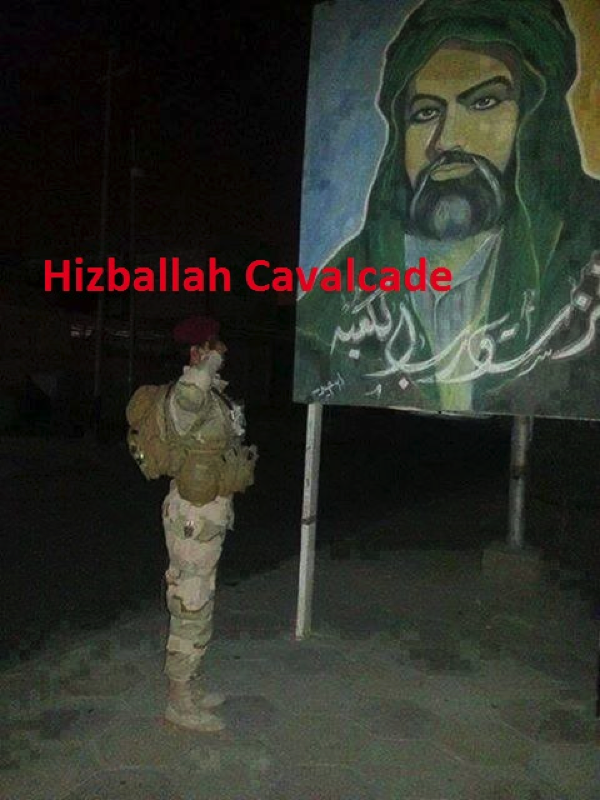

Figure 4: A photo uploaded in mid-January with the caption, “We will not be defeated”. The photo reportedly shows an Iraqi Army soldier saluting a Shia religious poster.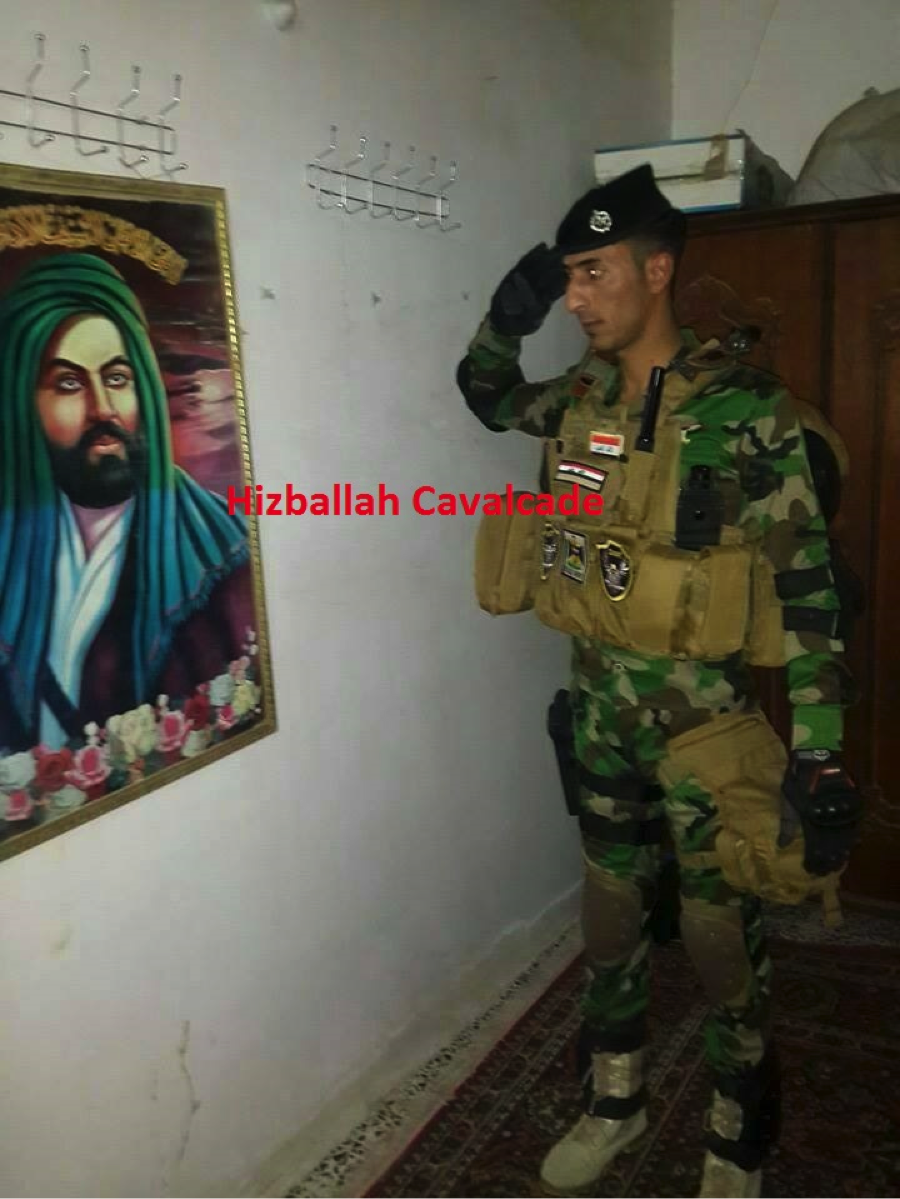
Figure 5: Photo claims to show an Iraqi soldier saluting a picture of martyred Shia leader, Imam Husayn. The photo was posted onto numerous social media pages catering to Shia Islamist fighters in Syria.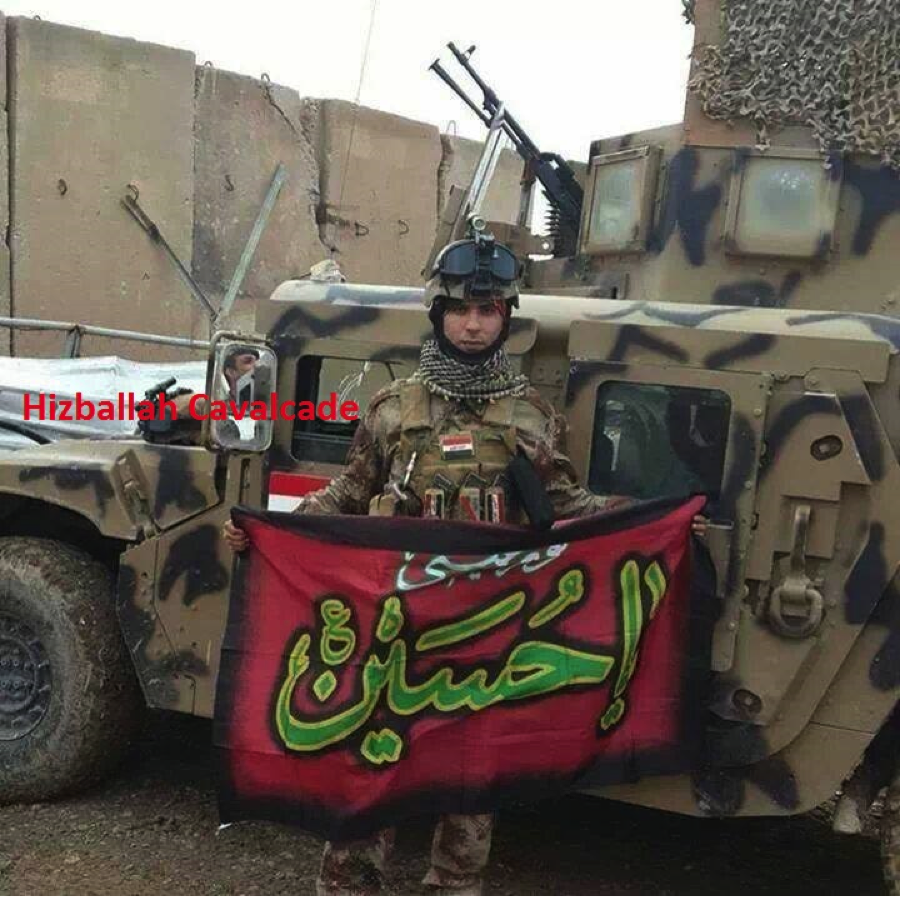
Figure 6: This photo claims to show an Iraqi soldier holding an Imam Husayn flag in front of an armored vehicle. The photo was widely circulated on Shia Islamist social media pages.
Figure 7: Photo purports to show an Iraqi soldier under a Shia banner following the, “Capture of Ramadi”. The photo was posted on Badr Organization and Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq social media pages.
Figure 8: This photo claimed to show an Iraqi soldier saluting Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei.
Figure 9: First uploaded to Shi’a Islamist social media in May 2013, this photo claims to show an Iraqi soldier atop an armored vehicle holding a Shi’a religious banner.
Figure 10: An Iraqi armored personnel carrier (APC) flying flags for Shia Imam Husayn with a sign partially reading, “Welcoming visitors to Imam Husayn [mosque and shrine in Karbala, Iraq]”. While the context of the photo is probably more innocuous—It is likely this APC was simply part of a guard set up in Karbala and was used to welcome pilgrims—ISIS/Sunni Islamist activists and Shia Islamist groups circulated the photograph as proof of the Iraqi Army’s sectarian loyalties.
