For prior issues, see: #4, #3, #2, and #1.
—

Click the following link for a safe PDF copy: Ṣirāṭ al-Ḥaqq Magazine Issue #5
______________
Source: RocketChat
For prior issues, see: #4, #3, #2, and #1.
—

Click the following link for a safe PDF copy: Ṣirāṭ al-Ḥaqq Magazine Issue #5
______________
Source: RocketChat

Click the following link for a safe PDF copy: Islamic State’s Wilāyat al-Hind — Oh Muslims of Bangladesh- Halfway Done, Now Strive For the Rule of God
________________
Source: RocketChat

The Islamic State today looks different than it did five years ago and is far more integrated now as an organization amongst its global network than al-Qaeda ever was. It has been 10 years since the Islamic State announced itself as a caliphate and more than five years since it lost its last vestige of territory in Syria. However, with the Islamic State back in the news due to an increasing external operations capacity (with attacks in Iran, Turkey, and Russia this year as well as numerous broken up plots in Europe), there is a fundamental misunderstanding of how the group operates today. In many ways, it is either incorrectly viewed through the lens of how al-Qaeda operates (a decentralized branch network), since it had previously been a part of al-Qaeda’s global network, or based on how the Islamic State operated when it was at its prior zenith when it controlled territory in Iraq and Syria. It is also likely why some within the U.S. government may have misinterpreted signals intelligence by pushing the idea that the Islamic State leader targeted in Somalia at the end of May, Abd al Qadir Mumin, became the group’s caliph. These changes in the past five years are crucial for policymakers to understand because the way the threat presents itself today will look different from how policymakers dealt with the issue last decade when much of the focus was on the Islamic State’s territorial control in Iraq and Syria.
The most important body for understanding the Islamic State today is its General Directorate of Provinces, which has previously been based in Syria, but new information suggests that at least at the highest levels of it might now have centrality in Somalia. When one understands that structure, the Islamic State’s actions globally make more sense. It is also why we see far more interaction and connection between its various wilayat (provinces) today than in the past. In many ways, the key aspects that animate the Islamic State as an organization (governance, foreign fighter mobilization, and external operations) remain, they have just moved from primarily being based out of or controlled by its location of origin in Iraq and Syria to being spread across its global provincial network. Its aims remain the same, even if the organization has adapted to a changed environment. It is also why the challenge from the Islamic State today is different from the past and why it is in some ways also more resilient now to pressure than before.
This makes the challenge of the Islamic State more difficult from a security perspective than in the past when there was the ability to primarily zero-in on its efforts in Iraq and Syria. Today, only focusing on Iraq and Syria or any other province independent of understanding its connections to other parts of the group’s global network will lead to missing crucial details due to expediency. This is why, although it is understandable that the United States has shifted a lot of its manpower and budgeting to more existential and larger problem-sets such as China and Russia, it would be a mistake to neglect the Islamic State as a continuing, but evolving security challenge. Therefore, it is still useful to continue to have and add more funded government positions across different agencies and departments to focus on tracking this threat to better get ahead of the next surprise. Otherwise, mistakes of misinterpretation will be made as in the past.
Click here to read the rest.
For prior issues, see: #3, #2, and #1.
—

Click the following link for a safe PDF copy: Ṣirāṭ al-Ḥaqq Magazine Issue #4
__________________
Source: RocketChat
For prior issues, see: #2 and #1.
—

Click the following link for a safe PDF copy: Ṣirāṭ al-Ḥaqq Magazine Issue #3
_______________
Source: RocketChat
Previously, I tracked the bayat campaign for Abu Ibrahim after Abu Bakr’s death and then for Abu al-Hasan after Abu Ibrahim’s death. This post will do the same with the announcement of Abu al-Hasan’s death and Abu al-Husayn al-Husayni al-Qurashi as the new leader of the Islamic State. As I said in the original post:
There are two main reasons for this: 1. pledges are leader-specific rather than group-specific and thus need to be renewed with each succession and 2. it is a way to legitimize al-Qurashi’s rule and create a media event so that the group can promote itself as it transitions to a new phase.
The first reason is also something that IS pointed to when it began to overtly feud with al-Qaeda (AQ) in 2013, by saying that following Abu Mus’ab al-Zarqawi’s death, his successor Abu Hamzah al-Muhajir gave baya to the newly created Islamic State of Iraq’s leader Abu ‘Umar al-Baghdadi and even after Abu ‘Umar was killed, when Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi took over in 2010 and then Usamah Bin Laden was killed in 2011, Abu Bakr never publicly gave baya to Ayman al-Zawahiri, even if al-Zawahiri claims he gave it to him privately. Therefore, from the perspective of IS this whole process is not trivial, but important for legitimacy of its leadership and to potentially weed out any insubordination before it manifests into something larger as it already did in the past vis-a-vis AQ.
This post will be updated with the latest official pledges.
—
December 1, 2022:
Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyah – Sambisa Region











Wilāyat Khurāsān




























Wilāyat al-‘Irāq

























Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyah – al-Buhayrah Region





December 2:
Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyah – al-Faruq Region

















Wilāyat al-Shām

































Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyah – Banki Region






December 3:
Wilāyat al-Yaman




Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyah – Krenoa Region





Wilāyat al-‘Irāq
















Wilāyat al-Sāḥil – Azawagh, Tri-Border, and Burkina Faso Regions
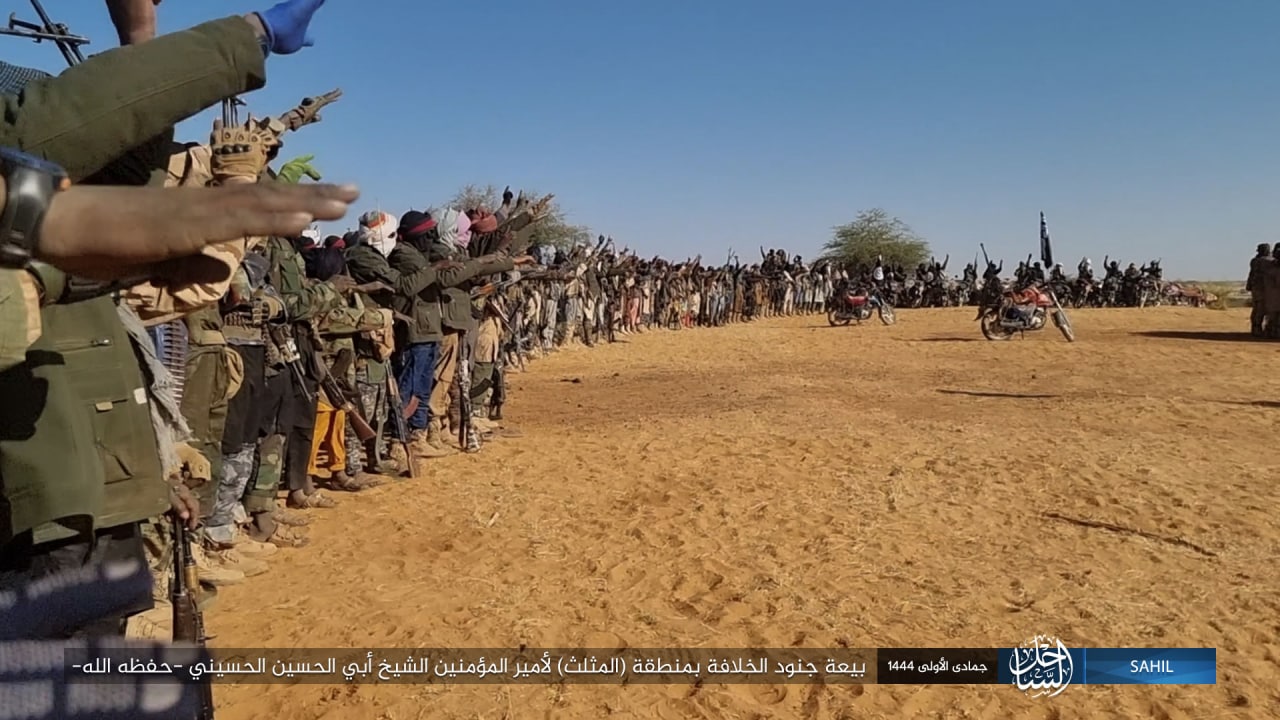





