Figure 11: Top photo: “This is how they kill us”. Bottom photo: “And this is how we treat them”. The top picture shows Iraqi soldiers executed by ISIS. The bottom references reports of Shia Muslims taking in Sunni Muslim refugees from Anbar.[8] The photo was not widely distributed, but could be found on pages and profiles catering to Iranian-backed Shia Islamist organizations (mainly Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq).
Figure 12: This photo, spread on Sadrist and Sadr-splinter group social media, claims to show an Iraqi soldier reaching out to a Muqtada al-Sadr poster.
Figure 13: Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq leader Qais al-Khazali smiles (right) while Iraqi Sunni MP Ahmed al-Alwani is detained by Iraqi security forces (left).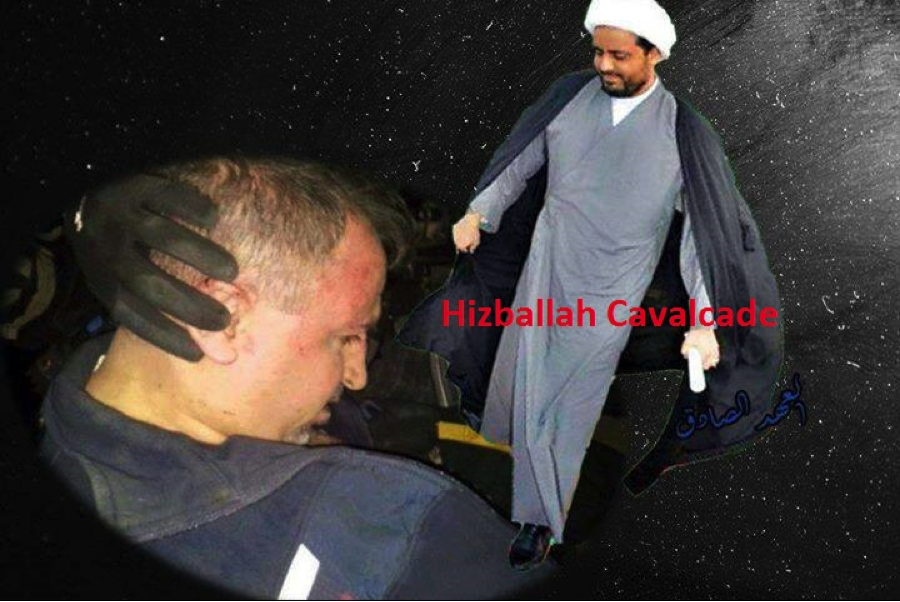
Figure 14: Qais al-Khazali is portrayed as walking on the captured Iraqi Sunni MP Alwani.
Figure 15: “Thus, we support you”. An AAH poster shows AAH leaer Qais al-Khazali looking down on Iraqi army soldiers and an Iraqi helicopter.
Figure 16: Selfie Taunts: On the right an ISIS supporter holds up a picture near the Imam Husayn Mosque/Shrine complex in Karbala. The sign reads, “Qadimoun” (“We are coming”). As a response to the pro-ISIS message, (on the left) “We are waiting for those coming, [we] the young men of sacred Karbala Soldiers of Husayn”.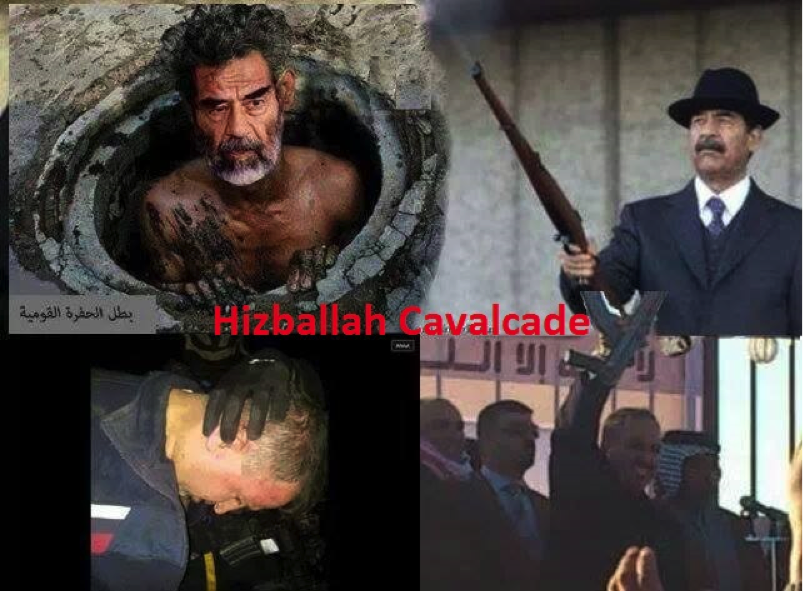
Figure 17: Right Left (top) An edited photo shows deposed Iraqi leader Saddam Husayn emerging from a dirty sewer. Left (bottom) Alwani is shown following his capture. The photo was spread on Sadrist and Iranian-backed Shia Islamist pages. The image promotes a theme of “how the mighty have fallen.” 
Figure 18: Another photo released on social media claiming to show Iraqi APCs flying Shia religious flags. The photos were shared online by ISIS sympathizers and Shia Islamist groups. The latter used the photos as a subtle way to suggest the Iraqi Army had Shia Islamic sectarian loyalties.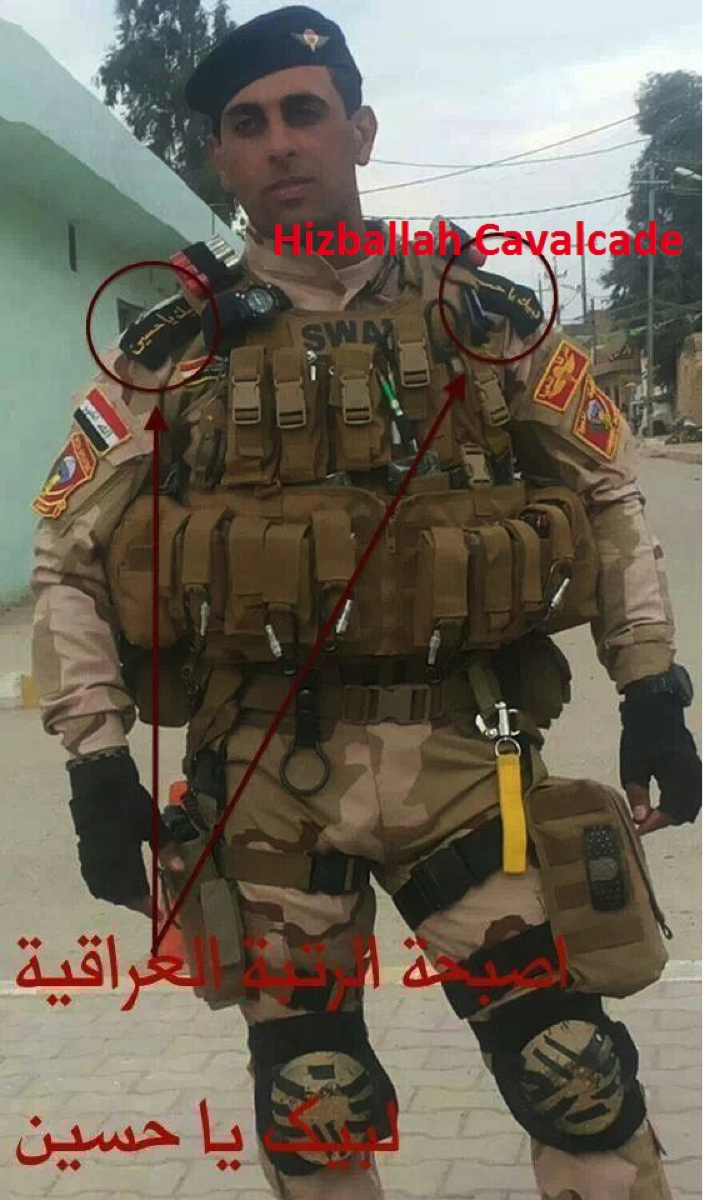
Figure 19: Shia Islamist and Sunni supporters of the protests and of ISIS circulated this photo on social media (including Twitter and Facebook). The photo purports to show an Iraqi Special Forces/SWAT member wearing epaulettes reading, “Labayk ya Husayn” (“At your service, O Husayn”), a Shia slogan used to show support for the Shi’ism’s first Imam.
One video uploaded claimed to show Iraqi units assembling before heading into Anbar and flying Shia religious flags. Due to the lower quality of the images in the video, the claim could not be confirmed. Accounts affiliated with Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq also uploaded a response to the offensive against ISIS. In their clip, a man sets up a system for a unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) which then spots what can assumed to be ISIS positions. The ISIS positions are then destroyed. The clip was entitled, “A message from Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq to Da’sh” (note: Da’sh is the Arabic acronym for ISIS).
Hizballah Cavalcade: Faylak Wa'ad al-Sadiq: The Repackaging of an Iraqi “Special Group” for Syria
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Faylak Wa’ad al-Sadiq: The Repackaging of an Iraqi “Special Group” for Syria
By Phillip Smyth

Figure 1: Faylak Wa’ad al-Sadiq’s logo. The top line reads: “The Islamic Resistance in Iraq” (“Al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya fi al-Iraq”). The bottom says, “The Truthful Promise Corps” (“Faylaq al-Wa’ad al-Sadiq”). The logo features the map of Iraq in the center with a blackened figure holding an RPG-7.
Officially known as Al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya fi al-Iraq-Faylaq al-Wa’ad al-Sadiq or The Islamic Resistance in Iraq-The Truthful Promise Corps (FWS), this organization has made some waves in Arabic-language media following the discovery of some of its images on social media networks.[1] Led by a Secretary General, FWS’s current leader is Iraqi Shia Sheikh Abu ‘Ammar al-Tamimi (A.K.A. Shiekh ‘Ammar). The organization also claims to be based in the holy city of Najaf, Iraq. It is clear from assessing the trajectory of public statements and their social media presence that the FWS appears to be increasing its public presence in an effort to establish the belief there are further organized Shia Islamist force deployments in Syria.
The group’s name references Lebanese Hizballah’s Secretary General’s long-standing goal to kidnap Israeli soldiers. This “promise” came to fruition in July 2006, when fighters from Lebanese Hizballah attacked an Israeli military convoy and kidnapped two Israeli soldiers and killed three. The attack spurred what would turn into the more than a month long 2006 Hizballah-Israel War.[2]
It is unclear whether it was created immediately following the 2006 Hizballah-Israel War or if it was established later in 2010-2011.
Reportedly, the FWS was first established to “fight the U.S. occupation of Iraq and the collaborators [associated with it]”.[3] In January 2012, FWS claimed it had no interest in running for elections or becoming part of the Iraqi government.[4] In August 2012, the FWS’s spokesperson Sheikh ‘Amr al-Lami, claimed the group changed paths and stated it would instead focus on civil projects. One year later, the organization claimed to have sent its first fighters (from a “military wing”) to Syria in order to, “defend shrines”.[5] “Shrine defense” has been the most prevalent narrative used by Iranian-backed Shia Islamist fighting groups which have deployed to Syria.
The group also made its first video and a group musical anthem public in January 2014. Though it appears to have been uploaded in February 2012. It is possible FWS uploaded the clip many months ago, then made it “private”, only to re-release it as part of a ramping-up of their public image. In the short clip, the FWS-subgroup which claims the attack is called Kata’ib Musa al-Khadhim-Sariyya ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir (The Musa al-Khadhim Brigade-‘Ammar Ibn Yasir Unit). Musa al-Khadhim references the seventh Imam in Twelver Shia Islam.[6] The targeted vehicle in the clip appears to be a U.S. armored HMMWV. [7] The naming of subdivisions after imams is a common form utilized by Iranian-backed Iraqi special groups.[8]
Little was known about the organization during the Iraq War (2003) and it had few announcements. The group also claimed to have its own webpage (since 2011). However, when the page is visited, it does not load.[9] Instead, with public appearances and statements by its leadership, it seems that since the summer of 2013, FWS has been dusted-off and repurposed for a new mission in Syria. September 2013 saw FWS start its initial postings on social media pages it had done little with since opening them in 2011.
This may indicate that the FWS was little more than a front-type group during the Iraq War (2003) which may now field rebranded fighters from other groups for the fight in Syria. In turn, this helps create perception of broader Iraqi Shia support for the concept of Wilayat al-Faqih and of this ideological grouping’s war in Syria. Comments on the page largely praised the leadership of Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq. This mirrors newly created front groups such as Harakat Hizballah al-Nujaba (or Harakat al-Nujaba), which fields fighters from Kata’ib Hizballah and Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq (AAH), has a leader from AAH’s ranks, yet is cast as independent organization. Photos of fighters from Harakat al-Nujaba front militias in Syria and those from Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq have found a presence on FWS’s Facebook page and adjoining profiles.
In addition to the organization’s name and links to other Iraqi Shia “special groups”, another element further cementing its relationship with Iran and its proxy militant groups, was the group claiming adherence to the concept of Wilayat al-Faqih. Wilayat al-Faqih, or the Absolute Guardianship by a Jurisprudent is Iran’s form of radical theocratic governing system. In August of 2013, the reported leader of FWS visited Beirut and confirmed his loyalty to the political-religious ideology.[10] The lead jurisprudent, or Wali al-Faqih, who is followed by FWS is Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei. The organization’s imagery also details their loyalty to Khamenei.
Little is known about FWS’s combat abilities, force size, or deployments. In photos released by the group, it has been shown they have what can be considered a normal small-arms accompaniment, ranging from PKM-type machineguns to Kalashnikov pattern rifles. One important detail about deployments in Syria was that the FWS has only claimed (so far) to have specifically fought in one area, Aleppo. This further helps tie the group to Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq’s Harakat al-Nujaba and their Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir (LAIY). LAIY was the first Iraqi Shia Islamist group to announce they were fighting in Aleppo. The announcement also coincided with the December 2013-January 2014 increase in announced Shia Islamist military activities in Rif Aleppo and the city.

Figure 2: These photos, posted in mid-December, claimed to show an FWS fighter in Aleppo, Syria.
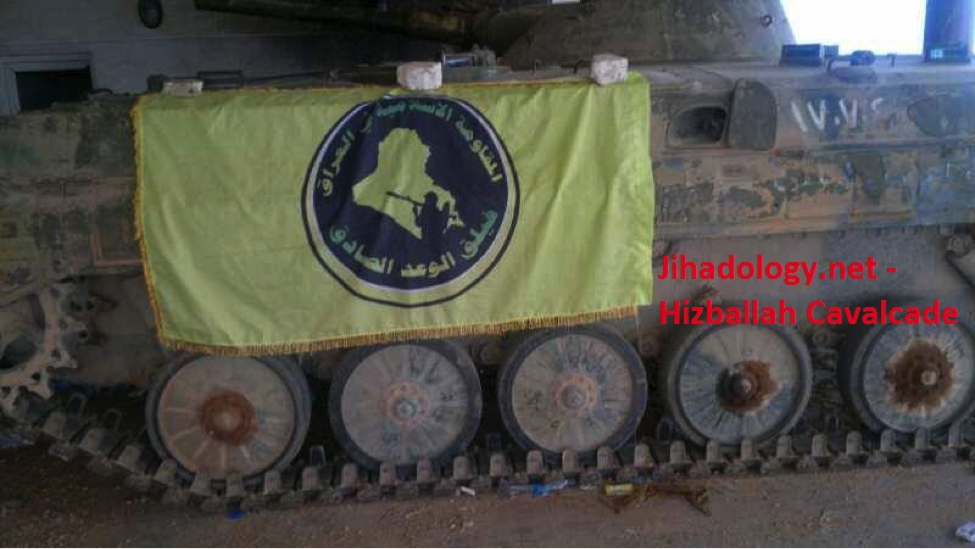

Figure 3: The FWS flag flies on a BMP-1 armored personnel carrier. It is unknown whether this flag was placed on an Iranian, Iraqi, or Syrian BMP-1 infantry fighting vehicle.

Figure 4: “ma’rkat al-haq dhud al-batl al-wa’ad sadiq qadm” or the “Battle of truth against falsehood, the truthful promise is coming”.
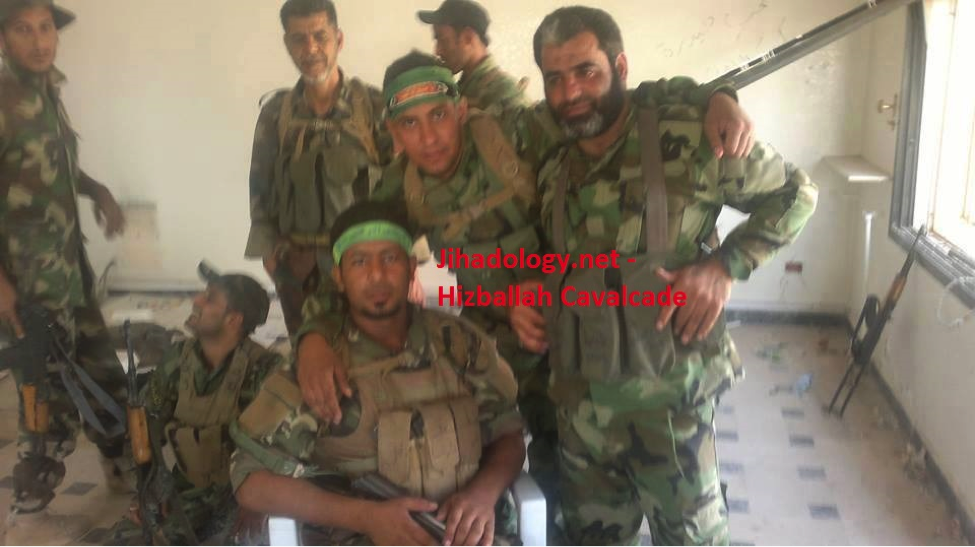

Figure 5: This photo claims these are Faylak Wa’ad al-Sadiq personnel. However, the photo has been posted by other Shi’a Islamist fighting groups.

Figure 6: Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei and Muhammed Muhammed Sadiq Sadr look from the sky down at burned-out U.S. armored vehicles. An Iraqi flag graphic is flows from the lower-right corner.

Figure 7: Another poster featuring Iranian Surpreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei and Muhammed Muhammed Sadiq Sadr.
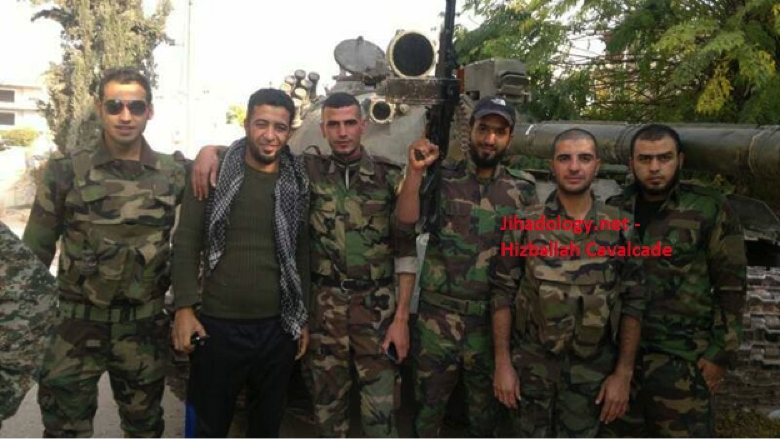

Figure 8: FWS fighters pose in front of a tank.
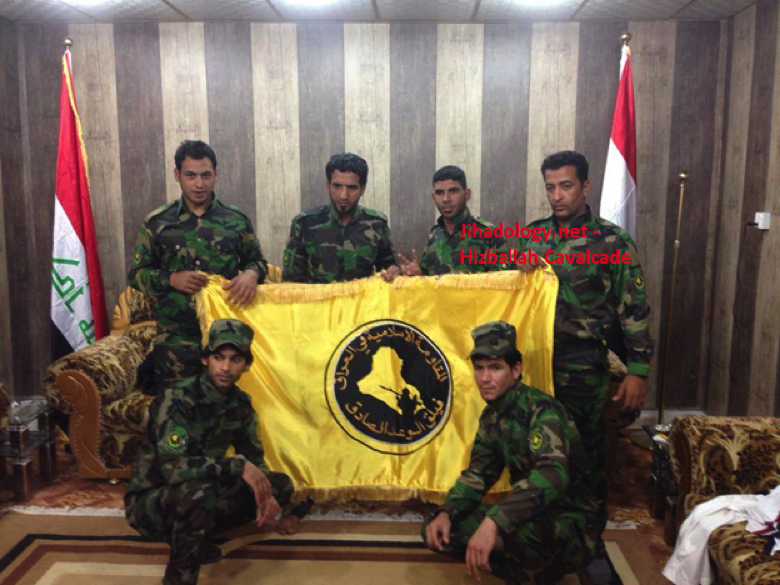

Figure 9: Uniformed FWS members pose with the group’s flag while flanked by Iraqi flags. Note the FWS patches worn by these 6 members.

Figure 10: The FWS flag.
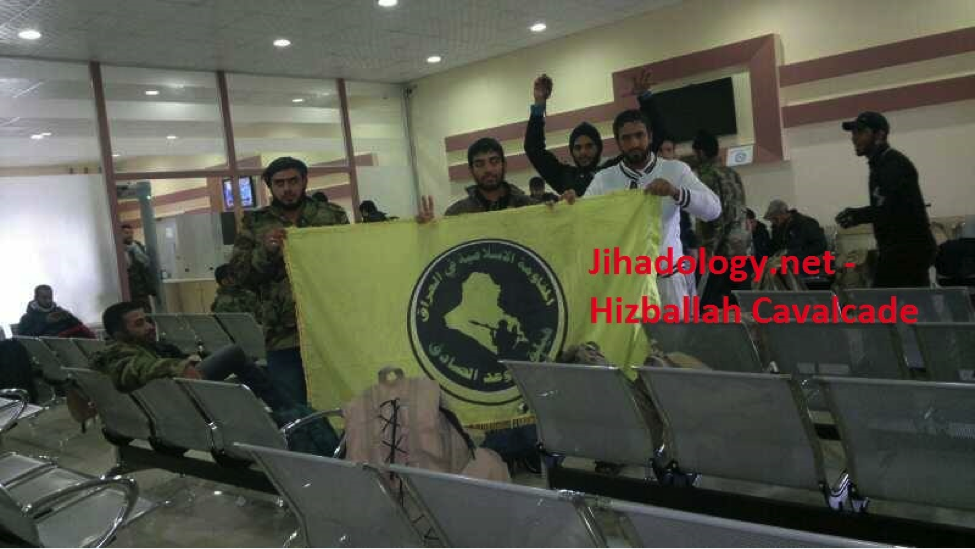

Figure 11: FWS fighters hold up the group’s flag.

Figure 12: Another piece of FWS symbolism.
Hizballah Cavalcade: Deck the Halls with a Minority Alliance: Shia Militia Social Media Messages to Christians
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Deck the Halls with a Minority Alliance: Shia Militia Social Media Messages to Christians
By Phillip Smyth
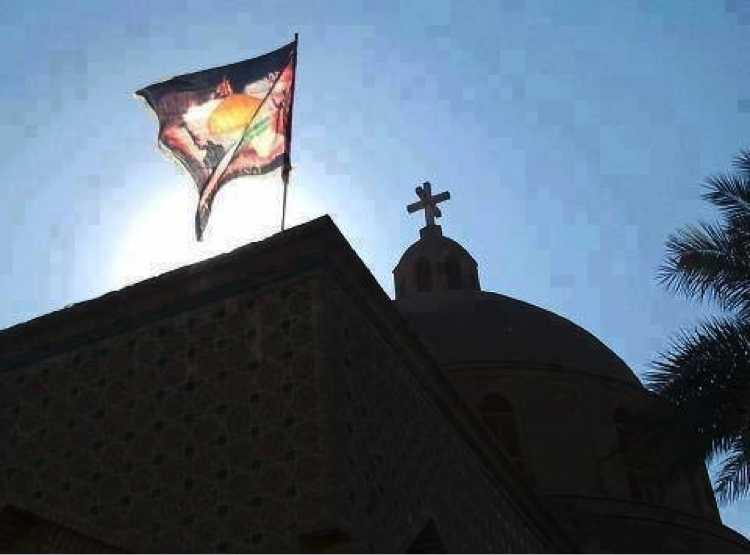

Figure 1: This photo, purporting to show a Shia banner on a church (possibly in Iraq) has been circulated around as a symbol of Shia-Christian unity and coexistence. The photo has been present on a multitude of Iranian-backed Shia Islamist group Facebook pages.
Minority alliances in the Middle East are hardly a new trend. During the Syrian Civil War there has been deliberate engagement by some minority elements to build more effective political alliances and fighting groups based on minority identification. This has particularly been the case with the mainly Alawite support base for Syrian leader Bashar al-Assad and his system’s relationship with Druze and Christian elements within Syria.[1] The trend of marketing the Syrian leader as both a secularist and as one who will take care of other minority groups has been a major theme in pro-Assad open source media circles.[2]
Nevertheless, Bashar al-Assad’s power bloc is not the only group touting their minority alliance credentials in the face of a mainly Sunni Islamist rebel enemy. In fact, Shia Islamist militias backed by Iran, which are also engaged in fighting these rebels, have also actively attempted to court Christians. These groups have tried to build a minority alliance sentiment with a number of strategically placed photos on their hive-like social media accounts. While this is but one of many different trends found on Shia Islamist militia social media pages, it does play to grander narratives.
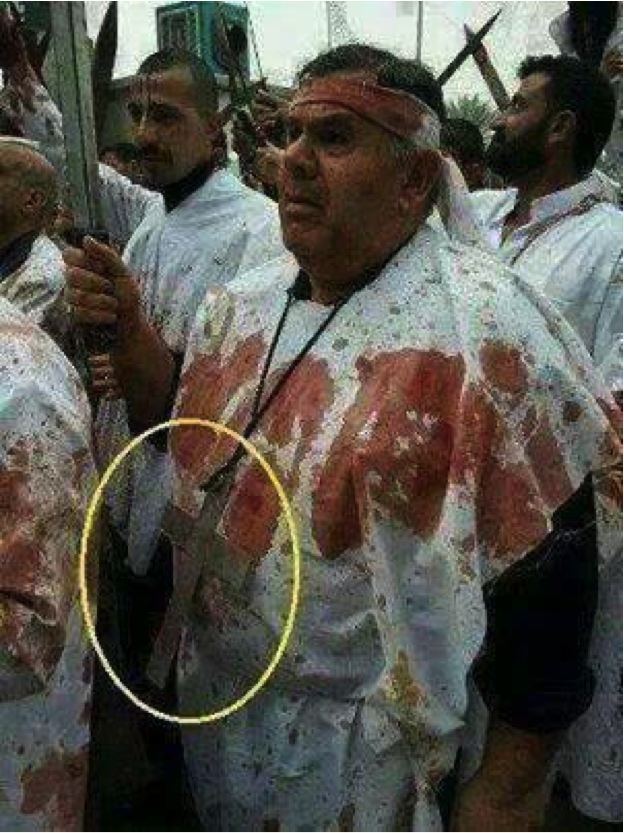

Figure 2: A photo showing a man covered in blood from what can be assumed was his own practice of zanjeer zani (Shia self-flagellation using a sword or knife). Note how a crucifix around his neck is circled. Some pro-Shia-militia-in-Syria social media pages have suggested the man is a Christian showing his devotion to historical Shia leader, Husayn. Other pages have used the photo as a symbol of Shia respect for Christians (and vice versa).
Lebanese Hizballah has actively engaged Lebanon’s Christian (primarily Maronite Catholic) community. In 2006 the group became a senior partner with Michel Aoun’s mainly-Christian Free Patriotic Movement in the March 8th Alliance.[3] Lebanese Hizballah has also attempted to court Lebanon’s Christian community in recent years. In 2012 around Christmas, pro-Hizballah writers published pieces touting the group’s outreach to Christians.[4] The group also issued a 2013 Christmas greetings to Christians and held meetings with the community.[5]
Since Shia militia groups in Syria have branded their enemies as al-Qa’ida style extremist “Takfiris”, it allows for continued marketing of Shia group activities as a hard power counter. Many Christians in Syria arrived in the country due to attacks they suffered in Iraq. Other Syrian Christians worry about their presence in the country with ascendant Sunni Islamist extremist groups in the country.
The goal of these photos appears to be less of an attempt to recruit Christian fighters for Shia militia ranks.[6] Instead, they are used to create the image of cross-sectarian unity. This form also pushes a narrative that Christians can not only find protection with Shia Islamist militias, but that these organizations will both respect them and act as viable long term allies. This messaging structure also plays off of earlier themes adopted by many regional Christian groups, namely the fear of being drowned in a “Sunni Sea”.

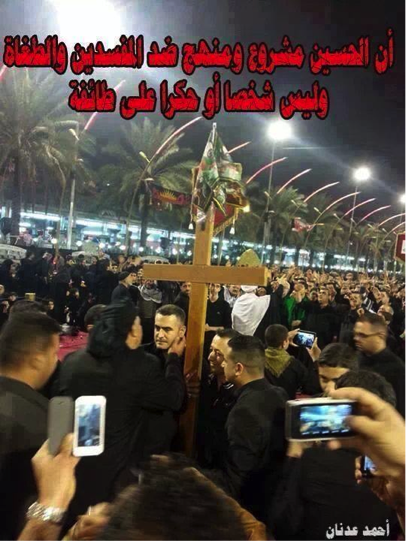
Figure 3: A photo supposedly showing Christians in Iraq engaging in a Shia pilgrimage. This photo also received many different captions. The main theme behind the captions promoted Christian-Shia brotherhood.

Figure 4: A photograph claiming to show an Iraqi church which had hung Shia banners to help usher in the New Year. This picture started to appear on Shia Islamist militia pages in December 2013. The photo was unclear, but implied it was taken in November during Ras as-Sanah al-Hijriyah (the Islamic New Year). Rebel activists seized upon the photograph, claiming it showed a church being desecrated with Shia flags in Syria.

Figure 5: A picture promoting ‘Syrian unity’ between Shia and Christians. This picture has appeared on a small number of Iraqi Shia-manned militia group Facebook pages.

Figure 6: In April, Shia militia pages claimed this fighter was a “Christian martyred defending the Shrine of Sayyida Sukayna bint Husayn [the Sayyida Ruqayya Mosque]”. Some Shia militia pages referred to him as the “Son of the Virgin Mary”.

Figure 7: A photo showing a Syrian fighters accoutrements. Included are small medallion-like pictures of Lebanese Hizballah leader Sayyid Hassan Nasrallah and a crucifix. It noted in the caption that these items belonged to a Christian soldier named George Elias and that he wore them around his neck.