December 4:
Wilāyat al-Ṣūmāl




















Wilāyat Wasaṭ Ifrīqīyah







Wilāyat al-Sāḥil – Anderamboukane Village









December 5:
Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyah – Central Nigeria






Wilāyat al-Shām





















Wilāyat Bākistān















Wilāyat Mūzambīq






Wilāyat Wasaṭ Ifrīqīyah – Beni Region




December 7, 2022:
Tūnis


Wilāyat al-Hind – Kashmir








Wilāyat Mūzambīq – Nangade Region





December 8, 2022:
Lubnān






December 14, 2022:
Wilāyat Saynā’




December 17, 2022:
Wilāyat Sharq Asīā




December 19:
Wilāyat Lībīyā




There are two main reasons for this: 1. pledges are leader-specific rather than group-specific and thus need to be renewed with each succession and 2. it is a way to legitimize al-Qurashi’s rule and create a media event so that the group can promote itself as it transitions to a new phase.
The first reason is also something that IS pointed to when it began to overtly feud with al-Qaeda (AQ) in 2013, by saying that following Abu Mus’ab al-Zarqawi’s death, his successor Abu Hamzah al-Muhajir gave baya to the newly created Islamic State of Iraq’s leader Abu ‘Umar al-Baghdadi and even after Abu ‘Umar was killed, when Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi took over in 2010 and then Usamah Bin Laden was killed in 2011, Abu Bakr never publicly gave baya to Ayman al-Zawahiri, even if al-Zawahiri claims he gave it to him privately. Therefore, from the perspective of IS this whole process is not trivial, but important for legitimacy of its leadership and to potentially weed out any insubordination before it manifests into something larger as it already did in the past vis-a-vis AQ.
This post will be updated with the latest official pledges.
—
March 11, 2022:
Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – Karkūk




























Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyyah – Lake Chad Basin

























Wilāyat al-Shām
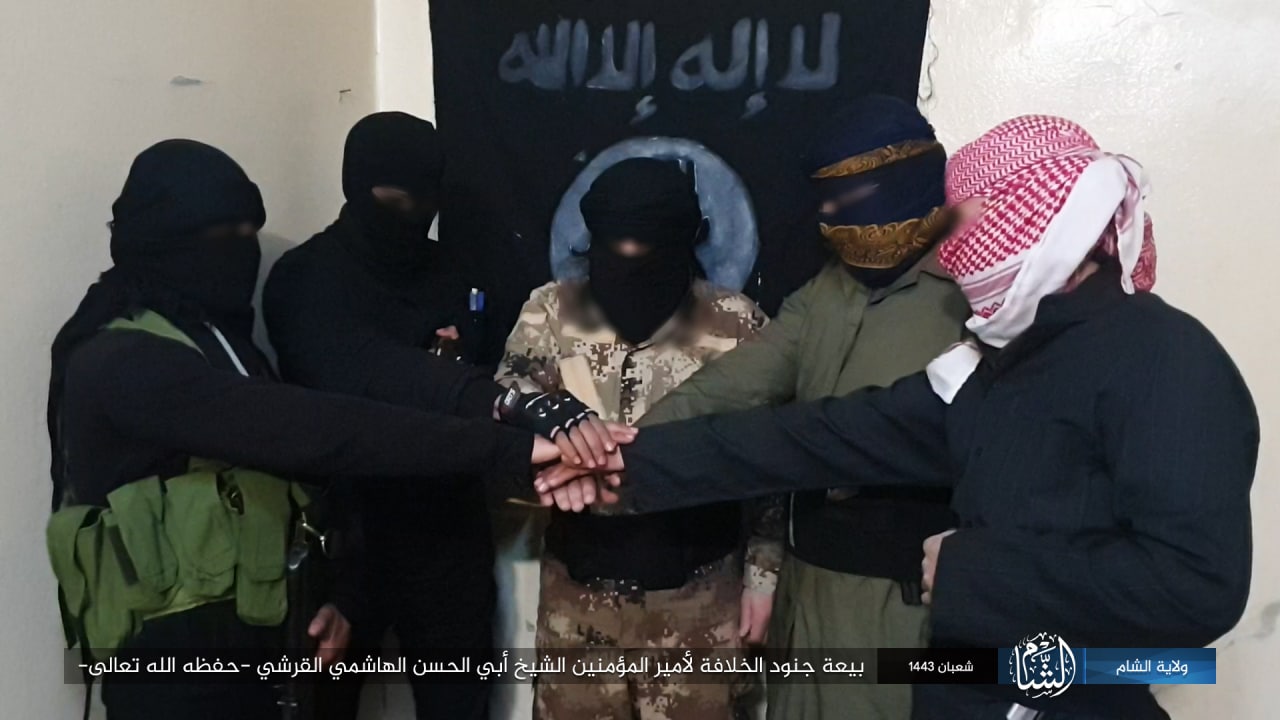


































Wilāyat al-Ṣūmāl








Wilāyat Sharq Asīā






March 12, 2022:
Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – al-Ānbār












Wilāyat al-Yaman




Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – Ṣalāḥ al-Dīn














Wilāyat Khurāsān






























Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyyah – al-Faruq Region













Wilāyat Lībīyā



Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyyah – Sambissa








Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyyah – Sahel Region
























Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyyah – Kerenoa Region





Wilāyat Bākistān









Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – Shamāl Baghdād


Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – al-Janūb


Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – Diyālā
















Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – Nīnawā


Wilāyat al-Hind








Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – Dijlah




Wilāyat Saynā’












Wilāyat Wasaṭ Ifrīqīyah













—
Earlier this morning, the Islamic State announced the creation of a new Wilayat al-Hind. While the claim is related to an attack in Kashmir, it likely will also apply to any activity in India in the future as well. As Mina al-Lami notes, this is not the first time IS has claimed an attack in Kashmir before. Previously it was under its Wilayat Khurasan, which is most associated with its operations in Afghanistan and Pakistan. Therefore, once again, IS is reorganizing its provincial structure. This new system is part of a broader change since the fall of IS’s territorial control in Baghuz, Syria, which ended almost two months ago now. Recently, IS inaugurated a so-called Wilayat Wasat Ifriqiya for its operations in the Democratic Republic of Congo and Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi’s recent video highlights a so-called Wilayat Turkiya for a phantom province in Turkey, which could become more relevant in the future, but time will tell. Either way, it is clear that IS is making a number of changes to further bolster its capabilities outside of Iraq and Syria.
For now, you will find below details on what we know about IS’s prior activities in Kashmir. If anyone wants to add anything to the following dossier let me know and I will post it so there is a fuller picture. From oldest to most recent.
—
December 25, 2017:
Part of a broader thread
Online accounts affiliated with so-called Islamic State (IS) have shared a video showing a pledge of allegiance to the group made by “mujahidin in Kashmir”, possibly paving the way for an IS declaration of a new branch there.
— Mina Al-Lami (@Minalami) December 25, 2017
December 26, 2017:
‘Rebel group’ in Indian-occupied Kashmir pledges allegiance to IS – The Express Tribune
January 23, 2018:
Representations of Mahmud of Ghazni in the Islamic State’s texts – Neil Aggarwal, Contemporary South Asia: https://bit.ly/2PXTSYM
February 9, 2018:
An Idea or a Threat? Islamic State Jammu & Kashmir – Amira Jadoon, Combating Terrorism Center: https://bit.ly/2nWjR5i
February 26, 2018:

March 12, 2018:
IS emir in J&K, two others gunned down – Times of India
Annonce de la mort d'Abu-l-Bara al-Kashmiri, qui était apparu en décembre 2017 dans une vidéo où son groupe faisait allégeance à l'#EI au #Cachemire. pic.twitter.com/EftuH6715I
— Romain Caillet (@RomainCaillet) March 13, 2018
March 13, 2018:
The pseudo-IS leader in #Kashmir, Essa Fazli or Abu Yahyā al-Istashadi, reported killed by the Indian army pic.twitter.com/l7vmQwqqdt
— Tore Hamming (@ToreRHamming) March 13, 2018
March 14, 2018:

March 30, 2018:

May 11, 2018:

June 15, 2018:

June 17, 2018:
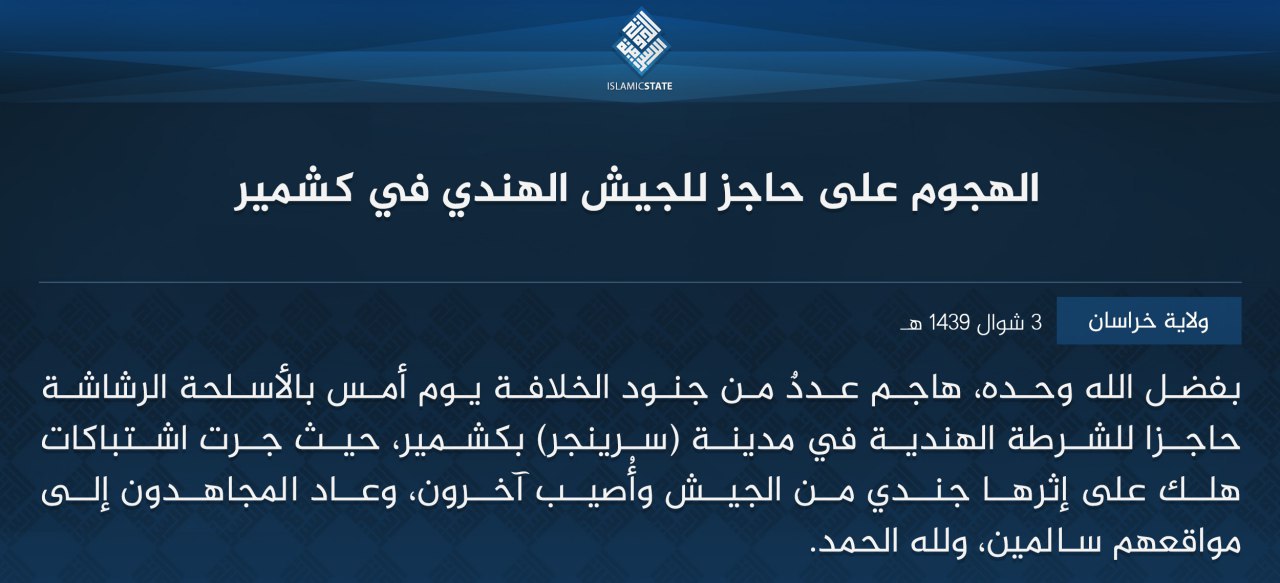

June 22, 2018:
Four ISJK militants killed in Army’s Anantnag operation – The Hindu

July 25, 2018:

August 4, 2018:

August 7, 2018:

August 22, 2018:

September 11, 2018:

September 12, 2018:
Islamic State in Jammu and Kashmir (ISJK) announces the death of its 3rd amir, Abu Anwar al-Kashmiri.
Third amir to be killed in 6 months pic.twitter.com/WSH1MJYcie
— Tore Hamming (@ToreRHamming) September 12, 2018
November 11, 2018:

December 6, 2018:
December 31, 2018:
January 11, 2019:
Thread:
Pro-ISIS graffiti around the Srinagar area of India-held Kashmir. Photos from this week.
1/2 pic.twitter.com/1Ouxjy1s6O
— F. Jeffery (@Natsecjeff) January 11, 2019
May 10, 2019:

