NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Breaking Badr, The New Season: Confirmation of the Badr Organization’s Involvement in Syria
By Phillip Smyth ([email protected])
From May-June, 2013, the Iranian-backed, Iraqi Shia, Badr Organization upped their rhetoric regarding the group’s potential involvement in the Syrian Civil War. This rhetoric resulted in a Hizballah Cavalcade post which attempted to assess whether the group was in fact sending fighters to Syria. Despite their threats, only a few propaganda photos and the death of a possible Badr Organization fighter were available. Thus, the results were inconclusive. Nevertheless, it was still established the group may become more involved in the fighting or that they were preparing a phased approach to publicize Badr’s participation in the fighting.
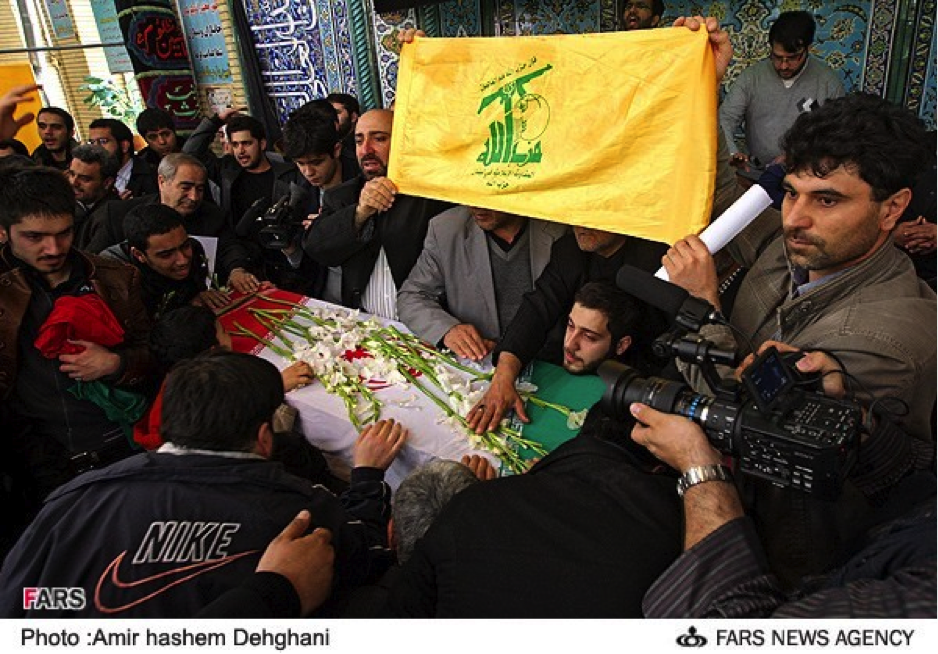
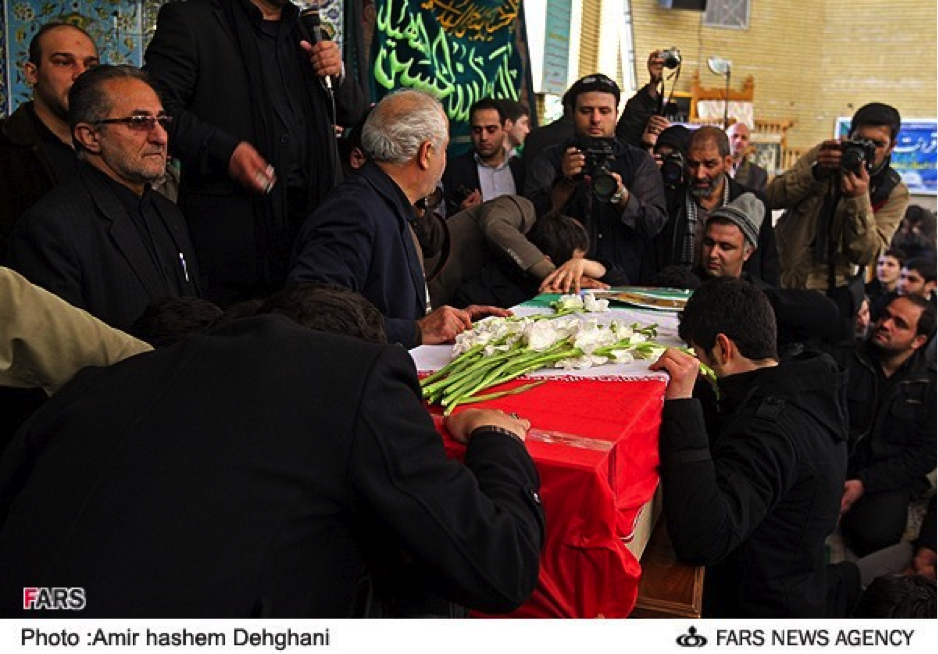
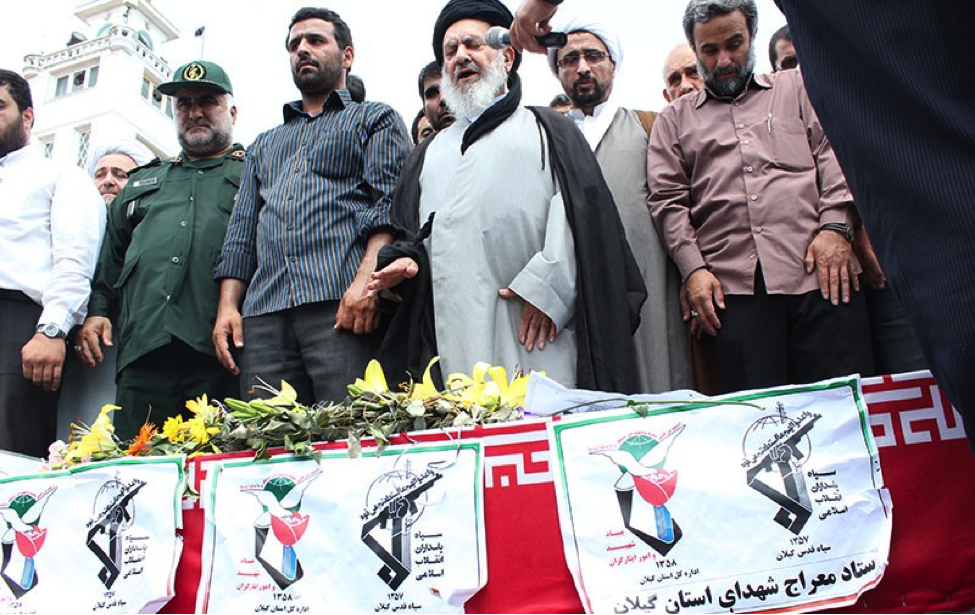
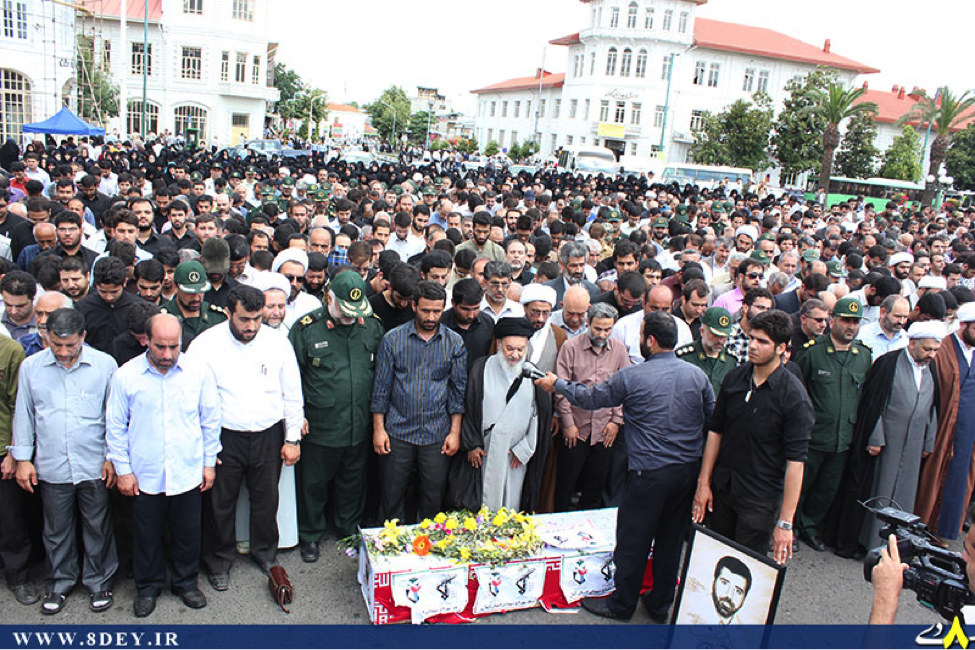
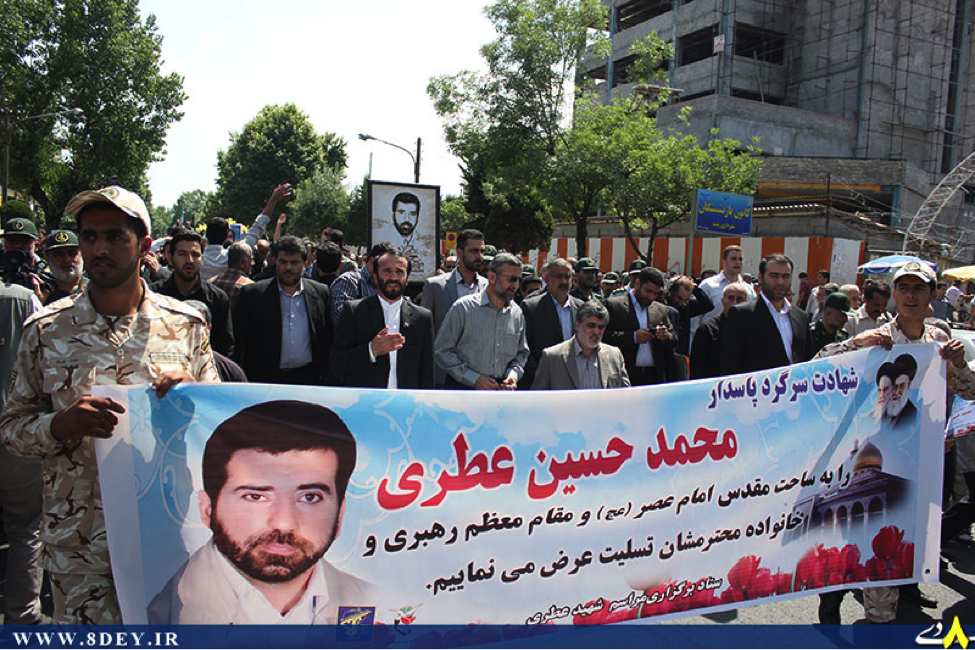
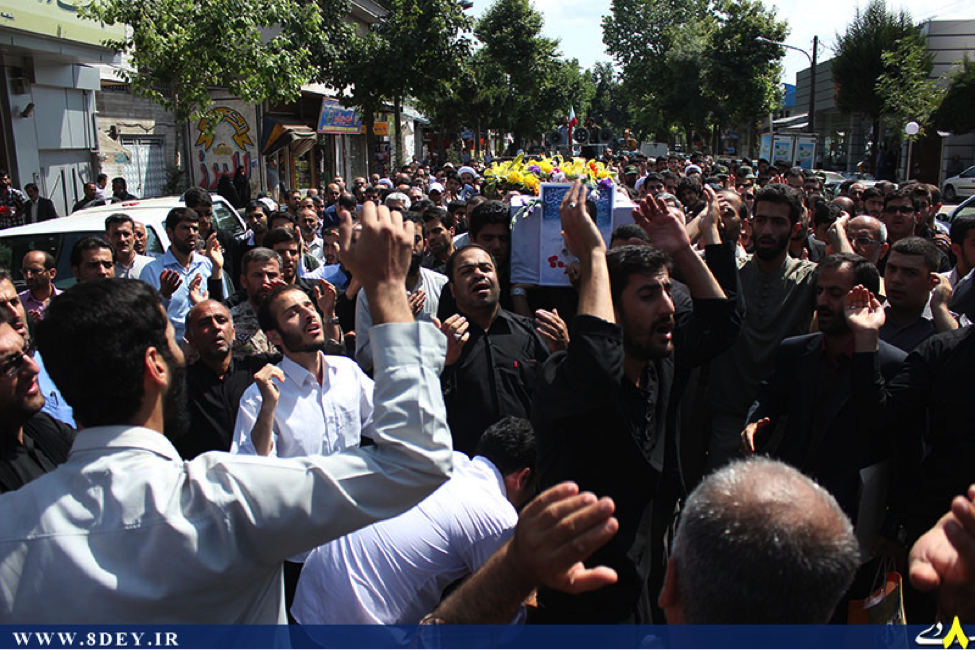
On July 13th, the group announced via Facebook that it had sent “Over 1,500” militiamen to Syria. By late-July, 2013, the Badr Organization’s Military Wing openly announced it had lost members in Syria and held public funerals for them. According to the Badr Organization Military Wing’s Facebook page, one of these funerals was held in Baghdad. The Badr Organization Military Wing also released one photo which supposedly shows some of their members in Syria.
With the death announcement for one of the Badr Organization’s men came the claim he belonged to “Quwet Shahid al-Sadr” (Forces of the Martyr Sadr). The Forces of the Martyr Sadr is not a separate or new militia operating in Syria. Instead, it is simply the name the Badr Organization has given to the group of its fighters operating in Syria.
Regardless, unlike other Iranian-backed organizations which have increased the amount of photos, videos, and social media announcements since the beginning of July, the Badr Organization has only released limited amounts of information about its forces and operations inside Syria.
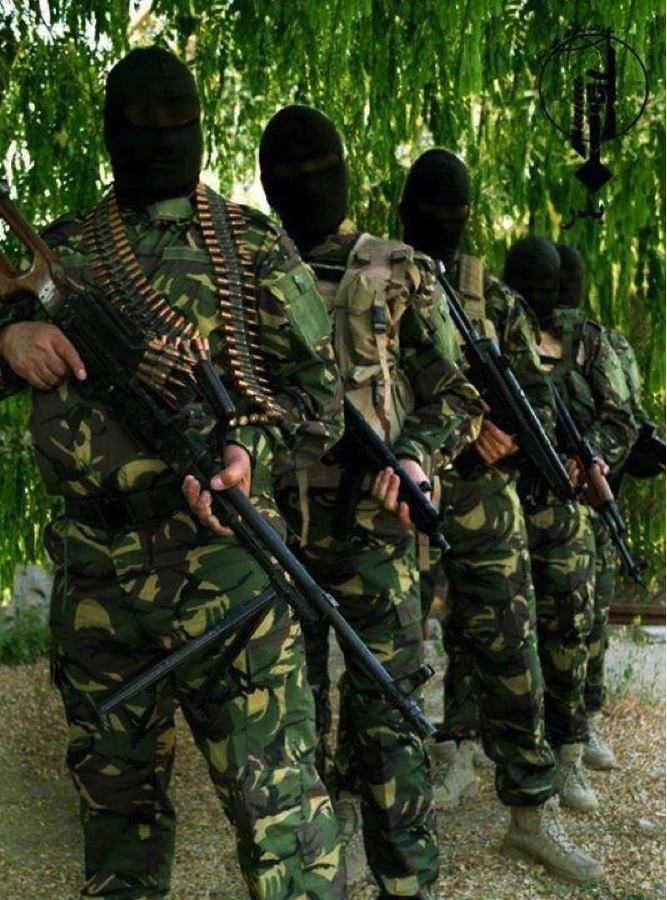

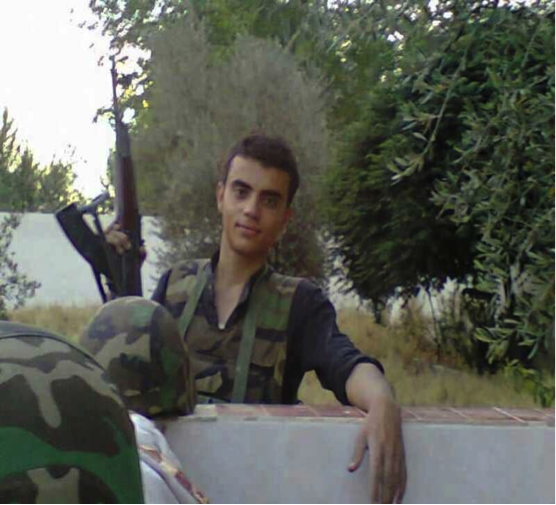
Figure 1: On July 13, 2013, the Badr Organization’s Military Wing posted this photograph with the announcement that over 1500 of its fighters had been sent to Syria.

Figure 2: The Badr Organization’s Military Wing claimed this photo showed members of the group operating in “Defense of Saydah Zaynab”. Some of the fighters are familiar faces and can be seen in propaganda for Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas.
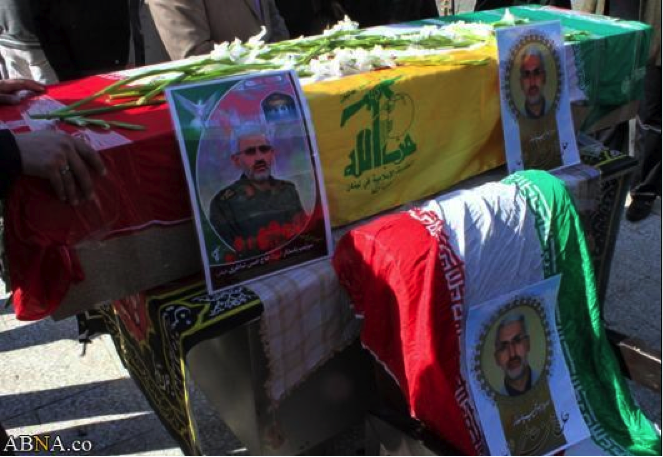
The Badr Organization’s Losses In Syria
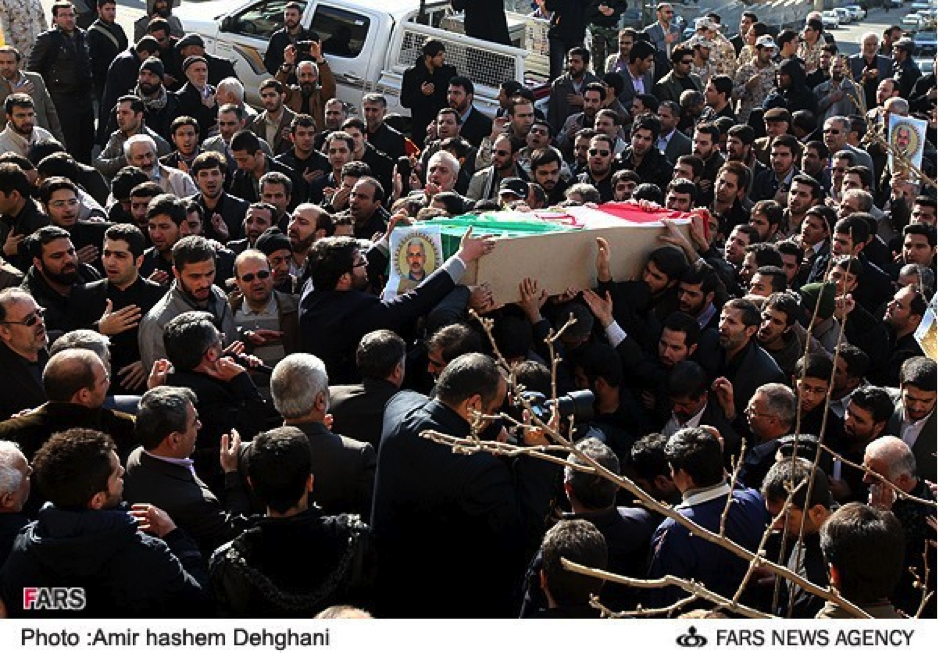
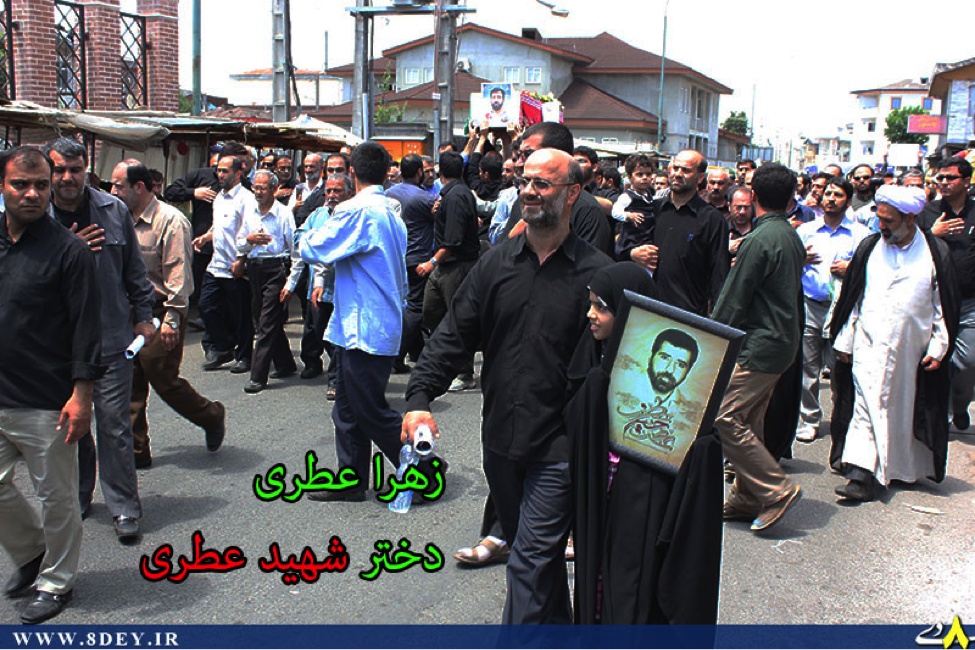
Name: Abu Dhar al-Sa’wdi
Death Announced: July 21, 2013
Notes: Unlike other martyrdom posters which, have only announced the dead as having “Defended Zaynab”, this poster clearly mentions that al-Sa’wdi was killed “in Syria”.

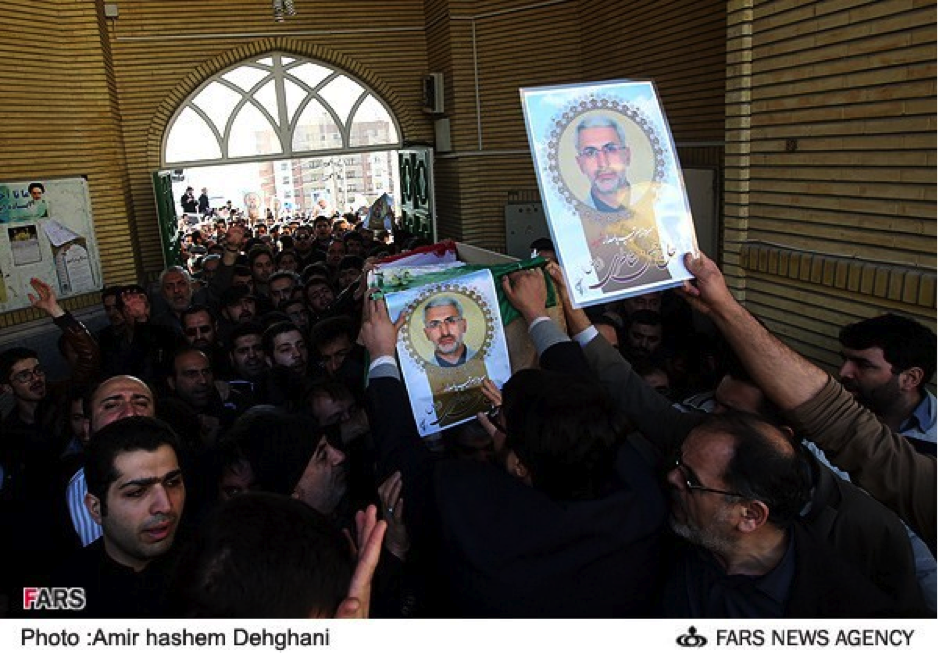
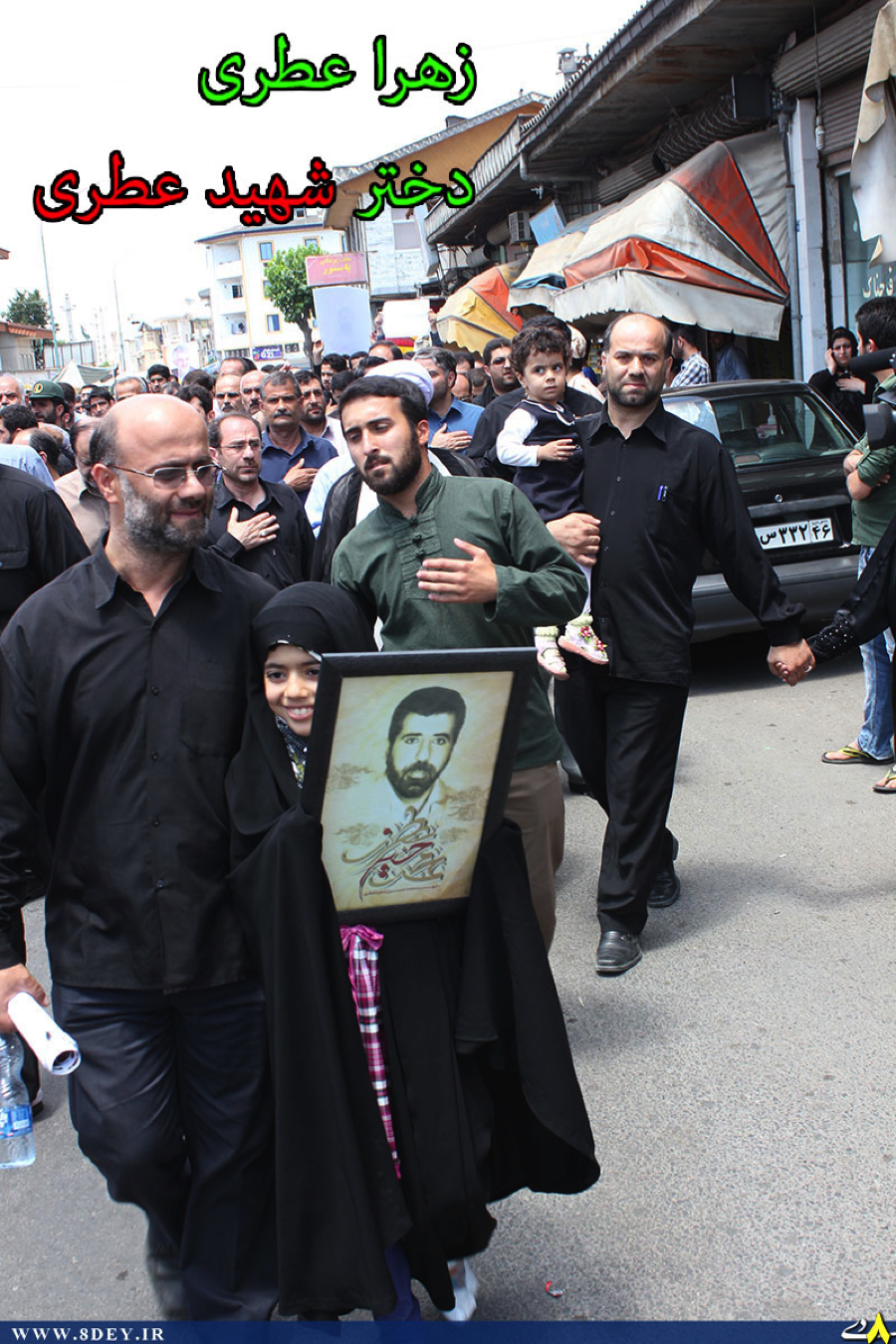
Name: Abu Sajad al-Hawli
Death Announced: July 28, 2013
Notes: Only one photograph has been released on social media of Abu Sajad al-Hawli’s funeral. His death was first announced on the Badr Organization Military Wing’s official Facebook page.

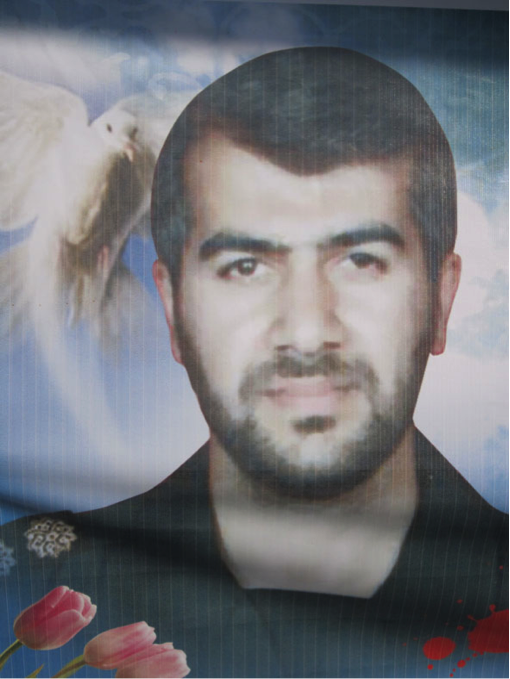
Figure 3: Abu Sajad al-Hawli’s martyrdom poster features the golden dome of the Saydah Zaynab Shrine in the background.
Author: phillsmyth
Hizballah Cavalcade: The Lion of Damascus, and Afghans, and Africans! Oh My!: Fighters From Exotic Locales In Syria’s Shia Militias
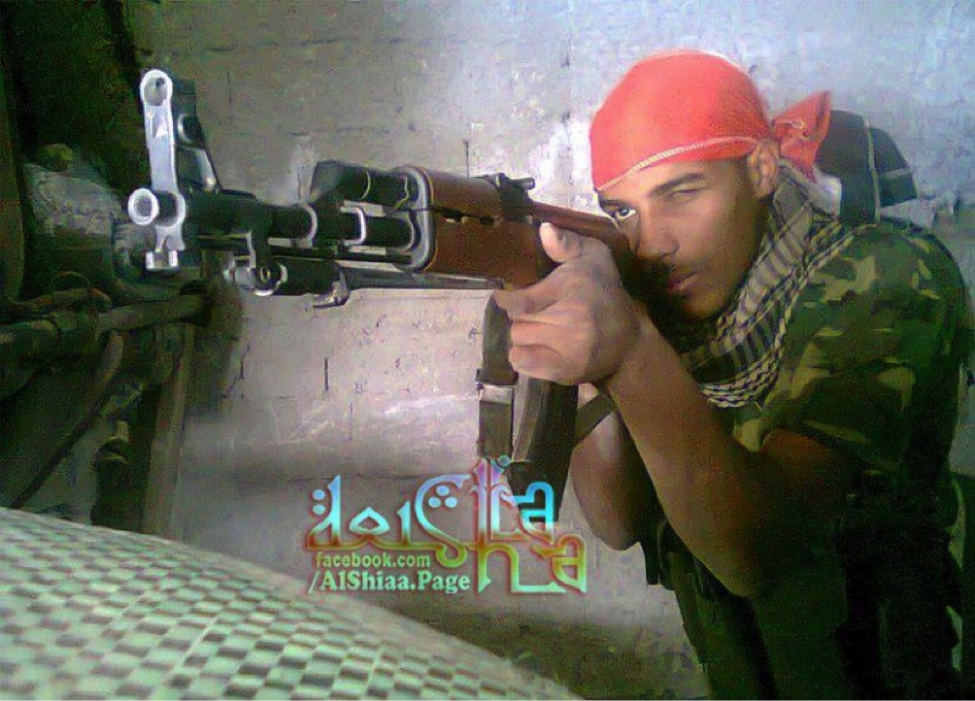 Figure 3: The original photo of Kuwni circulated on Facebook pages managed by pro-LAFA/LAFA administrators.
Called the, “First African martyr” for the Sayyidah Zaynab Shrine, Muhammed Suleiman al-Kuwni was reported dead on the pro-LAFA/LAFA administered “Al-Shiaa” Facebook page on July 26, 2013. One pro-LAFA Facebook page claimed Kuwni was killed due to injuries he suffered during fighting. Interestingly, Kuwni was not reported to be a member of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas or of another announced Shia militia in Syria. Instead he was simply listed as a “Defender of…Zaynab”.
His death was later reported by Iranian media outlets on July 27, 2013.[8] On that same day Iranian media started covering Kuwni’s story, Hizballah’s SouthLebanon.org webpage also included a prayer for him.[9] Most importantly, both Iranian and pro-LAFA Arabic language sources reported Kuwni was originally from the West African state of Côte d`Ivoire, home to almost half a million Shia Muslims.[10]
Stories about Kuwni did not include details on any burial plans. Additionally, more comprehensive information covering his family, or a detailed biography stating where he was originally from in Côte d`Ivoire was also not presented.
Hizballah and Iranian activities have been rather extensive in West Africa.[11] According to the U.S. Department of Treasury, Hizballah has also pieced together an extensive fundraising and recruiting network in Côte d`Ivoire.[12] It is possible Kuwni passed through Hizballah recruitment in Africa, was trained (likely in Lebanon), and was then deployed to fight in Syria. However, his case remains unique and unusual. Iran has primarily utilized Arabic-speaking proxies from Iraq and Lebanese Hizballah to bolster Assad. The addition of African fighters demonstrates Tehran is more open to using proxies from all over the world.
[1] See: https://www.syriaonline.sy/?f=Details&catid=12&pageid=4174.
[2] See: https://www.khaama.com/afghans-involvement-in-syria-war-to-be-investigated-mosazai-1562
[3] See: https://algadtv.com/?p=53142
[4] See: https://freehalab.wordpress.com/2013/06/06/assads-foreign-jihadists-and-mercenaries/
[5] Grant Farr, “The Hazara of Central Afghanistan”, in Barbara Brower and Barbara Rose Johnston (eds.), Disappearing Peoples?: Indigenous Groups and Ethnic Minorities in South and Central Asia, (Walnut Creek, California: Left Coast Press, Inc., 2007), P. 164.
[6] See: https://www.hazara.net/news/news2012/khoemini/khoemini-anniversary-kabul.html. See also: https://www.brianglynwilliams.com/pdfs/20120301114407597.pdf and https://www.csmonitor.com/2005/0824/p06s01-wosc.html.
[7] See: https://www.khaama.com/afghans-involvement-in-syria-war-to-be-investigated-mosazai-1562.
[8] The first Iranian story covering Kuwni’s death was published by Iran’s AhlulBayt News Agency. See: https://www.abna.ir/data.asp?lang=1&id=445548. The same story and published photograph have been reproduced by a number of Iranian news websites. See: https://valieamr.com/Default.aspx?PageName=news&ID=20336&Language=1, https://eslamabadkhabar.ir/shownews.php?idnews=42108, and https://www.fardanews.com/fa/news/276512/%D8%B4%D9%87%D8%A7%D8%AF%D8%AA-%D9%86%D8%AE%D8%B3%D8%AA%DB%8C%D9%86-%D8%A2%D9%81%D8%B1%DB%8C%D9%82%D8%A7%DB%8C%DB%8C-%D9%85%D8%AF%D8%A7%D9%81%D8%B9-%D8%AD%D8%B1%D9%85%D8%B9%DA%A9%D8%B3.
[9] See: https://www.southlebanon.org/?p=79659.
[10] Shireen Hunter, Iran’s Foreign Policy in the Post-Soviet Era: Resisting the New International Order, (Santa Barbara, California: Praeger, 2010), P. 227.
[11] In Nigeria, Hizballah has been involved in maintaining arms caches and the creation of groups pushing Iranian revolutionary ideology. Nigeria even has its own political organization (the Islamic Movement of Nigeria) which was created as a near mirror image of Lebanese Hizballah. See: https://www.islamicmovement.org/ and https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-africa-17908704. See also: https://www.foxnews.com/world/2013/07/12/nigeria-judge-refuses-bail-for-3-lebanese-nigerians-accused-hoarding-hezbollah/ and https://www.haaretz.com/news/features/.premium-1.530327. For some earlier examples (2009-2010) of Iranian diplomatic, cultural, and financial moves in West Africa, see: https://www.irantracker.org/analysis/ahmadinejad-west-africa-iranian-outreach-reveals-tehran-foreign-policy-aug-3-2010-3242. See also: https://www.aei.org/article/foreign-and-defense-policy/regional/subsaharan-africa/forgotten-africa-turns-to-iran-as-a-result-of-western-neglect/.
[12] See: https://www.treasury.gov/press-center/press-releases/Pages/jl1980.aspx and https://www.treasury.gov/press-center/press-releases/Pages/tg149.aspx.
Figure 3: The original photo of Kuwni circulated on Facebook pages managed by pro-LAFA/LAFA administrators.
Called the, “First African martyr” for the Sayyidah Zaynab Shrine, Muhammed Suleiman al-Kuwni was reported dead on the pro-LAFA/LAFA administered “Al-Shiaa” Facebook page on July 26, 2013. One pro-LAFA Facebook page claimed Kuwni was killed due to injuries he suffered during fighting. Interestingly, Kuwni was not reported to be a member of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas or of another announced Shia militia in Syria. Instead he was simply listed as a “Defender of…Zaynab”.
His death was later reported by Iranian media outlets on July 27, 2013.[8] On that same day Iranian media started covering Kuwni’s story, Hizballah’s SouthLebanon.org webpage also included a prayer for him.[9] Most importantly, both Iranian and pro-LAFA Arabic language sources reported Kuwni was originally from the West African state of Côte d`Ivoire, home to almost half a million Shia Muslims.[10]
Stories about Kuwni did not include details on any burial plans. Additionally, more comprehensive information covering his family, or a detailed biography stating where he was originally from in Côte d`Ivoire was also not presented.
Hizballah and Iranian activities have been rather extensive in West Africa.[11] According to the U.S. Department of Treasury, Hizballah has also pieced together an extensive fundraising and recruiting network in Côte d`Ivoire.[12] It is possible Kuwni passed through Hizballah recruitment in Africa, was trained (likely in Lebanon), and was then deployed to fight in Syria. However, his case remains unique and unusual. Iran has primarily utilized Arabic-speaking proxies from Iraq and Lebanese Hizballah to bolster Assad. The addition of African fighters demonstrates Tehran is more open to using proxies from all over the world.
[1] See: https://www.syriaonline.sy/?f=Details&catid=12&pageid=4174.
[2] See: https://www.khaama.com/afghans-involvement-in-syria-war-to-be-investigated-mosazai-1562
[3] See: https://algadtv.com/?p=53142
[4] See: https://freehalab.wordpress.com/2013/06/06/assads-foreign-jihadists-and-mercenaries/
[5] Grant Farr, “The Hazara of Central Afghanistan”, in Barbara Brower and Barbara Rose Johnston (eds.), Disappearing Peoples?: Indigenous Groups and Ethnic Minorities in South and Central Asia, (Walnut Creek, California: Left Coast Press, Inc., 2007), P. 164.
[6] See: https://www.hazara.net/news/news2012/khoemini/khoemini-anniversary-kabul.html. See also: https://www.brianglynwilliams.com/pdfs/20120301114407597.pdf and https://www.csmonitor.com/2005/0824/p06s01-wosc.html.
[7] See: https://www.khaama.com/afghans-involvement-in-syria-war-to-be-investigated-mosazai-1562.
[8] The first Iranian story covering Kuwni’s death was published by Iran’s AhlulBayt News Agency. See: https://www.abna.ir/data.asp?lang=1&id=445548. The same story and published photograph have been reproduced by a number of Iranian news websites. See: https://valieamr.com/Default.aspx?PageName=news&ID=20336&Language=1, https://eslamabadkhabar.ir/shownews.php?idnews=42108, and https://www.fardanews.com/fa/news/276512/%D8%B4%D9%87%D8%A7%D8%AF%D8%AA-%D9%86%D8%AE%D8%B3%D8%AA%DB%8C%D9%86-%D8%A2%D9%81%D8%B1%DB%8C%D9%82%D8%A7%DB%8C%DB%8C-%D9%85%D8%AF%D8%A7%D9%81%D8%B9-%D8%AD%D8%B1%D9%85%D8%B9%DA%A9%D8%B3.
[9] See: https://www.southlebanon.org/?p=79659.
[10] Shireen Hunter, Iran’s Foreign Policy in the Post-Soviet Era: Resisting the New International Order, (Santa Barbara, California: Praeger, 2010), P. 227.
[11] In Nigeria, Hizballah has been involved in maintaining arms caches and the creation of groups pushing Iranian revolutionary ideology. Nigeria even has its own political organization (the Islamic Movement of Nigeria) which was created as a near mirror image of Lebanese Hizballah. See: https://www.islamicmovement.org/ and https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-africa-17908704. See also: https://www.foxnews.com/world/2013/07/12/nigeria-judge-refuses-bail-for-3-lebanese-nigerians-accused-hoarding-hezbollah/ and https://www.haaretz.com/news/features/.premium-1.530327. For some earlier examples (2009-2010) of Iranian diplomatic, cultural, and financial moves in West Africa, see: https://www.irantracker.org/analysis/ahmadinejad-west-africa-iranian-outreach-reveals-tehran-foreign-policy-aug-3-2010-3242. See also: https://www.aei.org/article/foreign-and-defense-policy/regional/subsaharan-africa/forgotten-africa-turns-to-iran-as-a-result-of-western-neglect/.
[12] See: https://www.treasury.gov/press-center/press-releases/Pages/jl1980.aspx and https://www.treasury.gov/press-center/press-releases/Pages/tg149.aspx.
Hizballah Cavalcade: Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir: A New Shia Militia Operating In Aleppo, Syria
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir: A New Shia Militia Operating In Aleppo, Syria
By Phillip Smyth ([email protected])
Click here for a PDF version of this post

Figure 1: The logo for Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir. The group’s name is stylized into a pattern which includes the Lebanese Hizballah/Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps style symbol of a fist gripping an AK-47. (In Gold) “Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir” (‘Ammar Ibn Yasir Brigade) and (in blue) “Al-Muqawama al-Islamiya” (“The Islamic Resistance”).
Since the first announcement of organized Iraqi Shia fighting on behalf of the Assad regime in Syria, their geographic displacement in the country was often matched with their propaganda statements. Both Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas and Liwa’a Zulfiqar have stated on their multitude of social media platforms, videos, and through photographs, that their primary area of operation is Damascus. In particular, the Saydah Zaynab Shrine features heavily in their propaganda and the groups are self-proclaimed “Defenders” of the Shrine.
However, with the creation of Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir (‘Ammar Ibn Yasir Battalion or LAIY), the “Defenders of the Saydah Zaynab Shrine” narrative is now encompassing an organization which—according to its statements and other sources—does not operate in Damascus or directly maintain a presence at the Saydah Zaynab Shrine. In fact, LAIY advertises the fact that it is operating in the areas surrounding the northern Syrian city of Aleppo. In videos released by the group onto YouTube, the films’ titles proclaim LAIY fighters are present in rural sections of Aleppo. While this could not be independently confirmed, it would appear the group is attempting to cast another narrative that LAIY is the pro-Assad Shia militia organization which handles combat operations in the Aleppo area.
The fact the group is announcing it is operating in Aleppo is very important when assessing the manner Iranian-backed Shia militias have been utilized in Syria. Initially, most analysts and journalists have acknowledged these groups have fought around the Saydah Zaynab Shrine in Damascus or, as with Lebanese Hizballah, fought at Qusayr. This represents a major departure from the accepted line and shows that Iraqi-staffed Shia militias are likely operating in other urban areas throughout the country.
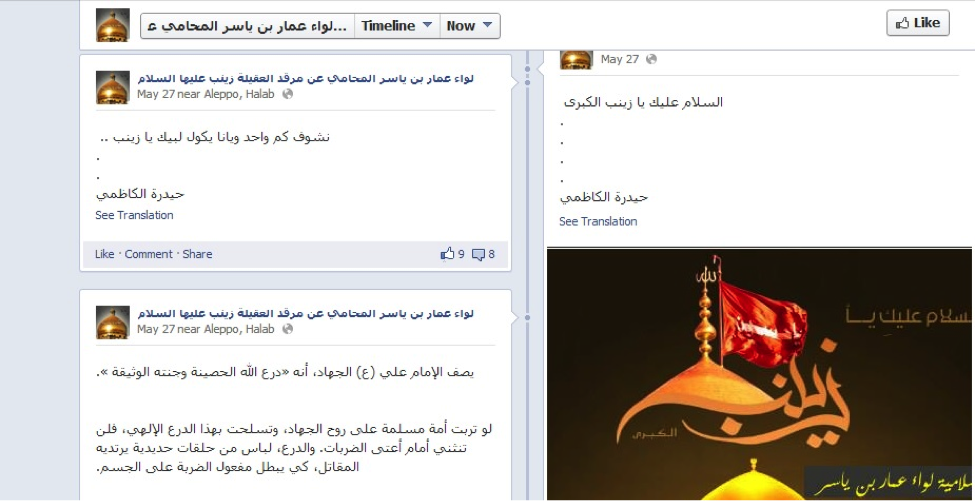
Figure 2: Since the creation of LAIY’s official Facebook page, the group has made attempts to demonstrate they are posting statuses from Aleppo.
Initially, LAIY announced their presence to the world through the creation of a Facebook page made at the end of May, 2013. The page only posted basic status updates including quotes from Lebanese Hizballah General Secretary and in a blatant display of their loyalty to Iran, postings of two photographs featuring Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. The caption for one of the photographs read, “Labayka ya Khamenei” (“We are here for you, O Khamenei”). Other early photographs emphasized the same “Defenders of the Saydah Zaynab Shrine” narrative first promoted by Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas and Lebanese Hizballah.
The logic behind the continuance of the “Defenders of the Saydah Zaynab Shrine” narrative for a group not directly defending it, is likely a way to express that despite LAIY not directly defending the shrine, the very fact they are countering anti-Assad forces in other parts of Syria helps save the shrine. Extending the narrative in this way allows for later potential announcements addressing the presence of other pro-Assad Shia militia in other areas of Syria. The rhetoric also acts and as a blanket explanation for why the groups’ directly cooperate and back the regime of Bashar al-Assad. For LAIY’s messaging campaign, it is key to demonstrate that backing Assad on all fronts means the Saydah Zaynab Shrine and other Shia religious structures will be protected.
Off of the internet, LAIY made its presence known in the same way Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada did during the Spring of 2013; Via extravagant funeral cum demonstrations for fallen members of the organization. On June 4, a large funeral in Iraq’s Maysan was held for seven members of LAIY. Like Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada, at the group funeral, representatives from the organization announced they would defend shrines, “All over the world”.[1]
LAIY has also exhibited a number of advanced messaging strategies. When the organization was announced, it already had its own song (posted below), a symbol, fighters dressed in similar combat fatigues, and a clear messaging strategy to address its presence in Syria.
LAIY’s Name
Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir takes its name from ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir. Described by historian Matti Moosa as, “one of Ali’s [considered by Shia to be the Islamic prophet Muhammed’s true successor for leadership of the Muslim community] most zealous companions and champions”, Yasir is revered by Shia for his loyalty.[2]
The group’s name also references the tomb of ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir which was located in Raqqa, Syria. The tomb was blown-up by Sunni Islamist rebels forces in March, 2013. These forces also recorded the destruction of the tomb and distributed their video online.[3] The video then made its rounds on pro-Assad media outlets. In terms of narrative development, the adoption of the name of a destroyed Shia shrine in Syria further underlines the line the group previously established as, “Defenders of shrines”.
Nevertheless, there have been no specific mentions of the destruction of ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir’s tomb via the group’s statements to the media or through their social media presence.
LAIY’s complete name is, Al-Muqawamah al-Islamiya fi Iraq Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir Hizballah al-Nujaba’ (The Islamic Resistance In Iraq ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir Brigade Hizballah Movement of the Outstanding). Adding further complication to the group, LAIY claims to be a part of Harakat Hizballah al-Nujaba’ or Harakat al-Nujaba’ (The Hizballah Movement of the Outstanding). This group, in and of itself, is also new. Harakat Hizballah al-Nujaba’ draws its name from the regularly used “Hizballah” term, a name found and utilized by a multitude of Iranian-backed organizations. It has also added that it is a “Harakat” or “movement”, most likely a way to appear as if it has greater numbers. The addition of the term, “al-Nujaba’” (plural for “The Outstanding”) references a term sometimes used in relation to the return of Imam al-Mahdi (for Shia, the Mahdi will return in a messianic form and establish a truly just earthly regime).[4]
LAIY’s Links, & Ideology
Based on the large amount of imagery, videos, and direct statements praising Iran’s Supreme Leader, Ayatollah Khamenei and repeated insistences where the group has said it is, “at Khamenei’s service”, LAIY does not hide its allegiance to Iranian leadership and ideology. The utilization of the exact “Defense of the Saydah Zaynab Shrine” narrative, honed by Lebanese Hizballah, Iran, and Iran’s many Iraqi Shia proxies—Many of whom have contributed fighters to the battle in Syria—also demonstrates a mirroring of larger Iranian strategies.
Sheikh Akram al-Kaabi, a founder and leader of Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq, an Iranian-backed organization which has lost members in Syria, has also featured prominently in LAIY propaganda. Al-Kaabi has described as a “Leader” by the group’s Facebook page and on posters the group has issued. The link to Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq further suggests LAIY and Harakat Hizballah al-Nujaba’ may be front groups for other existing Iranian-backed Iraqi Shia parties. Additionally, imagery used for martyrdom posters matches those found with Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq. These posters normally feature Grand Ayatollah Muhammed Sadiq al-Sadr and Iranian Supreme Leader, Grand Ayatollah Khamenei with a dark background or one featuring the Saydah Zaynab Shrine (see: Hizballah Cavalcade’s Roundup of Iraqi’s Killed in Syria, Parts 1, 2, and 3).
The utilization of the phrase, “Islamic Resistance” has also been a hallmark for Iranian-created organizations and has made a strong presence among the multitude of groups under Tehran’s guidance. Lebanese Hizballah calls itself, “Al-muqawama al-islamiya fi lubnan” (“The Islamic Resistance in Lebanon”).[5] Both Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq and Kata’ib Hizballah have characterized themselves as the “Islamic Resistance in Iraq”.[6]
Hizballah Cavalcade: The Songs of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas: Militant Iraqi Shia Music & Syria
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
The Songs of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas: Militant Iraqi Shia Music & Syria
By Phillip Smyth ([email protected])
Click here for a PDF version of this post
Remember the war against Franco?
That’s the kind where each of us belongs.
Though he may have won all the battles,
We had all the good songs.
– Tom Lehrer, “The Folk Song Army”, 1965.
*Note: The author has counted at least thirty different songs available online which have been produced to praise LAFA. Most of these songs were not included due to their lack of popularity in LAFA social media circles.
When journalist Nicholas Blanford first announced Iraqi Shia were fighting alongside the forces of Syrian president Bashar al-Assad, his main source for this assessment was a music video.[1] From a period extending from fall 2012-summer 2013, Shia Islamist organizations operating in Syria have released more music videos and have been actively using them in a complex messaging strategy.
The utilization of musical propaganda has been a key propaganda strategy used by radical Shia Islamist organizations.[2] Lebanese Hizballah has employed a number of bands to sing songs promoting the group’s narrative since the 1980s. In 2008, the Iraqi government found the songs made for Muqtada al-Sadr so threatening, they banned them.[3]
Due to Shia Islamist involvement in the Syrian Civil War, Iraqi Shia who favor Muqtada al-Sadr and pro-Iranian Shia parties, have produced a wide variety of songs praising Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas (LAFA). These songs are often overtly sectarian and offer blatant threats against the Syrian rebels.
The Iraqi-produced music videos, created to honor Iranian-backed Shia fighters attached to LAFA, also occupy a strange ideological gray-area. The singers often praise and or have praised Muqtada al-Sadr and the Liwa’a al-Yum al-Mawud (the Promised Day Brigade). However, Sadr has not publicly supported Shia militiamen fighting in Syria.[4] Some of the same musicians who sing for LAFA, have also backed organizations which have fought Sadr, namely Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq (AAH).[5]
Other Iraqi influences are quite extensive in newly made music about LAFA, including the musical rhythm styles. Demonstrating that these songs are aimed at an Iraqi audience, they are often sung in the Iraqi dialect of Arabic. All of the singers and songwriters who have made these songs have also had extensive background experience singing for Shia Islamist organizations, performing religious songs, and have gained the majority of their fans from their online presence.

Figure 1: ‘Ali al-Muwali poses for a picture which includes the Saydah Zaynab shrine.
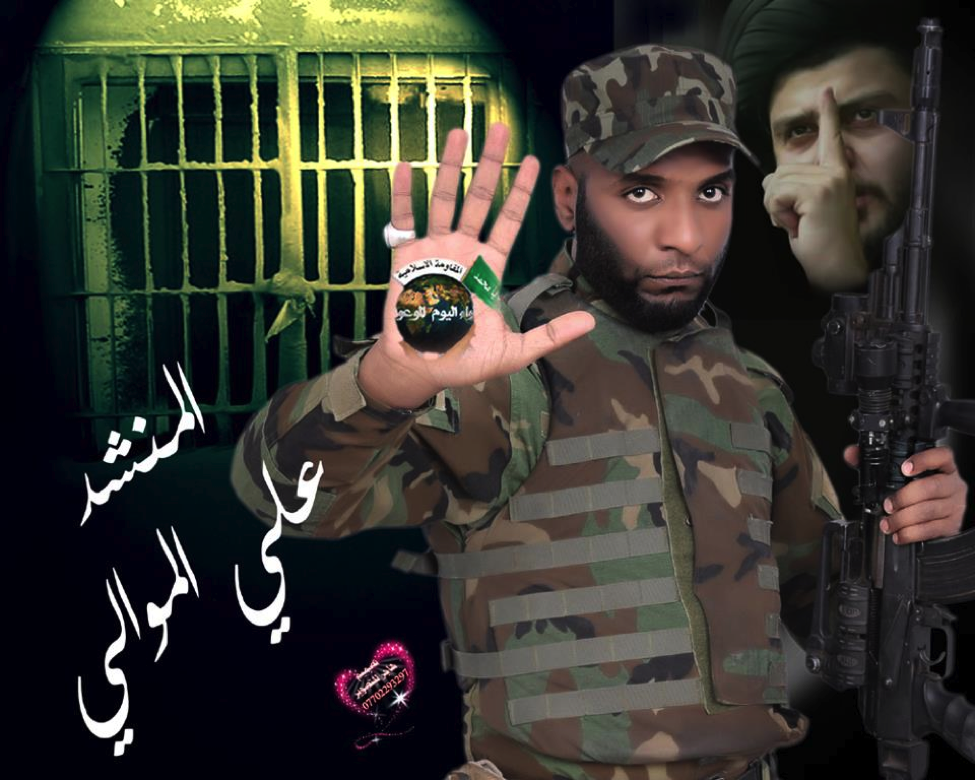

Figure 2: Muwali has not hidden his links to Liwa’a al-Yum al-Mawud. In his left hand, the group’s logo is visible.
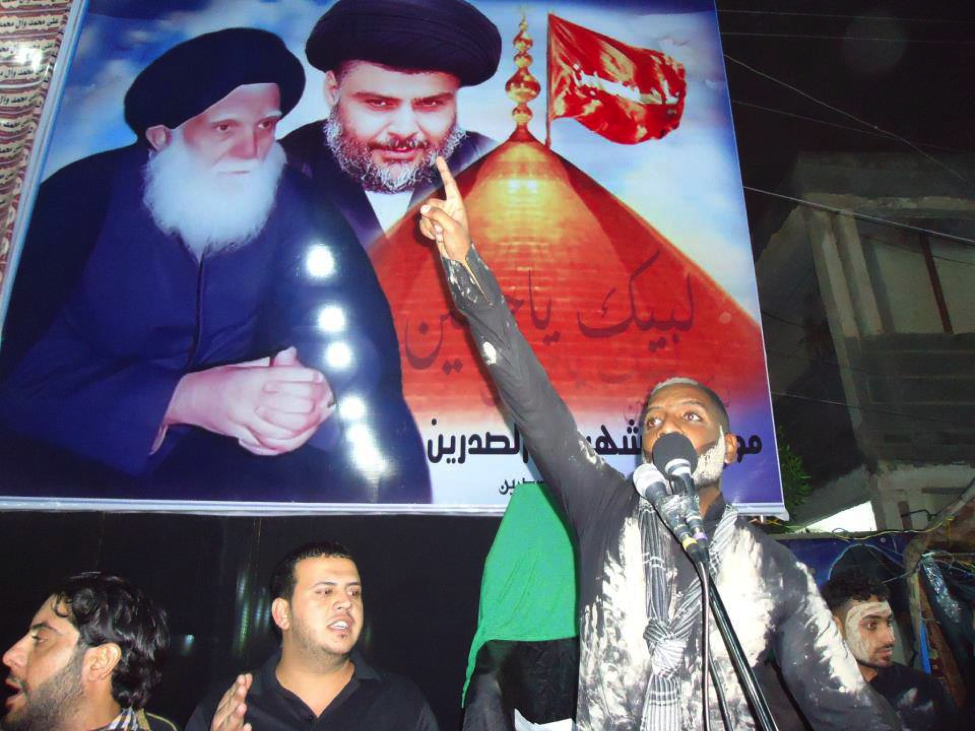

Figure 3: Muwali singing to Sadr supporters.
Released on September 5, 2012, the music video which first burst onto the scene carrying the message of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas was “Ya Zaynab” by ‘Ali al-Muwali. While the initial music video did not receive as much attention in pro-LAFA social media circles, a more popular edit of the song with a new music video quickly became well-known. Appearing on YouTube at the end of December, the new video and song soon became the anthem for LAFA. It is clear from the song’s lyrics, music video, and time of release that its creation was timed to coincide with further announcements about the group’s existence.
While the initial music video was less popular than the re-edited LAFA video, the song clearly promoted a militant message. Prior to singing about LAFA, singer of “Ya Zaynab”, ‘Ali al-Muwali had made a number of songs dedicated to praising attacks against U.S. and Coalition troops in Iraq. These songs appeared to be created for Liwa’a al-Yum al-Mawud. Muwali’s personal Facebook page includes two “Likes” for Liwa’a al-Yum al-Mawud Facebook pages.
Another early song and music video utilized by Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas first appeared online in early February 2013. The song emerged on YouTube and in forums under a variety of titles. However, the primary title it was given was, “Liwa’a Abu Fadl in Syria Third Release”. It’s probable the singers and songwriters came from the same groups found in other videos on this post.
As with LAFA’s edited music video for “Ya Zaynab”, this song’s video showed footage of LAFA fighters engaged in combat and samples from a film about the Battle of Karbala. The song also featured threats against the Free Syrian Army and overt messages appealing to Shia-identity. “Liwa’a Abu Fadl in Syria Third Release” was later used as background music in a video showing members of Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada inspecting dead Syrian rebels (see the first video on the post).
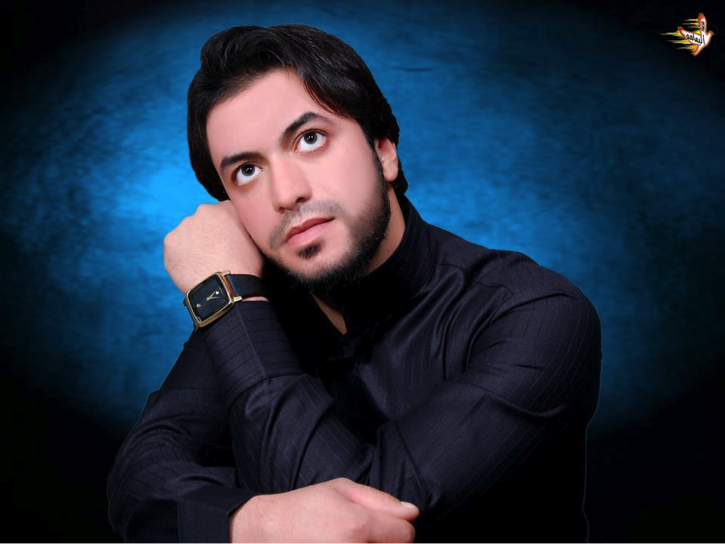

Figure 4: Pro-LAFA Iraqi singer, Muhammed Abu ‘Azrael al-Karbalai.
Between April-May, 2013 a number of songs were released by Iraqis praising the Abu Fadl al-Abbas Brigades. “Dedicated to the Abu Fadl al-Abbas Shia Brigade”, was released in mid-May by Pro-Muqtada al-Sadr singer Muhammed Abu ‘Azrael al-Karbalai on Iraqi Shia forums.[6] It warned the rebel Free Syrian Army, telling them “Do not cross the line…We will silence you” and also praised the Syrian army, “O Syrian army, focus and show them what you can do” The song also expressed fears of what would happen if the forces of Bashar al-Assad did not win, saying, “Oh, [Syrian] army, God knows what will happen if you fail!”
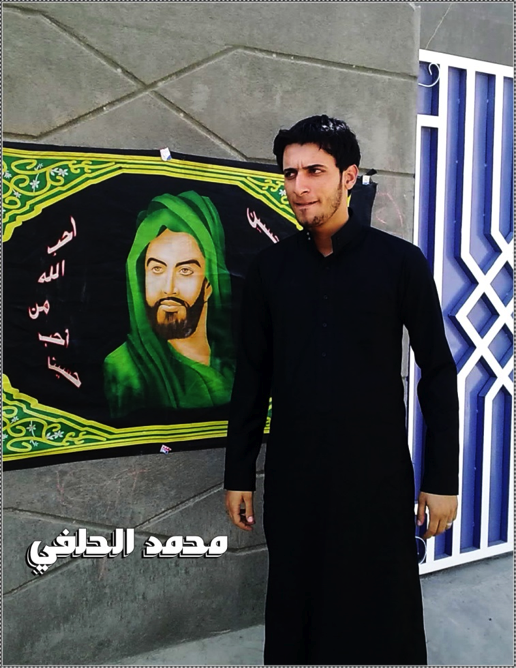

Figure 5: Muhammed Helfi stands in front of a picture of Husayn, one of the most important figures in Shia Islam.
Another LAFA song, performed by Muhammed al-Helfi was called, “Zealous to Defend Saydah Zaynab”. Helfi, an Iraqi Shia and pro-Sadr singer (he has also performed with pro-Sadrist singer Laith al-Ruba’ie) adopted Shia identity messaging and delved into conspiracy narratives to explain the war in Syria. In the song, al-Helfi rehashes claims of a “Saudi and Jewish” conspiracy against the Shia. The narrative presented matches those produced by LAFA and other Iranian-backed organizations. “We are all for Zaynab”, Helfi sings, “we know the difference between precious and cheap…We get rid of the cheap…We Shia know our worth.”

Figure 6: Abbas al-Khazali.
Another Iraqi-produced song was dedicated specifically to Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas on April 6. The song threatens Syrian rebels and praises Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas. In fact, LAFA’s Sung by Abbas al-Khazali, the music video shows Shia fighters dressed in similar combat gear as LAFA and armed with M16A2 rifles. There is also a shot of these Shia fighter-cum-singers capturing and abusing what can be presumably Sunni Islamist or Free Syrian Army fighters. The theme of capturing and abusing “Enemies of Shi’ism” has been a prevalent theme in songs released by Iraqi singers since April.
On April 19th, a pro-LAFA song was posted to YouTube. Much of the footage used showed LAFA operations, but when the music video begins, the main messaging thrust is one of Shia power over Sunni enemies. Men (assumedly Shia fighters) storm a building and forcibly detain these enemies. Later in the song, the singer calls Saudi Salafist Sheikh Adnan Al Aroor, “Black” (i.e. holding a black ideology).

Figure 7: An Ahmed Fatimi CD cover.
Ahmed Fatimi, another Iraqi singer, also sang a song in praise of the “Defenders of Zaynab”. The music video utilizes photographs of LAFA members and commanders first put online between the fall of 2012-spring 2013.

Figure 8: Ali al-Delfi and Ahmed al-Sa’adi pose on the cover of one of their 2012 CDs.
One of the first LAFA songs to be released in 2013 (March 5) was made by Ali al-Delfi and Ahmed al-Sa’adi. The song immediately became popular on forums and Facebook pages devoted to LAFA and other Iranian-backed Shia groups in Iraq. Demonstrating the song’s reach, in of the few pieces of video footage taken of LAFA fighters in Syria, the song was played on one of the fighter’s phones while LAFA was setting-up a sniper position.
On May 5, 2013, Ali al-Delfi and Ahmed al-Sa’adi released a song entitled, “Operetta for the Righteous”. The song was dedicated to the Iranian-backed Iraqi group, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq (AAH). Pointing to closer links between some Iraqi singers and the organizations they sing about the fact that new
Hizballah Cavalcade: Breaking Badr: Is Iraq’s Badr Organization Operating In Syria?
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Breaking Badr: Is Iraq’s Badr Organization Operating In Syria?
By Phillip Smyth ([email protected])
Click here for a PDF version of this post
Due to many public funerals, a number of Iranian-backed Iraqi organizations (Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq, Kata’ib Hizballah, and Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada stand as prime examples) have been identified as supplying combatants to fight in support of the regime of Bashar al-Assad in Syria. However, the Badr Organization, an Iraqi group which has pledged its loyalty to Tehran, was absent from announcements involving Iraqis killed in Syria and has been rather murky on whether it is fighting in Syria.

Figure 1: The Badr Organization Military Wing’s logo. Note its similarity to Lebanese Hizballah’s, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq’s, Kata’ib Hizballah’s and the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps’ logos
In February, 2013, Hadi al-Amiri, leader of Iraq’s Badr Organization, said Turkey and Qatar were supplying Al Qa’ida and that this was a declaration of war against Iraq.[1] During a June 21, 2013 interview with Reuters, Amiri said the group was contemplating intervening in Syria and could not, “sit idle while the Shi’ites are being attacked”. [2] Regardless, after assessing posted material issued by the Badr Organization’s social media webpages, it is becoming clear the group may actually be involved in the fighting in Syria.
Beginning life as the Badr Brigade, the militia for the Supreme Council for the Islamic Revolution in Iraq (SCIRI), the Badr Organization split from SCIRI and became its own political group.[3] In 2006, the Council on Foreign Relations reported the Badr Organization had upwards of 10,000 militiamen.[4]
Before and after the split with SCIRI, the Badr Organization received heavy funding, training, and equipment from Iran.[5] The group is also unabashed about its close links with Iran, especially Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, and Iranian proxy groups.
Despite material which affirms the group supports the actions of Lebanese Hizballah in Syria, the official Facebook page for the Badr Organization makes no mention that its militiamen may be also operating in Syria. Nevertheless, there are hints of involvement on the group’s page for the Badr Organization Military Wing, the Badr Organization’s militia. Throughout the Spring of 2013, the Badr Organization increased the level of supportive rhetoric for Lebanese Hizballah, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq, Kata’ib Hizballah, and Iran’s efforts in Syria. A June 21, 2013 photo’s caption said the, “Badr Military Wing will defend Zaynab to the last mujahid”.
Figure 2: Photo from the Badr Organization Military Wing’s Facebook saying the group will “Defend the Zaynab Shrine to the last holy warrior [mujahid]”.
Earlier, on April 22, 2013, The Badr Organization Military Wing produced and uploaded a song to YouTube. The song’s discription said it was, “A message from Badr to the unjust”and included the lyrics, “We will issue a death sentence against the Free Syrian Army (Jaysh al-Hurr) and no one will be able to defeat us.” The only images present during the music were those of a fighter armed with an RPG-7 in front of the Saydah Zaynab Shrine, the logo for the Badr Organization Military Wing, and the logo for the Badr Organization.
From May 5-9, 2013, a few photographs depicting Badr Organization fighters showing their “Soliderity” with members of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas (LAFA) appeared on various pro-LAFA, Badr Organization, and pro-Lebanese Hizballah websites. LAFA has acted as the main front for pro-Iranian fighters inside Syria.
Nevertheless, Badr’s symbols are not a pervasive presence on LAFA or Liwa’a Zulfiqar’s social media websites. Since the group reportedly did not suffer any killed in Syria before June, coverage of the organization’s possible involvement with LAFA or Liwa’a Zulfiqar was muted. The group’s social media posts appeared to do little more than offer visible support for the actions of other pro-Iranian Iraqi groups operating in Syria.

Figure 3: The photo was first posted on the Badr Organization Military Wing’s official and mirror Facebook pages. The photo shows Badr militiamen armed with Heckler and Koch MP5 submachine guns (though, it’s possible these are Iranian copies) and AK-47 style rifles.
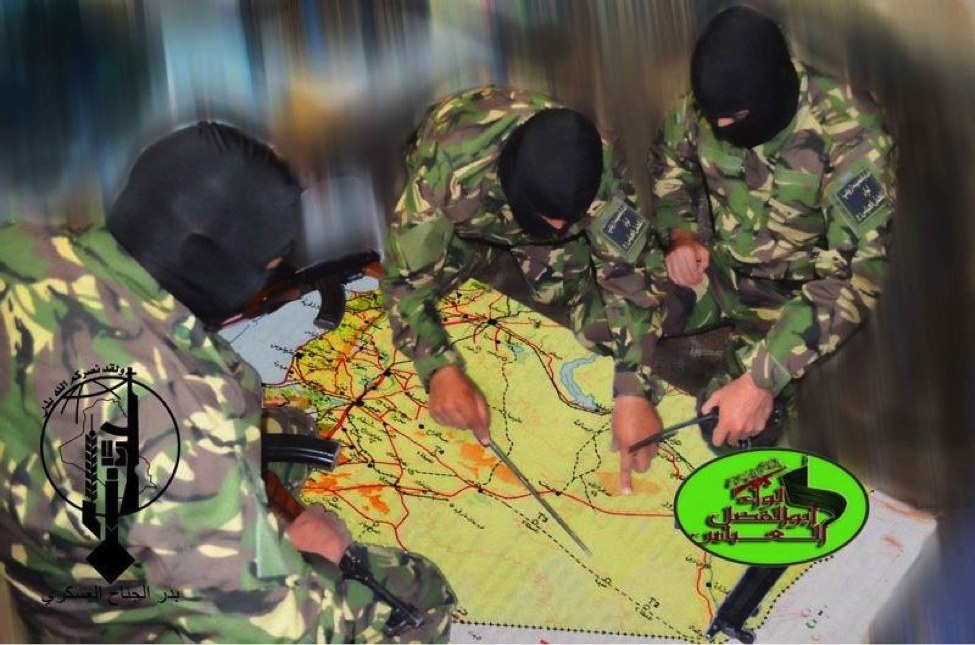

Figure 4: A photo first posted on Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas’s Facebook page claims to show Badr Organization militiamen studying a map of Syria. Most captions to go along with this photo claimed it was a photo to express solidarity with the defenders of the Zaynab Shrine.
However, the Badr Organization’s public statements regarding Syria grew louder after May 20, 2013. Immediately following attacks on buses carrying Iranian pilgrims near the Iraqi city of Tikrit, the Badr Organization Military Wing announced they would adopt a more threatening posture. [6] The statement said the “Plotters” of the attacks were the United States, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and “The Zionist Entity” (Israel), and that they would face a swift retaliation. It is important to note that the same compendium of enemies is blamed by Iran and its proxies operating in Syria for being behind forces opposing the regime of Bashar al-Assad. Interestingly, notwithstanding the other, often more horrific bombings Iraqi Shia suffered, and other attacks launched by Sunni Islamists against Shia in Iraq, the Badr Organization appeared to draw a redline with the attack on the Iranians. It is also possible the targeted bus was not carrying Iranian pilgrims as reported, but Iranian advisors or fighters, which would further inflame a pro-Iranian proxy group like Badr.[7]
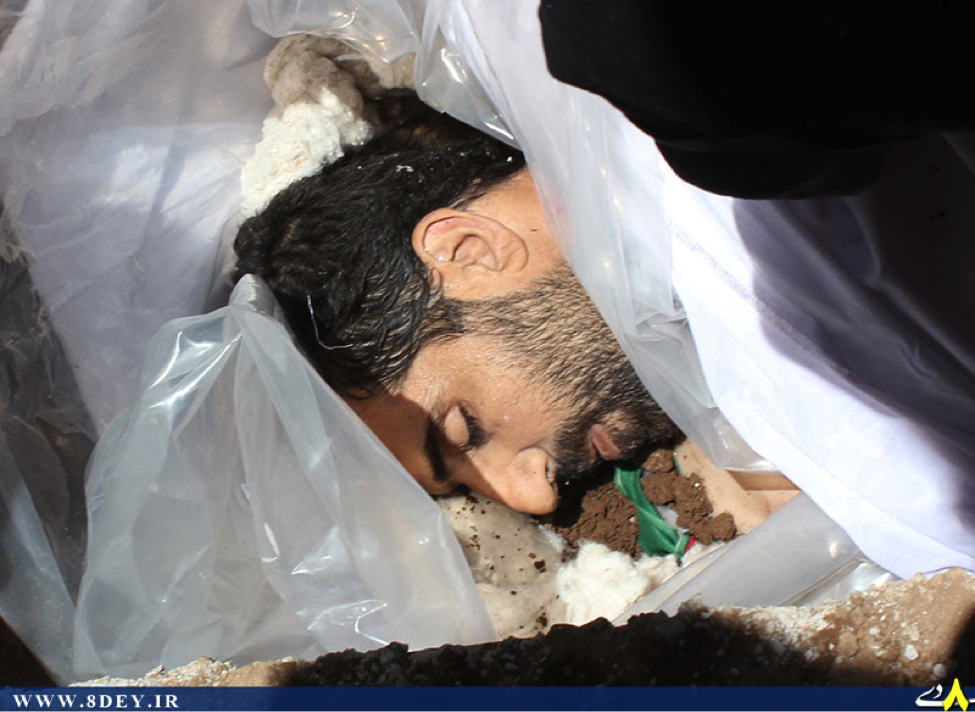
Based on the fact that other smaller Iranian-backed Iraqi Shia groups have sent fighters into Syria, it is possible the Badr Organization has also sent members. This possibility gained added credence on June 17, 2013 when the Badr Organization Military Wing announced a member had been killed “Defending the Saydah Zaynab Shrine”. Despite this announcement, it is still unclear whether the Badr Organization has committed sizable amounts of fighting men to the war in Syria.

Figure 5: May 20, 2013 Badr statement threatening Saudi Arabia, Qatar, “The Zionist entity”, and the U.S.
The Badr Organization’s First Martyr In Syria?
Name: Yasin Muhammed al-Zayn (A.K.A. Hadi)
Death Announced: June 17, 2013. (He was declared killed on June 17, 2013). The Badr Organization Military Wing’s Facebook declared his death on June 18, 2013.
Notes: Only on the Badr Organization Military Wing’s official page was al-Zayn claimed as a member of the Badr Organization. On his martyrdom poster, it was claimed al-Zayn was killed in the Zayn al-‘Abideen neighborhood of Damascus while “Defending the Saydah Zaynab Shrine”. Other pro-Assad/pro-Iranian backed Shia organization Facebook pages did not mention his affiliation with the Badr Organization. Additionally, no footage of al-Zayn’s funeral could be located. A personal martyrdom page was also created (on June 18, 2013) for al-Zayn.[8] On the page, no mention of any Badr affiliations was made. Interestingly, his death was not claimed by Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas or Liwa’a Zulfiqar, the two groups Iraqi Shia have fought for in Syria.
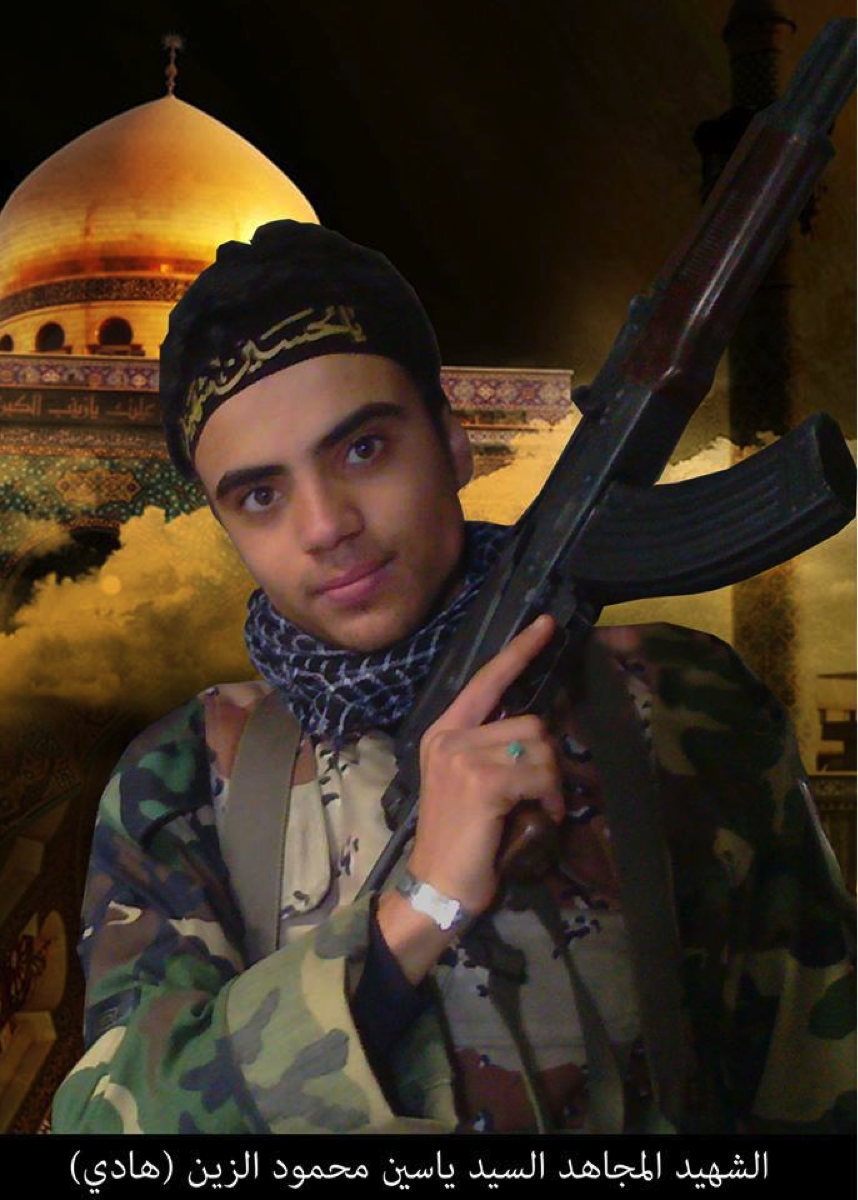


Figure 6: The Saydah Zanab Shrine’s golden dome features prominently in the background. No logos for the Badr Organization Military Wing were present on the martyrdom poster.



The Badr Organization’s Imagry For Syria
The Badr Organization Military Wing has created a number of provocative online photos dealing with events in Syria. When compared to other Iranian proxies, they have exhibited the most blatant links to Iran’s Supreme Leader. It is possible the group may be setting-up a religious pretext for their [future] involvement in Syria by continually showing pictures of Khamenei. Khamenei had already given religious sanction for Shia fighters to engage in battle in Syria.[9]

Figure 7: “Min Baghdad – al-Jadriat Labayk ya Zaynab” (“From Baghdad – al-Jadriya [a Baghdad neighborhood] We are here for you, O Zaynab”).

Figure 8: A photo published by the Badr Organization Military Wing showing members of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas. The image is attempting to convey that the Badr Organization has members within LAFA.
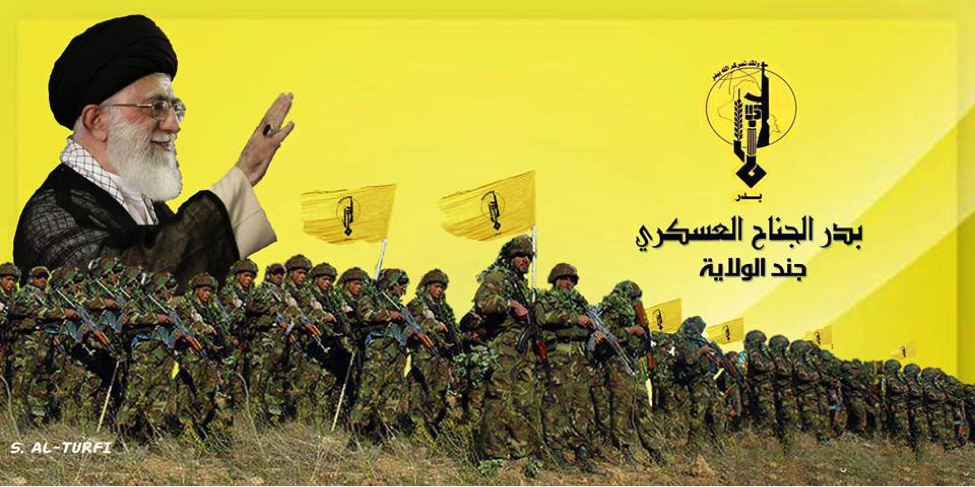

Figure 9: Iran’s Supreme Leader waves and smiles as Badr Organization militiamen stand below him.

Figure 10: This photo appeared on two pro-Badr Organization Military Wing pages on Facebook. Intriguingly, the photo is extremely blatant about the connection (logos from left to right) Asaib Ahl al-Haq, Lebanese Hizballah, the Badr Organization, the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps, and Kata’ib Hizballah share. Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei looks out from the globe.

Figure 11: Another online poster featuring the Badr Organization Military Wing and Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei. The background is a photo of Lebanese Hizballah marching with an added golden hue. [1] Michael Knights, “Syrian and Iraqi Conflicts Show Signs of Merging”, March 7, 2013, Policywatch 2042, Washington Institute For Near East Policy, https://www.washingtoninstitute.org/policy-analysis/view/syrian-and-iraqi-conflicts-show-signs-of-merging. [2] See: https://www.trust.org/item/20130621144421-omxch. [3] See: https://en.aswataliraq.info/(S(clhorg45ylfsgrrhg3vbwlmb))/Default1.aspx?page=article_page&id=147369&l=1. [4] See: https://www.cfr.org/iraq/iraqs-militia-groups/p11824#p6. [5] See: https://www.mcclatchydc.com/2005/12/12/v-print/13157/iran-gaining-influence-power-in.html. [6] See: https://now.mmedia.me/lb/en/mena/8-dead-in-iraq-bomb-attack-on-iran-pilgrims-officials-say. [7] Personal conversation with Michael Knights, June 24, 2013. [8] See: https://www.facebook.com/KlnaAlshhydAlmjahdYasynMhmwdAlzyn. [9] See:
Hizballah Cavalcade: Liwa’a Zulfiqar: Birth of A New Shia Militia in Syria?
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Liwa’a Zulfiqar: Birth of A New Shia Militia in Syria?
By Phillip Smyth ([email protected])
Click here for a PDF version of this post

On June 5, 2013, the same day Lebanese Hizballah declared victory at the Battle of Qusayr, a page for a new Damascus-based Shia militia group, Liwa’a Zulfiqar (LZ or the Zulfiqar Battalion), was created on Facebook. The group asserts it is, “Assigned to protect religious shines, especially the Saydah Zaynab [shrine]”. This claim is also held by Syria’s other main Shia militia, Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas (LAFA). However, Liwa’a Zulfiqar is not competing with Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas. In fact, most of its members and leadership appear to have been drawn from LAFA. Furthermore, Liwa’a Zulfiqar does not hide the fact that it was created out of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas. Along with new photographs, the new group has repackaged older LAFA photographs and claimed them as representations of the new group.
LZ’s formation results in a number of questions: Is Liwa’a Zulfiqar a genuinely new organization? Could it be another front for LAFA? Was LZ’s formation representative of something else going on within the ranks of Shia fighters in Syria?
Based purely on social media data, it appears LZ is less of a new organization, and probably a LAFA front or part of LAFA. At best, the group could be a repackaging of LAFA fighters into a new group which serves the same functions and cooperates closely with LAFA and the Syrian army. At the same time, the group could be little more than a web-based propaganda vehicle. Since the creation of a new organization would generate the sense that larger numbers of capable Shia fighters are flooding into Syria, LZ’s propaganda function may also be aimed directly at rebel morale.
Using unnamed sources, Al-Hayat newspaper reported the majority of LZ’s fighters have come from Muqtada al-Sadr’s Liwa’a al-Yum al-Mawud (Promised Day Brigades), Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq, and Kata’ib Hizballah.[1] The latter two groups have suffered casualties in Syria and have also been integral pieces of LAFA. If LZ is an actual organized entity, it has already established itself as primarily Iraqi Shia staffed. It is unknown whether the Iraqi make-up of the group is a deliberate measure to create a separate purely Iraqi staffed organization. However, based on LAFA’s history of having a membership of mixed nationalities, it is unlikely the group has been formed to suit such a purpose.
Still, new evidence about LZ’s origins may have come to light via a June 19th Reuters report.[2] Liwa’a Zulfiqar may instead be the outgrowth of infighting pitting Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas’s Syrian commanders, Assad militias, and trained Iraqi fighters who comprise a large chunk of LAFA’s membership. Citing claims by Iraq-based Shia militants, Reuters reported, “Two Iraqi fighters and three Syrian Shabiha died” in a short battle pitting local Assad’s forces against Iraqi Shia fighters. As a result, “divisions fester and Iraqi combatants have formed a new brigade, refusing to fight under Syrian command”. It is possible Liwa’a Zulfiqar is the “new brigade” mentioned in the report.
If Liwa’a Zulfiqar was established due to the infighting, it is highly probable that the old LAFA command and military apparatus has been replicated and simply given a new name. This would explain the repackaging of LAFA photographs and the claims that LAFA leadership now comprises LZ’s leadership.
Nevertheless, it is important to remember that LAFA and LZ would still be reliant on the cooperation of Assad’s forces. Heavy weapons provided to them by the Syrian army, including tank and artillery support, will still be necessary for LZ to mount any offensive or effective defensive operations. Furthermore, supplies for the group need to be funneled through the Assad regime, so a working relationship with Assad’s forces would be necessary.
Importantly, LAFA does not appear to have an interest in heightening any split. LAFA’s official Facebook page even announced the creation of LZ and posted some of their photographs. Also, LZ does not hide their support for the Assad regime. If a split resulting in the creation of LZ really did arise, it appears it was mitigated to the extent that the discord did not spill into public spheres, namely social media.
Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas & Liwa’a Zulfiqar’s Shared Members
Since the creation of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas and the creation of multiple social media (primarily Facebook) pages to market the group and its goals, very few of the group’s members have been photographed or named. However, LAFA’s leadership were often photographed (without their faces obscured) and claimed as group leaders. This has also been the case for LZ, which has publicized the leadership element of the organization.
Demonstrating its extremely close links to LAFA, LZ’s announced commanders were and may possibly still be LAFA leaders. This further points to the possibility LZ is little more than a subgrouping of fighters who operate under the main header of LAFA. Then again, it could also demonstrate the organization is a replication of LAFA with more Iraqi leadership.
LZ claims Abu Shahed and Abu Hajar as acting as a commanders (ranks were not given). Yet, these two commanders are already well-known to those following LAFA. In fact, the two have both been presented as LAFA leaders.
- Abu Jafar al-Assad (Abu Jafar): Often shown in LAFA’s photographs as a sniper. Abu Jafar is now named as a leading fighter for Liwa’a Zulfiqar. Photographs of Abu Jafar have been widely circulated on pro-Assad, pro-LAFA, Hizballah, and Syrian rebel websites. He’s most often affiliated with LAFA.
- Abu Hajar: Originally claimed as “Al-Qa’id” for LAFA. Abu Hajar was prominently displayed on many pro-LAFA websites.
- Abu Shahed: Originally listed as a “Mujahid” (holy warrior) for LAFA. Abu Shahed is now listed as a commander for LZ.

Figure 1: A banner featuring (shown wearing camouflage fatigues) Abu ‘Ajeeb (left), Abu Shahed (center), Abu Hajar (right) are pictured together as the leadership for LAFA. The photo of the banner was first posted on Facebook on June 6, 2013, 24 hours after the announcement of the creation of Liwa’a Zulfiqar.
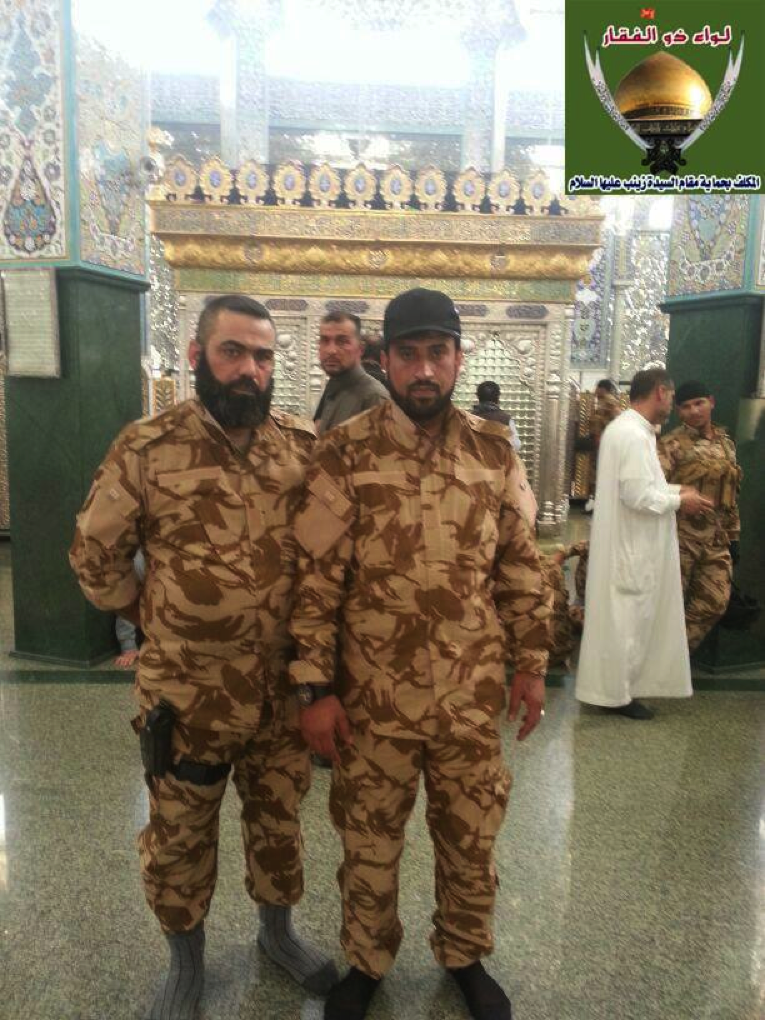

Figure 2: Abu Hajar and Abu Shahed stand together in the Saydah Zaynab Shrine.

Figure 3: Abu Shahed, shown in an April, 2013 LAFA photograph. In the picture he is wearing a desert pattern MARPAT style uniform. The photo has been reposted on LZ’s Facebook.
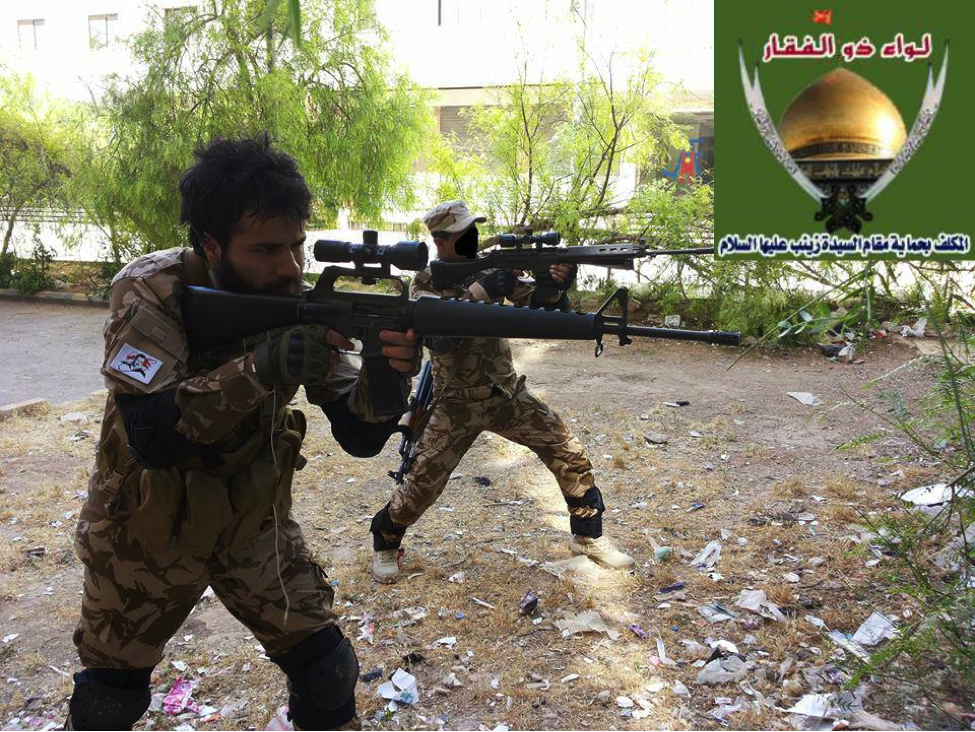

Figure 4: Abu Jafar al-Assad takes aim with an M16A1 style rifle. Another LZ/LAFA militiaman also takes aim with an FN FAL. A Bashar al-Assad patch is fastened to Abu Jafar’s arm.
Symbolism
The creation of Liwa’a Zulfiqar and their symbol also coincided with the creation of a new symbol for Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas. LAFA’s new logo was first adopted on the group‘s official Facebook page on May 31, 2013. Both logos include stylized images of crossed Zulfiqar-style swords. The dome of the Saydah Zaynab Shrine also features prominently.
It is important to note that both logos are quite similar in design. It can be assumed that this was not likely due to unoriginality, but instead was done to demonstrate common themes. The adoption of these new symbols is a clear example of the both organizations attempting to capitalize on the fate of the Saydah Zaynab Shrine and on placing clearly Shia symbols as centerpieces of their respective organizations.


Figure 5: Liwa’a Zulfiqar’s logo (Left).
Figure 6: Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas’s new logo (Right).
What’s In A Name?
As with Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas, Liwa’a Zulfiqar’s name has deep roots within Shia Islam. According to Shia tradition, the Zulfiqar was a sword which originally belonged to the Islamic prophet Muhammad. According to Shia tradition, the legendary double tipped sword had immense strength and was passed on to Imam ‘Ali by Muhammed as he lay dying. For Shia, the handover of the sword connoted the passing of the mantle of Islam’s leadership to ‘Ali. The sword also formed a central facet for ‘Ali’s renowned status as a warrior.[3]
A popular traditional Shia saying, which invokes Imam Ali and the Zulfiqar says, “La fata illa ‘Ali, la saif illa zulfiqar” (“No victor like Ali, no sword except the Zulfiqar”).[4] Jennifer G. Wollock also notes the Zulfiqar’s near mystical qualities saying, “[Zulfiqar is] famous in its own right…[J]ust as King Arthur’s sword Excalibur or Roland’s Durandal…[I]n the West.”[5]
For Shia Muslims, the Zulfiqar and its significance did not simply disappear with the assassination of ‘Ali. It is believed the sword is the weapon to be wielded by the Mahdi, Shi’ism’s messianic figure who will usher in a time of justice and end oppression.[6] For Shia, particularly Twelver Shia, the Mahdi is the true ruler of earth—the final Imam—hidden by Allah and set to return. Contemporarily, the messianic theme of connecting the Zulfiqar to the Mahdi is also still popular with many Shia.[7]
Accordingly, the Zulfiqar’s powerful symbolism is being wielded by LZ to demonstrate power, commitment to the protection of Shi’ism, traditional Shia themes, messianic motifs, and as a military symbol.
The Fighters of Liwa’a Zulfiqar
Interestingly, LZ’s photographic posts for their fighters seem to include shots of them dressed in desert-pattern camouflage. LAFA members photos are more generally seen in woodland and urban themed MARPAT-style camouflage clothing. The emphasis on the desert pattern uniforms may be LZ’s attempt to posit a clear and visible difference from LAFA.
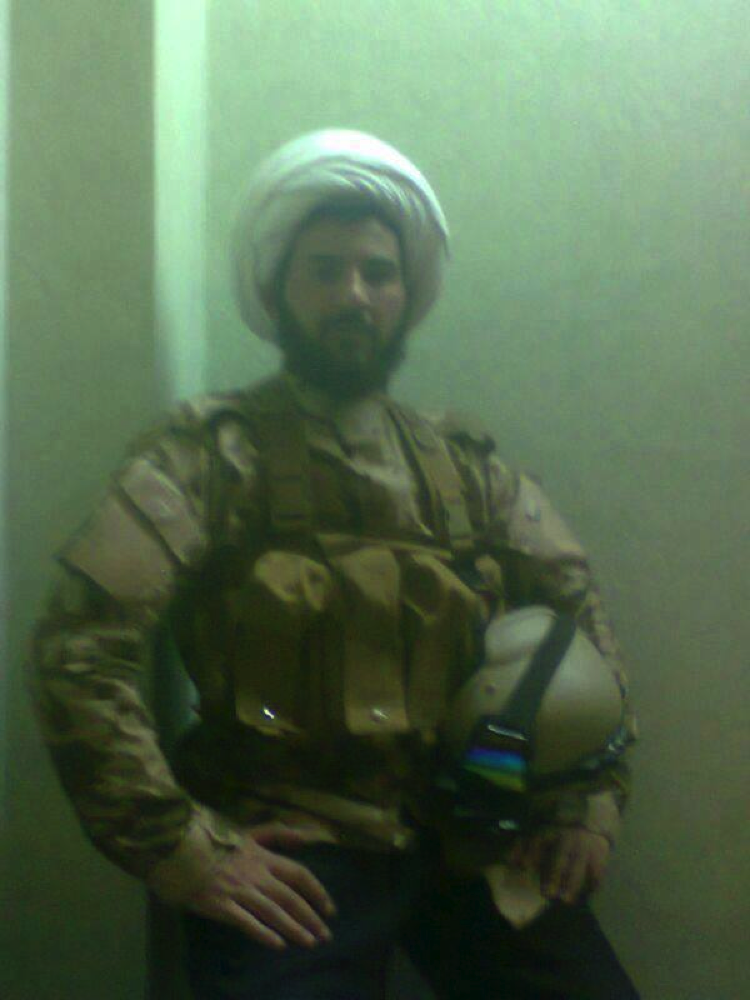

Figure 7: The fighter’s white turban and beard indicate he may hold the status
Hizballah Cavalcade: “Divine Victory” in Qusayr: Hizballah Promotes Their Success on the Web
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
“Divine Victory” in Qusayr: Hizballah Promotes Their Success on the Web
By Phillip Smyth ([email protected])

Figure 1: The green text on the sign reads, “Nasr Mubarak” (“Blessed Victory”); the red reads, “Al-Qusayr 2013”.
Throughout the month of May and into early June, the Battle for Qusayr pitted numerous rebel factions against the combined might of the Syrian military and Lebanese Hizballah. This period also witnessed Hizballah Secretary General Sayyid Hassan Nasrallah finally admit that Hizballah forces were not simply fighting to “Protect [Shia] shrines” or to “Defend Lebanese Shia border villages”.[1] Instead, all of Syria would be Hizballah’s battlefield until victory. As fighting in Syrian heated-up, Nasrallah promised to Hizballah supporters (on May 25, 2013), “I say to all the honorable people, to the mujahedeen, to the heroes: I have always promised you a victory and now I pledge to you a new one in Syria”.[2]
In many ways, the promise of victory in Syria harkened back to Nasrallah’s 2006, “wa’d sadiq” (“Truthful promise”). At the time, Hizballah’s leader had, before the July-August war, sworn he would undertake an operation to free prisoners in Israeli jails (namely, Samir Quntar).[3] The war was the summation of his promise. Following the war, Nasrallah’s “Truthful promise” became a common quasi-religious cum ideological narrative. With the 2006 war over, the phrase, “Divine victory”—a claim that the 2006 Hizballah-Israel war resulted in a Hizballah victory— was combined with “Truthful promise”. In turn, they both became common slogans utilized by Hizballah.
In an effort to demonstrate continuity with the narrative, Hizballah is reusing these themes once again in Syria.
The announcements of June 6, 2013, demonstrating Qusayr had been taken, resounded through Hizballah’s network of Facebook and forum pages. No more than an hour after it was declared that Qusayr had fallen to Assad’s and Hizballah’s forces, Hizballah partisans had already created numerous photos to praise the operation. Few photos of Hizballah fighters in Qusayr were released, but the video and photographic material which was made public emphasized a much more sectarian presentation of Hizballah’s fight for Syria.

Figure 2: Hizballah supporters envisioned Google producing a doodle to commemorate the group’s victory in Qusayr. The Google logo is in Hizballah’s green and yellow color scheme. Google’s “L” has been replaced by a round of ammunition. Additionally, the slogan featured on the top of Hizballah’s flag (which is Quran 5:56) has been placed above Google’s logo– “Indeed, the party of God are they that shall be triumphant”. A Hizballah fighter stands off to the left viewing a sign reading, “Welcome to Kossayr [sic]”. The date of the victory (June 5, 2013) is featured in the search-bar.
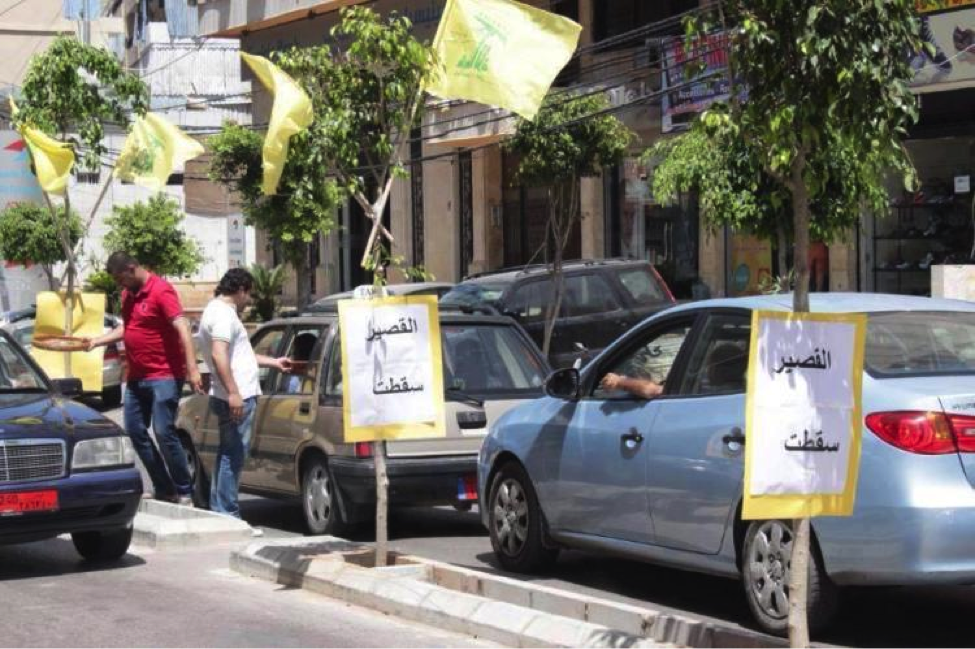

Figure 3: Hizballah supporters hand out candies. The sign reads “Al-Qusayr Saqatat” (“Qusayr has fallen”). Following Hizballah’s conquest of Qusayr, this photo became a common addition on most pro-Hizballah, pro-Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas, and a number of pro-Assad Facebook pages. Pro-rebel social media also featured the photograph in an effort to establish Hizballah’s hubris.
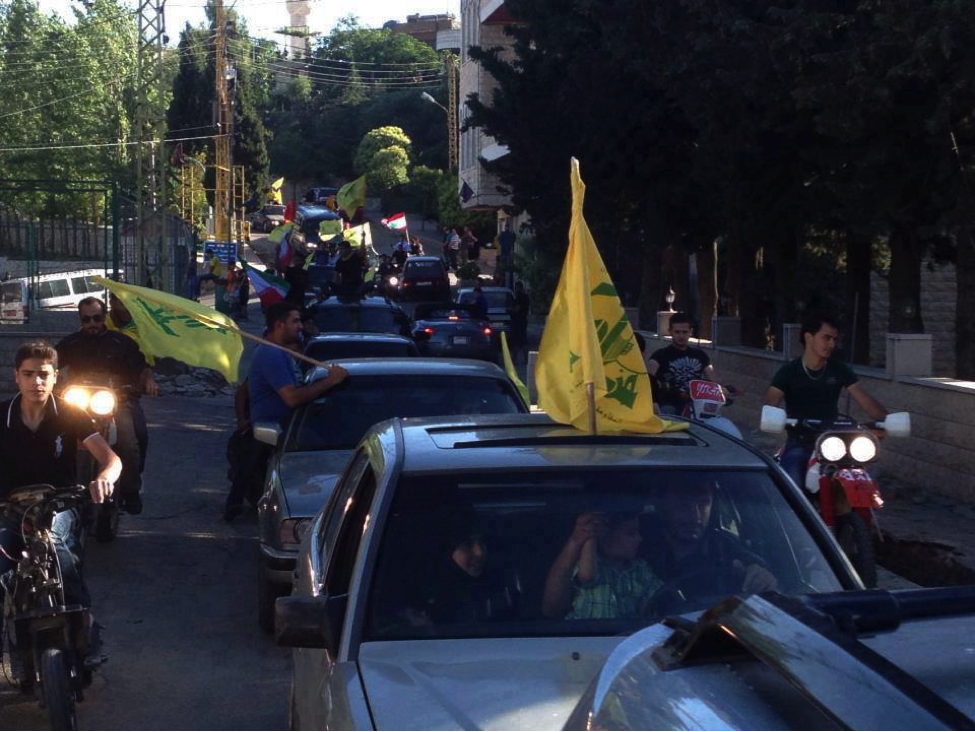

Figure 4: Hizballah supporters drive in a convoy flying Hizballah, Syrian (Assad pattern), and Iranian flags to celebrate the fall of Qusayr. This photo was later removed from the original Facebook page it was posted.
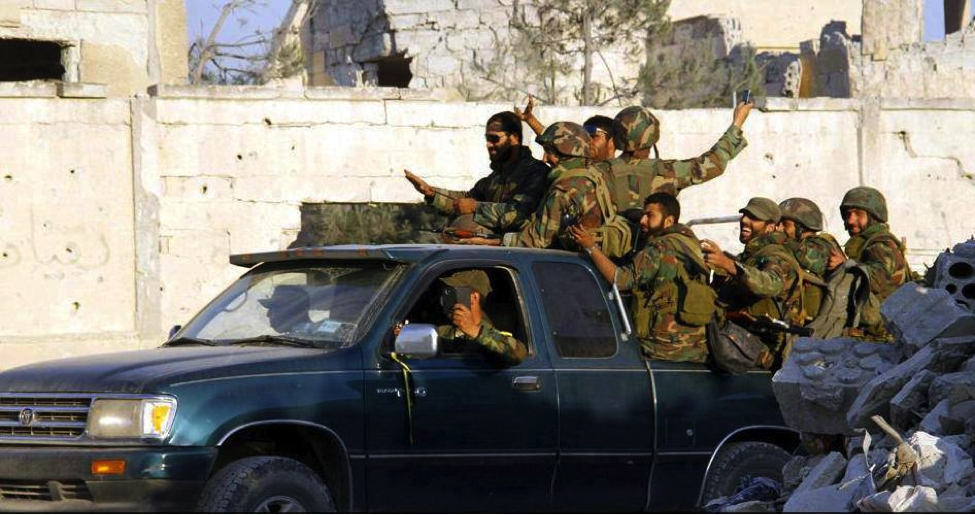

Figure 5: Jubilant Hizballah fighters roll through Qusayr on a pickup truck. This photo was featured on 7 major pro-Hizballah Facebook pages and a number of pro-Assad Facebook pages.

Figure 6: Hizballah supporters have tried to establish the Battle of Qusayr as a victory which is the equivalent to Israel’s 2000 withdrawal from Lebanon and the end of the 2006 Hizballah-Israel War (which Hizballah calls a “Divine Victory”).
Videos:
A commonality in all videos is that of open celebration. The firing of weapons, fireworks, and demonstrations involving vehicle convoys are omnipresent in released footage. Videos representing a clear sectarian-based shift also took center stage. Most importantly was one video of Hizballah fighters raising a banner reading, “Ya Husayn” (“O Husayn”) over the minaret of a captured Sunni mosque in Qusayr. The Hizballah fighters then chanted, “Labayka ya Husayn” (“We are here for you, O Husayn”). The clip was spread quite openly over Hizballah’s numerous Facebook, forum, and other social media sites and was then picked up by pro-rebel groups and other Arab media organs. In some ways, the video demonstrates that Hizballah views Qusayr as a Shia victory more than just a victory for the organization.
[1] See: https://www.nytimes.com/2013/05/26/world/middleeast/syrian-army-and-hezbollah-step-up-raids-on-rebels.html?pagewanted=all [2] See: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/lebanon/10081209/Two-rockets-aimed-at-Hizbollah-area-of-Beirut-leaves-at-least-four-people-wounded.html [3] See: https://articles.chicagotribune.com/2006-08-04/news/0608040294_1_sheik-hassan-nasrallah-hezbollah-tel-aviv/2. Quntar was held in an Israeli prison for a 1979 terrorist attack on Nahariya, Israel, During the attack, Quntar murdered a 4 year old and her father. See: https://lisagoldman.net/2008/07/22/samir-kuntar-in-his-own-words/
Hizballah Cavalcade: Iran’s Losses In the “35th Province” (Syria), Part 1
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Iran’s Losses In the “35th Province” (Syria), Part 1
By Phillip Smyth
Click here for a PDF version of this post
“Syria is…[Iran’s] 35th province and a strategic province for us. If the enemy attacks us and wants to take either Syria or Khuzestan, the priority for us is to keep Syria…If we keep Syria, we can get Khuzestan back too, but if we lose Syria, we cannot keep Tehran.” –Mehdi Taeb, a high-level Iranian cleric speaking to to Iran’s Basij (paramilitary group attached to the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps), February, 2013.[1]

Iran’s (Iraqi and Lebanese) Shia proxies are not the only groups losing members due to their involvement in combat in Syria. Iran is actively contributing infantry personnel to bolster regime of Bashar al-Assad. The Iranian Revolutionary Guard-Quds Force (IRGC-QF); Iran’s long-arm used to create, command, bolster Tehran’s proxies, and execute attacks overseas, has been rather active in Syria.[2] Their movements have not simply been limited to acting as behind-the-scenes guides for proxy or Assad’s forces. In fact, the IRGC-QF has engaged in combat and taken a number of casualties and their losses are becoming increasingly more public.
Back in August, 2012, 48 Iranian “Pilgrims” were kidnapped by Syrian rebels, when they were heading to the Saydah Zaynab Shrine.[3] Rebel forces accused these men of all being IRGC fighters.[4] It was later reported by the Iranians that the group included “Retired” IRGC members.[5] Rebels have also accused the IRGC of acting as commanders for Lebanese Hizballah’s May, 2013 offensive in Qusayr.[6]
Following Lebanese Hizballah’s official May recognition of their full-involvement in Syria, it would appear that Iran is not only becoming more open about their involvement, but also utilizing many of the same narrative points first honed by its regional Shia proxies.
February, 2013, witnessed the loss and public funeral of a senior IRGC-QF commander in Syria. It was claimed by Tehran he was simply working on “Reconstruction projects” in war torn Aleppo. Even with such a high-profile death, little additional information was offered by Iran regarding their activities in Syria.
However, In June, three IRGC members were claimed by Iranian sources to have been killed while operating around Damascus’s Saydah Zaynab Shrine. Proclaiming IRGC members have been killed defending the shrine recycles the exact narrative Lebanese Hizballah and other Iraqi Shia groups have been utilizing for many months. This line also demonstrates that Tehran has become more comfortable with using sectarian-based messaging to convey why it is willing to lose men in the Syrian war.
Based on the released data regarding killed IRGC-QF members, it is likely that Summer-Fall 2013 may witness several more announcements and public funerals.
As opposed to previous Hizballah Cavalcade posts, this post did not rely on the monitoring of social media, forums, or other sources. Instead, announcements of death and photographs were taken from official and officially approved Iranian sources.
__
Name: General Hassan Shateri (A.K.A. Hossam Khoshnevis)
Death Announced: February 13, 2013. It was claimed by Iranian media that Shateri was killed in Syria on February 12, 2013. His funeral was held on February 15, 2013.
Notes: Shateri was a high-level IRGC-QF leader and the highest ranking Iranian killed in Syria. His work with Lebanese Hizballah (and possibly other Iranian-backed organizations in Iraq) was of great importance to the Iranians.[7] This connection was displayed openly at his funeral with funeral-goers waving Lebanese Hizballah flags and placing a Lebanese Hizballah flag on his casket.
Iran’s English-language PressTV reported that Shateri was killed, “by unknown gunmen as he was traveling by road from Syria to Lebanon.” Iran also blamed “Suspected Israeli agents” for Shateri’s death.[8]
Mashregh News posted a number of photos showing Shateri going about his duties in Lebanon (one is reposted here).[9] In Iranian media, the narrative used to explain Shateri’s tasks in Lebanon and Syria was that he was an overseer for the reconstruction of south Lebanon (from damage suffered during the 2006 Hizballah-Israel War). Additionally, Iranian-government-backed Fars News Agency described Shateri’s presence in Syria as the result of, “Reconstruction and development projects” he was working on in Aleppo.[10]








Name: Lt. Colonel Amir Reza Alizadeh
Death Announced: May 4, 2013 (It was announced Alizadeh was killed in Syria on May 1, 2013).
Notes: Iranian reports claimed Alizadeh was killed by an explosion which occurred outside of the Iranian embassy in Damascus. The bombing, according to Iranian state media, was orchestrated by, “Wahhabi terrorists”.[11] Alizadeh’s funeral was held in Rudsar, Iran.[12]



Name: Mehdi Khorasani
Death Announced: June 10, 2013
Notes: Since Shanaei and Khorasani had a shared funeral service, photos for both are located after the entry for Shanaei. Iran’s Damghan News published a full album of funeral photographs. However, the link did not work two days after the photos were posted. Shanaei and Khorashani were pictured together holding AK-47 type rifles in front of the Saydah Zaynab Shrine. Their funeral was the first group funeral (for two or more killed) held in Iran for personnel killed in Syria.
Name: Ali Asqar Shanaei
Death Announced: June 10, 2013
Notes: Shanaei and Khorashani were pictured together holding AK-47 type rifles in front of the Saydah Zaynab Shrine. Their funeral was the first group funeral (for two or more killed) held in Iran for personnel killed in Syria.
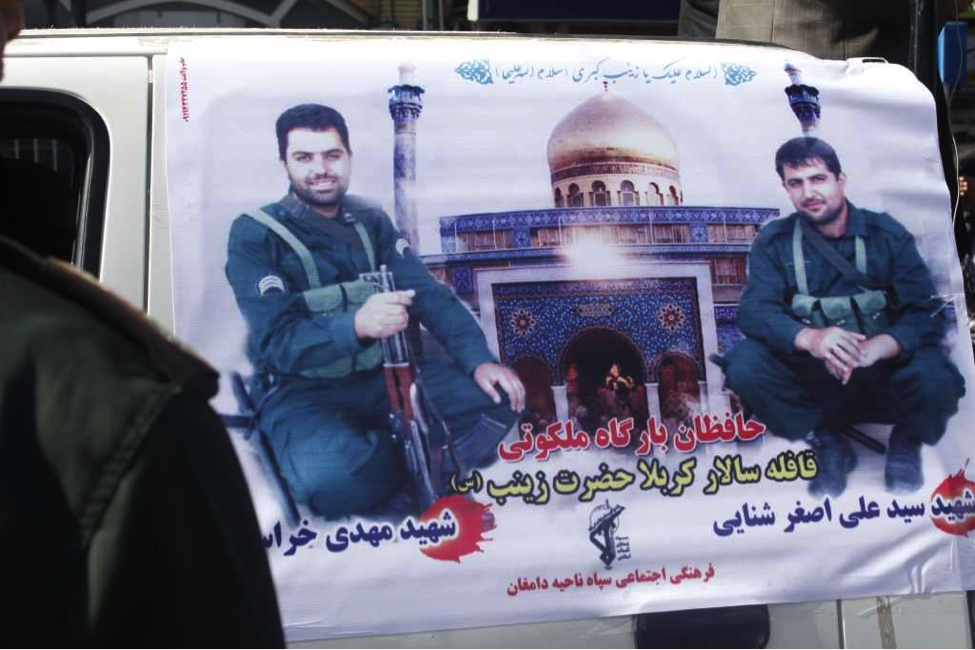
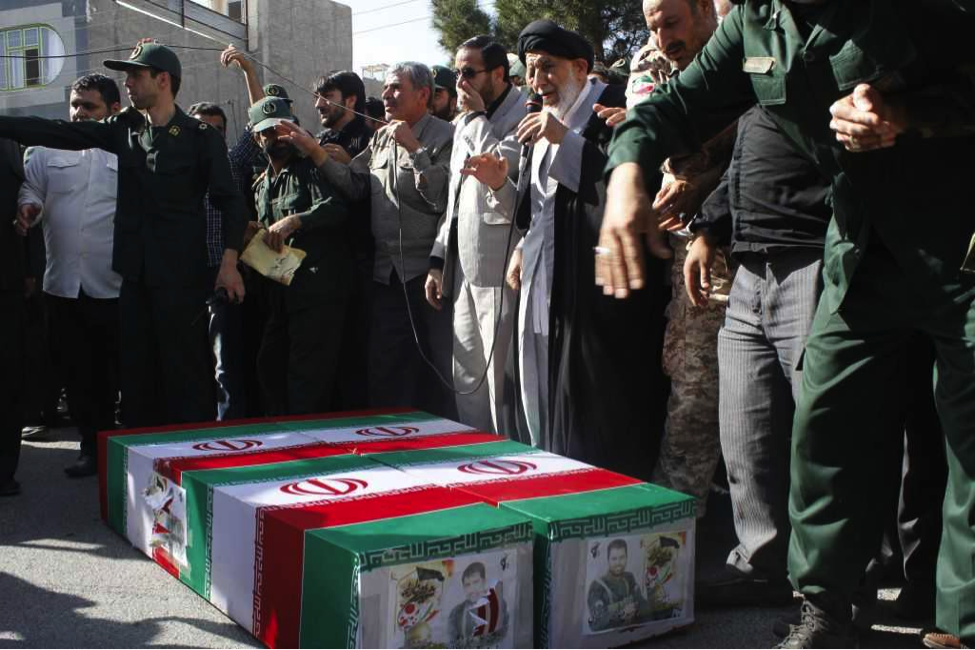
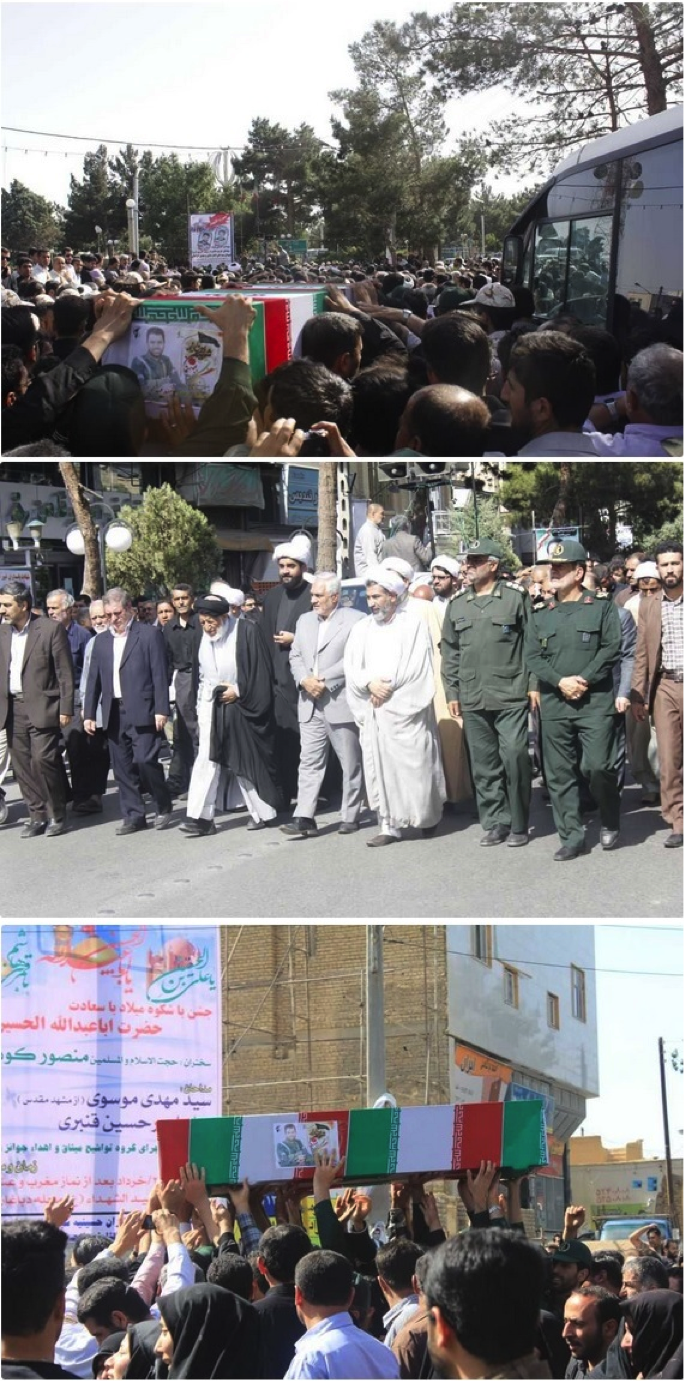



Name: Muhammed Husayn Atareh
Death Announced: June 10, 2013
Notes: Atareh’s casket included numerous IRGC symbols. It was also claimed that Atareh was killed in fighting around the Saydah Zaynab Shrine.









Name: Amir Kazem Zaydeh
Death Announced: June 9, 2013
Notes: Iran’s Mashregh News claimed Zaydeh was killed by a bomb during “Clashes with terrorists”.[13]

 [1] See: https://iranpulse.al-monitor.com/index.php/2013/02/1346/head-of-ammar-strategic-base-syria-is-irans-35th-province-if-we-lose-syria-we-cannot-keep-tehran/
[2] See: https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/113/hr854/text
[3] See: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/syria/9451858/Syria-48-Iranian-pilgrims-kidnapped-from-bus-travelling-to-Damascus-airport.html
[4] See: https://www.jpost.com/Middle-East/Tehran-warns-Syrian-rebels-to-free-captive-Iranians
[5] See: https://www.voanews.com/content/retired-iranian-revolutionay-guards-among-those-kidnapped-in-syria/1475622.html
[6] See: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C03FDXqkOkI. Reportedly, this is an intercepted radio transmission.
[7] See: https://english.farsnews.com/newstext.php?nn=9107144510
[8] See: https://www.presstv.com/detail/2013/02/14/288857/irgc-commander-assassinated-in-lebanon/
[9] See: https://www.mashreghnews.ir/fa/news/193817/%D8%AA%D8%B5%D8%A7%D9%88%DB%8C%D8%B1-%D8%A7%D8%AE%D8%AA%D8%B5%D8%A7%D8%B5%DB%8C-%D9%85%D8%B4%D8%B1%D9%82-%D8%A7%D8%B2-%D8%B3%D8%B1%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B1-%D8%B4%D9%87%DB%8C%D8%AF-%D8%AD%D8%B3%D9%86-%D8%B4%D8%A7%D8%B7%D8%B1%DB%8C
[10] See: https://abna.ir/data.asp?lang=3&Id=391473
[11] See: https://www.ido.ir/n.aspx?n=13920222001.
[12] See: https://www.mehrnews.com/detail/News/2046534.
[13] See: https://www.mashreghnews.ir/fa/news/222075/%D9%BE%D9%8A%DA%A9%D8%B1-%D8%B4%D9%87%D9%8A%D8%AF-%DA%A9%D8%A7%D8%B8%D9%85%E2%80%8C%D8%B2%D8%A7%D8%AF%D9%87-%D8%A8%D9%87-%D8%AE%D8%A7%DA%A9-%D8%B3%D9%BE%D8%B1%D8%AF%D9%87-%D8%B4%D8%AF-%D8%B9%DA%A9%D8%B3
[1] See: https://iranpulse.al-monitor.com/index.php/2013/02/1346/head-of-ammar-strategic-base-syria-is-irans-35th-province-if-we-lose-syria-we-cannot-keep-tehran/
[2] See: https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/113/hr854/text
[3] See: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/middleeast/syria/9451858/Syria-48-Iranian-pilgrims-kidnapped-from-bus-travelling-to-Damascus-airport.html
[4] See: https://www.jpost.com/Middle-East/Tehran-warns-Syrian-rebels-to-free-captive-Iranians
[5] See: https://www.voanews.com/content/retired-iranian-revolutionay-guards-among-those-kidnapped-in-syria/1475622.html
[6] See: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C03FDXqkOkI. Reportedly, this is an intercepted radio transmission.
[7] See: https://english.farsnews.com/newstext.php?nn=9107144510
[8] See: https://www.presstv.com/detail/2013/02/14/288857/irgc-commander-assassinated-in-lebanon/
[9] See: https://www.mashreghnews.ir/fa/news/193817/%D8%AA%D8%B5%D8%A7%D9%88%DB%8C%D8%B1-%D8%A7%D8%AE%D8%AA%D8%B5%D8%A7%D8%B5%DB%8C-%D9%85%D8%B4%D8%B1%D9%82-%D8%A7%D8%B2-%D8%B3%D8%B1%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B1-%D8%B4%D9%87%DB%8C%D8%AF-%D8%AD%D8%B3%D9%86-%D8%B4%D8%A7%D8%B7%D8%B1%DB%8C
[10] See: https://abna.ir/data.asp?lang=3&Id=391473
[11] See: https://www.ido.ir/n.aspx?n=13920222001.
[12] See: https://www.mehrnews.com/detail/News/2046534.
[13] See: https://www.mashreghnews.ir/fa/news/222075/%D9%BE%D9%8A%DA%A9%D8%B1-%D8%B4%D9%87%D9%8A%D8%AF-%DA%A9%D8%A7%D8%B8%D9%85%E2%80%8C%D8%B2%D8%A7%D8%AF%D9%87-%D8%A8%D9%87-%D8%AE%D8%A7%DA%A9-%D8%B3%D9%BE%D8%B1%D8%AF%D9%87-%D8%B4%D8%AF-%D8%B9%DA%A9%D8%B3
Hizballah Cavalcade: Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada: Another Supplier of Iraqi Shia Fighters in Syria
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada: Another Supplier of Iraqi Shia Fighters in Syria
By Phillip Smyth
Click here for a PDF version of this post

Figure 1: Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada’s symbol.
Following funerals for some of its members killed fighting in Syria, The Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada (The Battalion of the Sayyid’s Martyrs or KSS) has quietly established itself as an Iraqi Shia militia force contributing combatants to the battlefront in southern Damascus. At present, the KSS’s main raison d’être appears to be as a source for Iraqi Shia fighters who can be used to “Defend the Zaynab Shrine”, a major Shia Islamic site in Syria.
The first reports of KSS’s existence occurred on April 14, 2013. In one press report, it was stated that KSS initially went by the names of Kata’ib Karbala (the Karbala Battalions) and later as Kata’ib Abu Fadl al-Abbas.[1] Interestingly, a group which had targeted American and Coalition forces in Iraq was and Iranian-backed “Special group” called Kata’ib Abu Fadl al-Abbas.[2] Adding further significance to the KSS’s earlier names and its links to Syria; KSS sends its fighters to Syria where they act as an intrinsic part of the Syrian-based Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas (LAFA).
It was reported that the KSS was formed due to splits within the Iranian-created and backed Kata’ib Hizballah.[3] These contentions were initially based on nameless sources and were reported by a small number of Iraqi Arabic-language publications. It was also claimed that Abu Mustafa Sheibani (Hamid al-Sheibani), a pro-Iranian militia leader, who had been involved with the creation of many so-called “Special Groups” (including Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq and Kata’ib Hizballah) was KSS’s leader.[4] According to a Washington Institute for Near East Policy report, Sheibani “holds both Iranian and Iraqi citizenship” and when operating in Iraq, concentrated on the, “distribution of explosively formed penetrator (EFP) roadside bombs”.[5]
Based on the KSS’s few public appearances and its activity in Syria, it is likely the organization has a steady source of funding. Said funding allows the group to hold attention grabbing funerals and to put on airs of professionalism and organization. Nevertheless, based on Iraqi media, forums, and other social media sources, the size of the group’s membership, leadership, recruitment activities, and amounts of money it may receive remain unknown or unconfirmed.
Mirroring the activities of other Lebanese and Iraqi pro-Iranian groups, such as Kata’ib Hizballah, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq, and Hizballah, the KSS sent a number of fighters to serve in the ranks of the Damascus-based Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas. When these fighters were killed, LAFA was often the initial or only group which would claim them as members. Only when Iraqi family members of dead fighters were interviewed, was it revealed their deceased relatives were also members of KSS.[6]
Pointing to direct Iranian support for KSS, the bodies of fighters who belonged to the organization have, on all occasions involving a funeral, been returned to Iraq via Iran. On May 6, 2013, the funeral for Diya Issawi included claims he belonged to KSS and that his body was returned to Iraq from Iran, through Basra.[7] Later that month, on May 17, 2013, two more funerals were held for Iraqis killed in Syria. The first, for Hassan Ali Farhud, was held in Sadr City, a Shia section of Baghdad.[8] The second funeral, for Muhammed Aboud al-Maliki, was held in Basra. Paralleling the return of Issawi’s body, Farhud and Maliki’s bodies were delivered through Iran. (Note: Partial profiles for Farhud, Issawi, and Maliki, were provided on Hizballah Cavalcade’s “Roundup of Iraqis Killed in Syria, Part 2”).
During funerals for its members, the KSS has fielded guards dressed in matching camouflage fatigues and a full color guard holding a mixture of KSS and Iraqi flags. Coffins for the dead are usually covered with Iraqi national (often painted onto the casket) and KSS flags. In most cases, the funeral processions resemble other funerals held for members belonging to Kata’ib Hizballah and Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq.

Figure 2: KSS statement released on May 8, 2013.
Following the funeral for Issawi, KSS declared its goals in a press statement issued by its media office. The group stated its aims included the protection of “shrines across the globe”, the preservation of “Iraqi unity”, and an end to sectarian conflict. It was claimed by KSS that its enemies were “Sowing [Islamic sectarian] discord” due to their “suspicious motives”. The group also mentioned that Israel is “Cancerous”, the U.S. occupation of Iraq was a symbol of “Arrogance”, and called for Jerusalem to be liberated.[9] For all intents and purposes, KSS repeated many of the main talking points presented by Lebanese Hizballah and Iran, albeit with an Iraqi spin.[10]
Despite the group’s statement claiming it was against sectarianism, some Iraqi forums reported the group had threatened to kidnap Iraqi Sunni Muslims.[11] Nevertheless, the KSS’s military activities appear to be limited to engagements in Syria.
WARNING: GRAPHIC IMAGES
Videos featuring KSS members have also been a relative rarity. Save for the posting of funeral videos made for fallen KSS members, only one video—posted on May 28, 2013—claims to be a KSS-specific combat video. Released on YouTube, the film purports to show KSS members (likely attached to LAFA) operating in Syria and displaying the dead bodies of what the video refers to as, “Wahhabi Free Syrian Army mercenaries”. Further linking KSS to LAFA, the film was set to an Iraqi-made pro-Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas song, which first appeared online in early-2013. KSS members present in the film can also be seen wearing fatigues which are commonly worn by LAFA members.
When compared to LAFA and Lebanese Hizballah, social media and forum presence for Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada has been sparse. What appeared to be a main Facebook “page” was created for the group on April 19, 2013.[12] However, the page conveyed little information and most posted material came on the day it was created or on April 26, 2013. The majority of the postings were of edited photos (mainly of the Zaynab Shrine) which could also be found on most pro-LAFA and pro-Hizballah websites. It is unknown whether the page was sanctioned by the group’s leadership. Membership for the page stands at fewer than 200. Additionally, a preponderance of those who “liked” the page lived in Baghdad, Iraq.
Facebook “Groups” have also been created for Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada. Most of these groups have less than 300 members and tend to contain more information about the organization. Photos made specifically for KSS are present on these devoted KSS group pages. However, they tend to utilize imagery which has been used previously by LAFA. In general, KSS’s images are at times more amateurish than with other Shia militias operating in Syria.
The KSS’s dead maintain positions of prominence in KSS Facebook groups. On rare occasions, photos of live KSS members serving with LAFA have their faces blurred. One KSS group page even featured photos of what were presumably KSS fighters arriving by bus to the frontlines in Syria. Based on the captions provided for these and other photographs, it appears that KSS fighters may primarily originate from Basra, Iraq. Incidentally, the many mentions of Basra would also coincide with two of the three funerals for killed KSS members, since they also occurred in Basra.
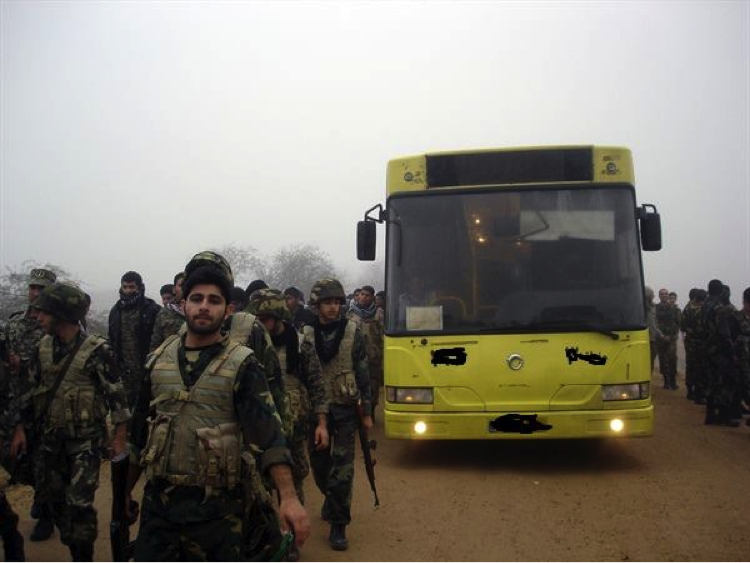
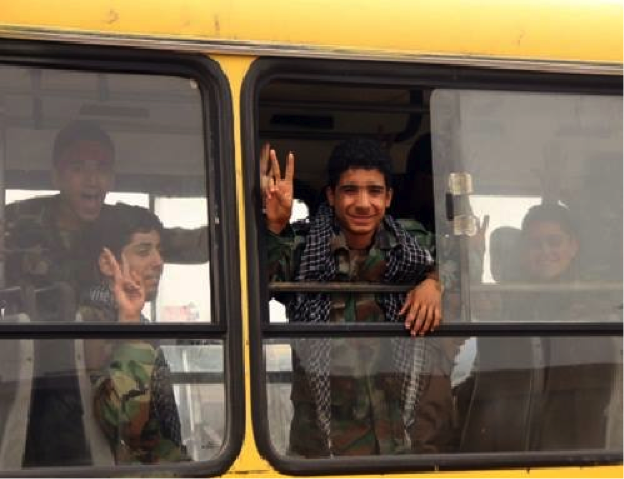






Figure 3: A KSS member is seen posing with a poster for Lebanese Hizballah leader Sayyid Hassan Nasrallah.
Underpinning the KSS’s Zaynab Shrine-centric role, their official symbol has a number of key images which emphasize Shi’ism, the Zaynab Shrine, and militarism. First, a stylized and green-colored image of Damascus’s Zaynab Shrine’s dome stands in the center with a red banner flying from the top. The raising of the red banner—symbolizing martyrdom and sacrifice—on top of the Zaynab Shrine has been used to great propagandistic effect by Shia groups such as Lebanese Hizballah and LAFA. The dome is flanked on two sides with images of AK-47 rifles. Around the dome on a roundel is a laurel wreath. At the bottom of the roundel are stylized blood drops. The blood drops may serve as a
Hizballah Cavalcade: Roundup of Iraqis Killed in Syria, Part 3
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Roundup of Iraqis Killed in Syria, Part 3
By Phillip Smyth
Click here for a PDF version of this post

Collecting information for profiles of Iraqi Shia killed fighting in Syria became more complicated following further acknowledgements by Hizballah’s leadership of their involvement in Syria.[1] Concurrently, Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas (LAFA), the Damascus-based pro-Assad Shia militia which includes a large number of Iraqi Shia, also became more open with their recognition of Lebanese Hizballah members killed serving with the group. Thus, announcements-of-death for Iraqi LAFA members were often mixed with large numbers of Lebanese Hizballah martyrdom announcements.
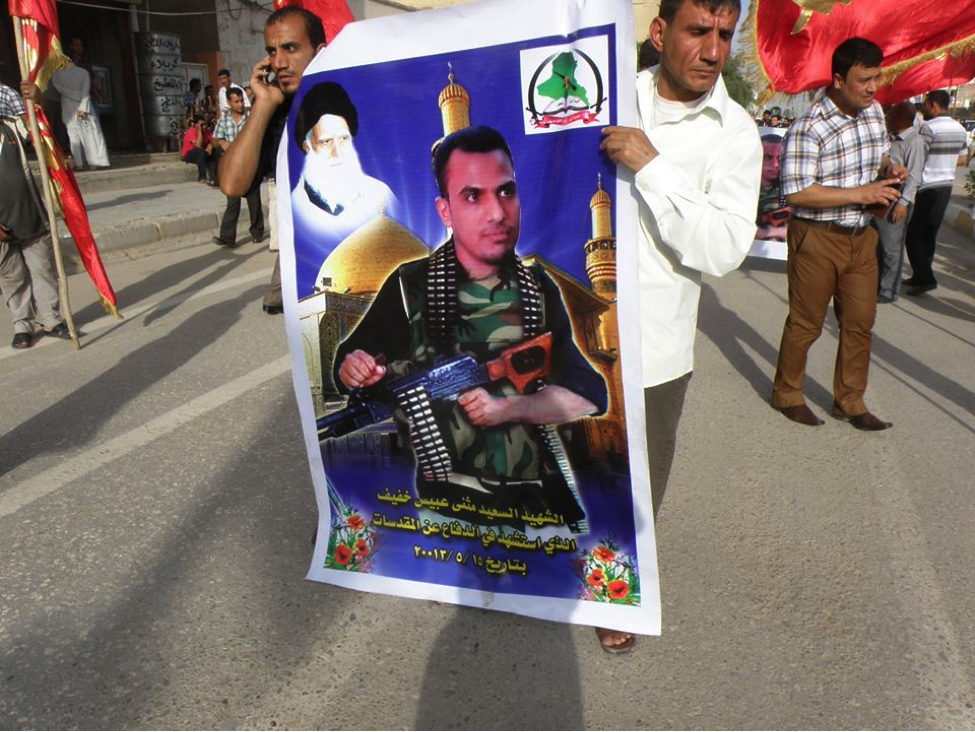
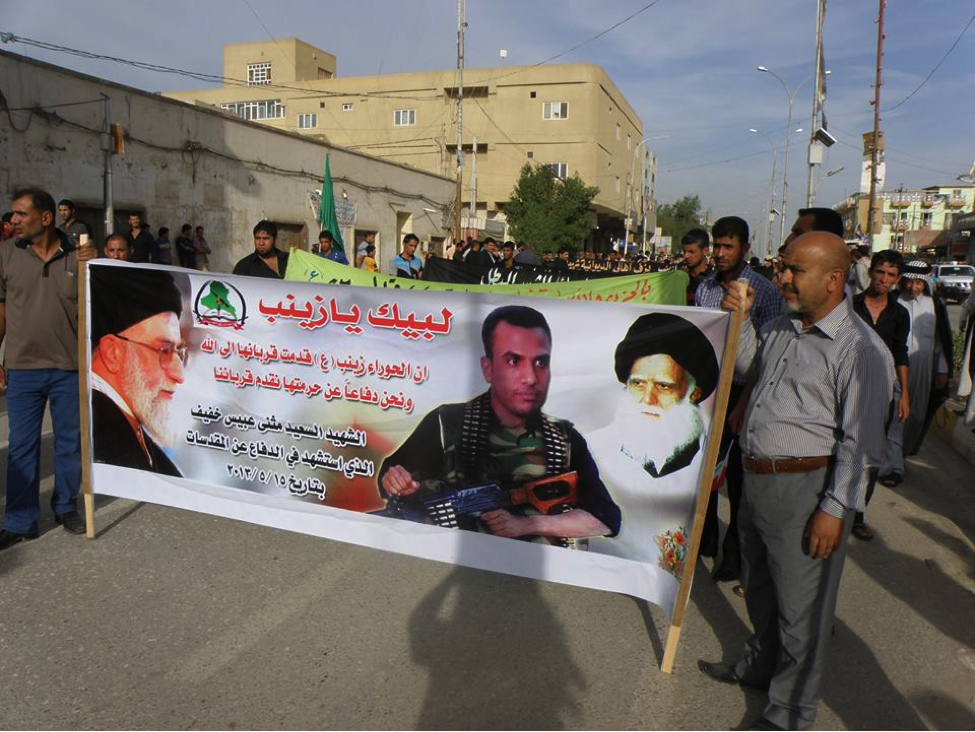
Martyrdom declarations for Iraqi Shia have also continued to follow a format where the majority of dead individuals have only one or two photographs of themselves released. Often, the photographs of these dead fighters are found on an official martyrdom poster produced by the Iraqi group to which these fighters originally belonged. On rare occasions, killed Iraqi Shia will have many photographs of them or their funerals displayed online. One Facebook-hosted funeral photo album, released for Al-Sa’id Mutheneh ‘Abees Khafeef, numbered around 80 photographs.
It has become increasingly clear that the majority of Iraqi Shia killed fighting in Syria have belonged to the Iranian created and backed, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq. Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq has not announced the loss of any of their members via their website. Instead, the group has relied on quasi-official and pro-Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas Facebook pages to report its dead. At times, announcements for killed Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq members have first emerged on Facebook pages and forums (including official forums) for Lebanese Hizballah. This likely demonstrates another deep link the group has with Lebanese Hizballah.[2]
Kata’ib Hizballah, another Iraqi organization created by the Iranians, had announced that it lost a number of members in Syria in mid-March-mid-April. However, this organization has not issued any new statements regarding further losses.[3]
This post only includes five dead from a period starting on May 18, 2013 and ending on May 31, 2013. One killed Iraqi Shia fighter reported dead on May 9th, was also confirmed. Despite the lower number of Iraqi Shia declared as, “killed fighting in Syria”; there is a strong possibility reported numbers of Iraqi Shia killed in Syria may rise in the coming weeks.
Nine pro-Hizballah, pro-Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas, Iraqi Shia, and pro-Assad Facebook pages (all Shia oriented) were utilized in the collection of information for this list. Two pro-Hizballah forums—one official and one quasi-official—were also employed for confirmation purposes.
__
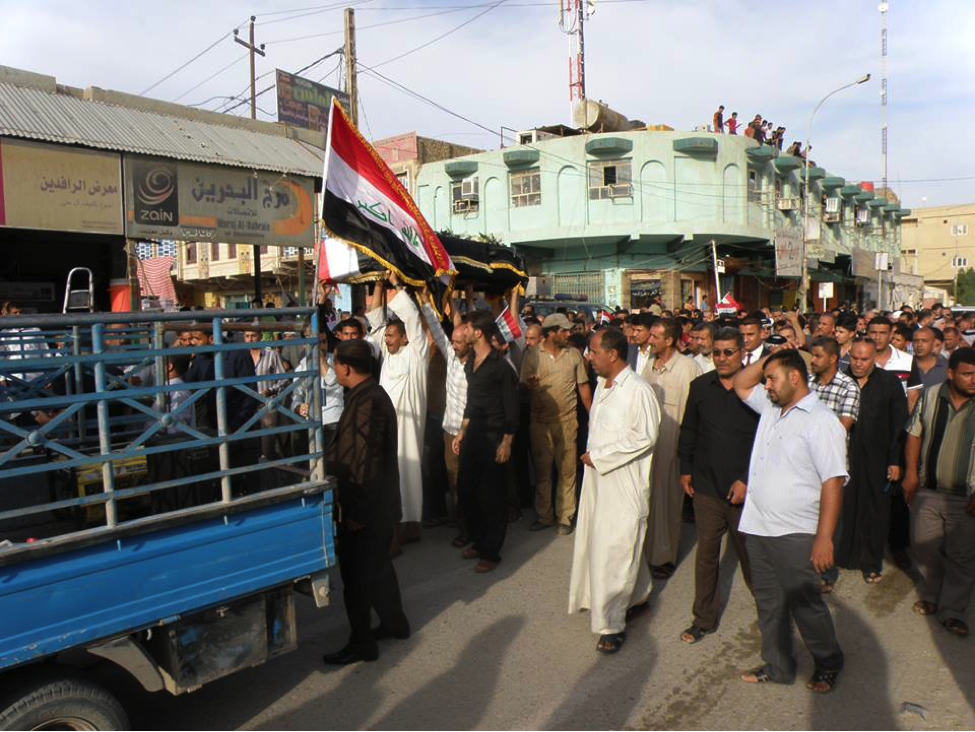
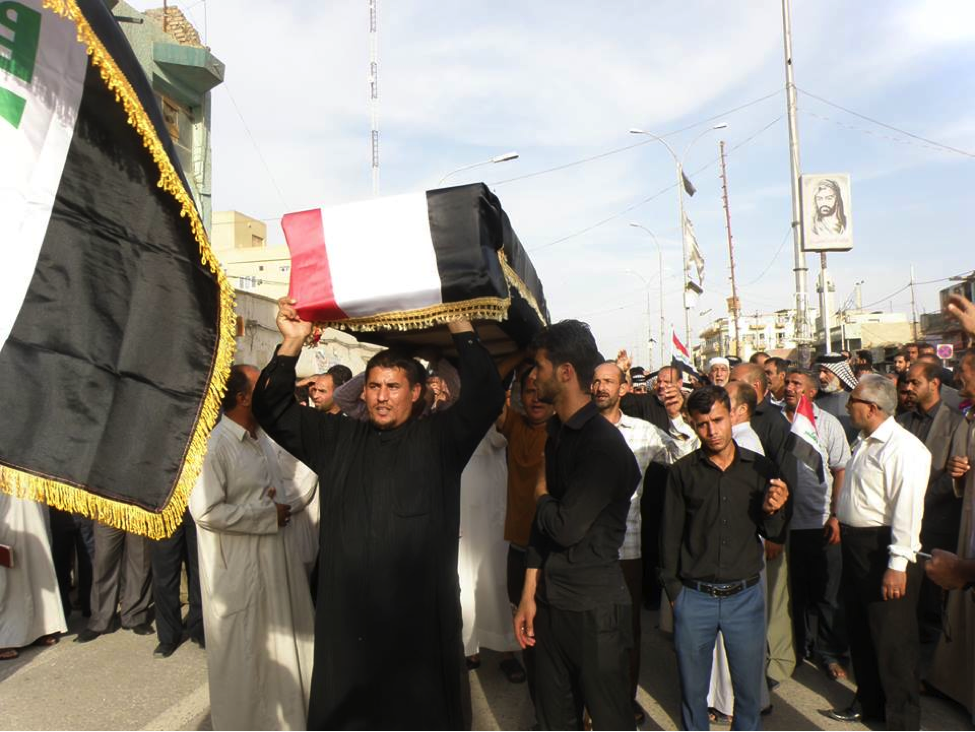
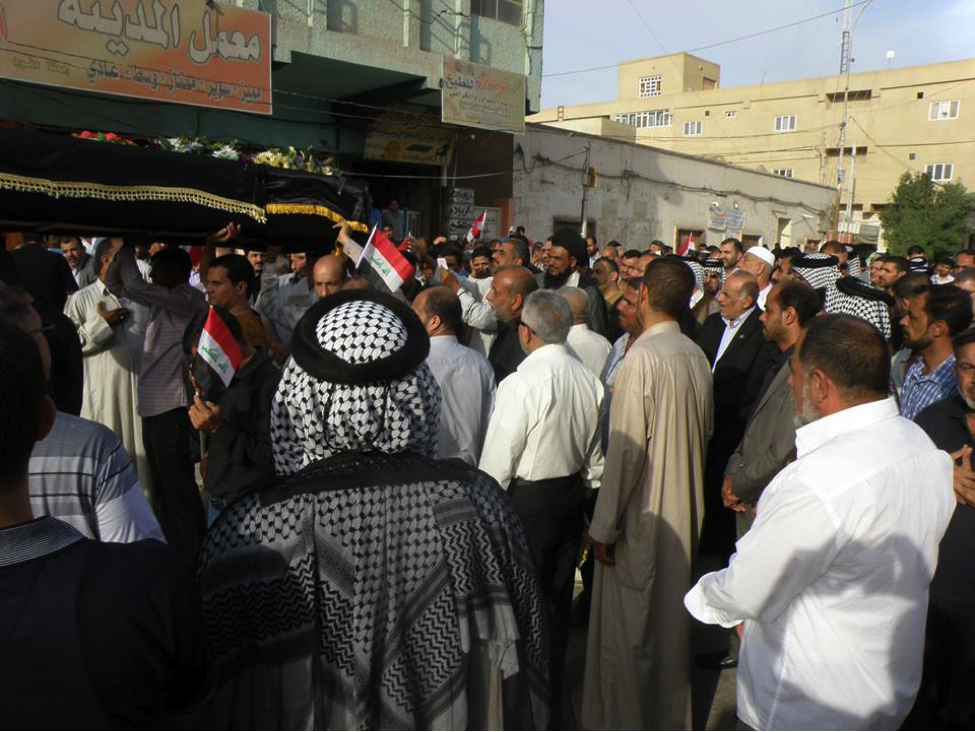
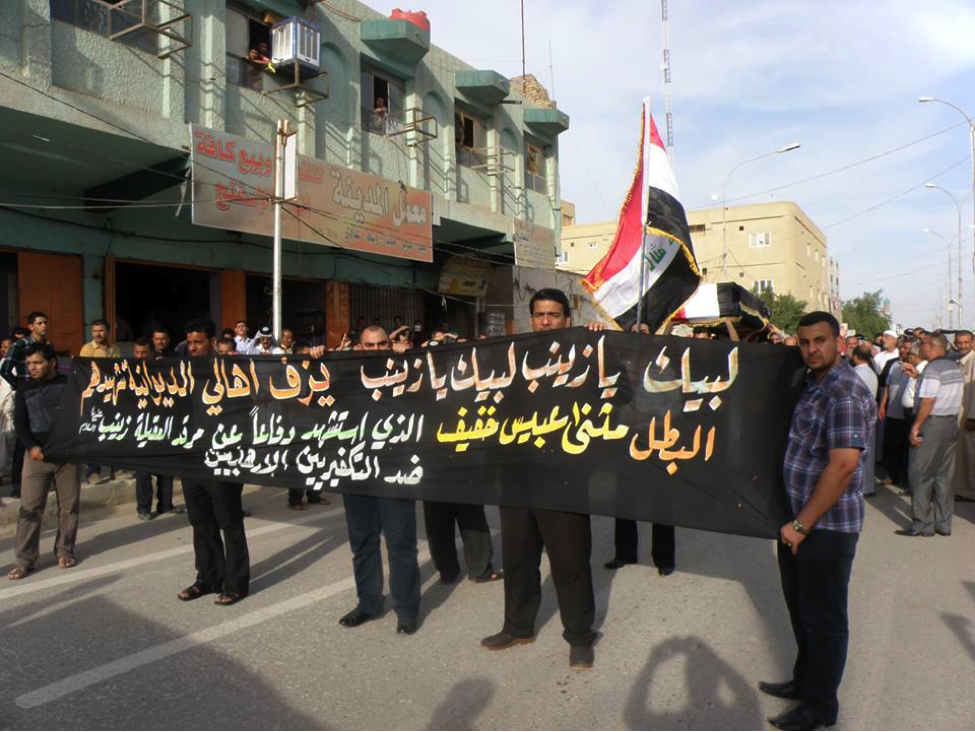
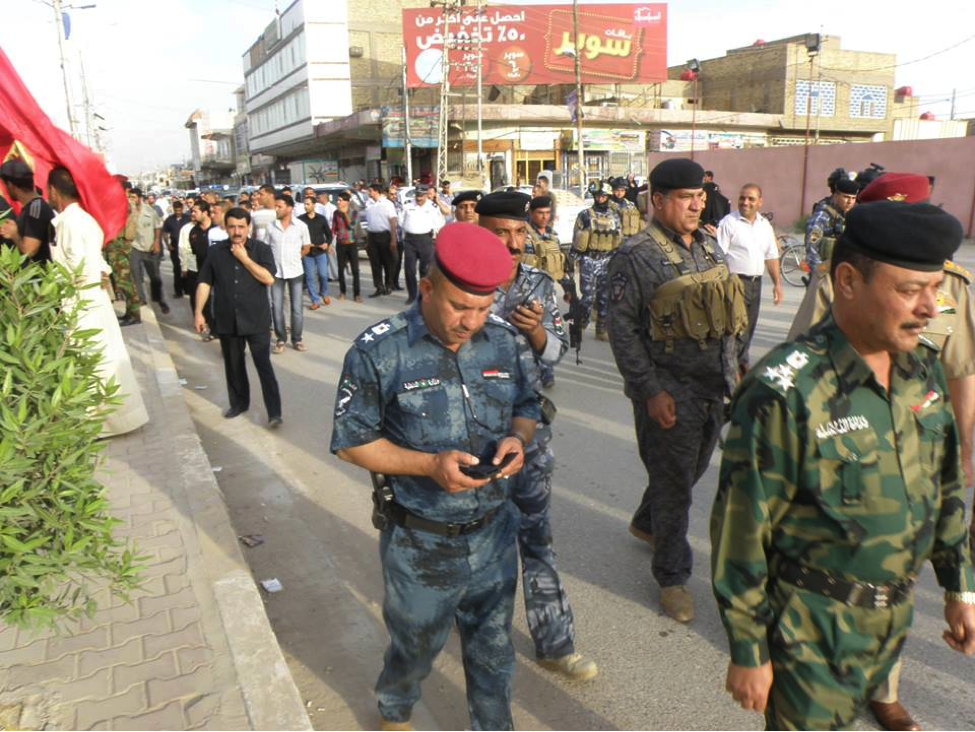
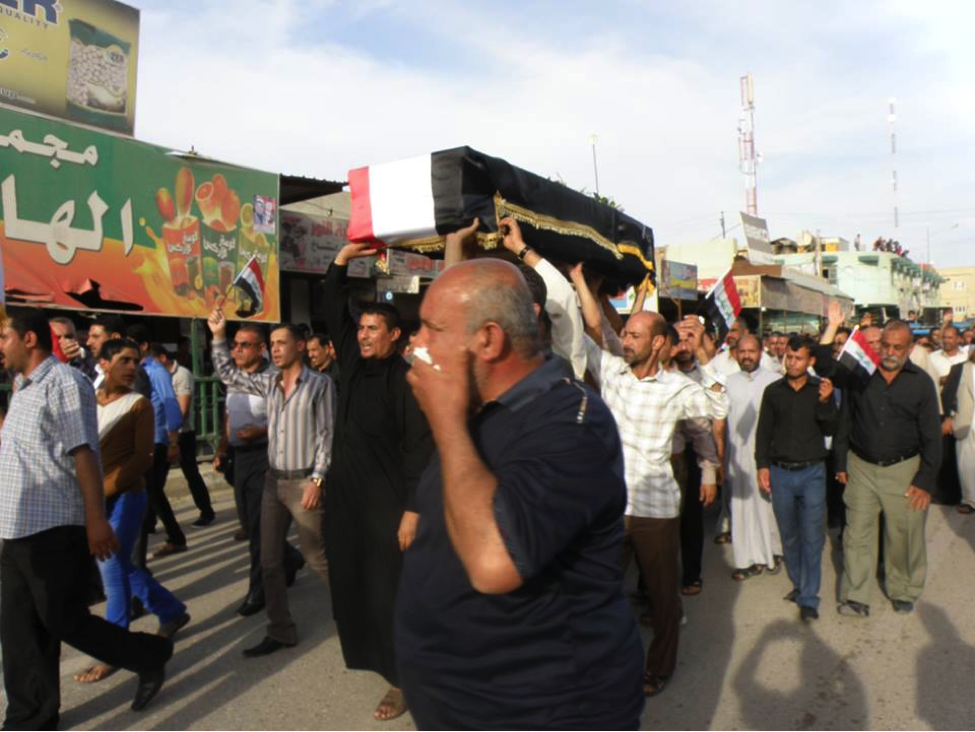
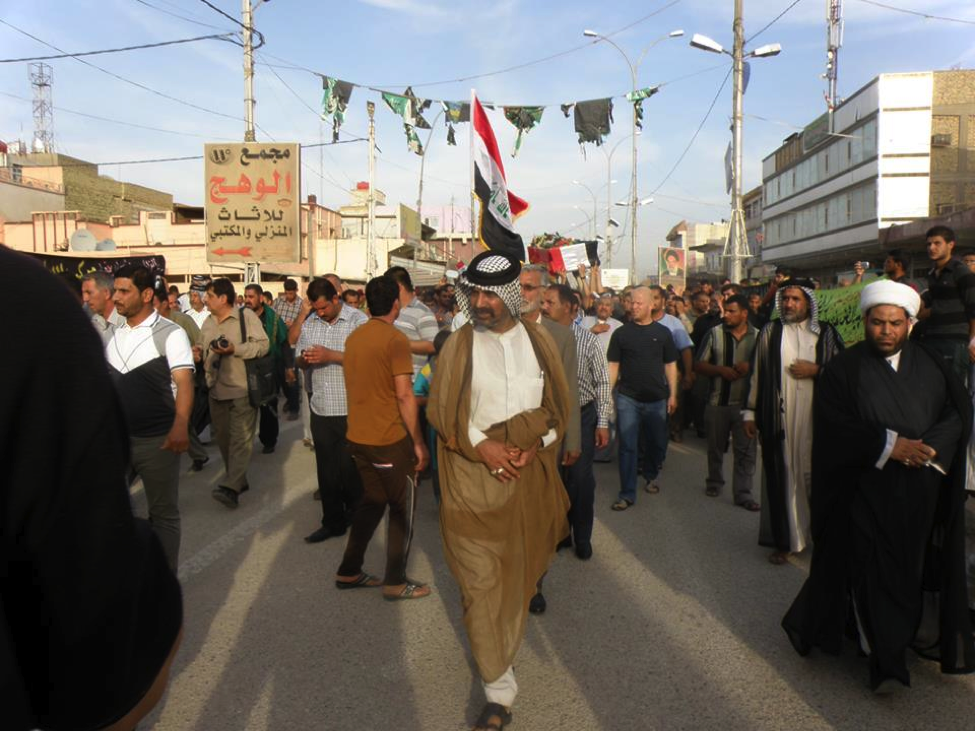
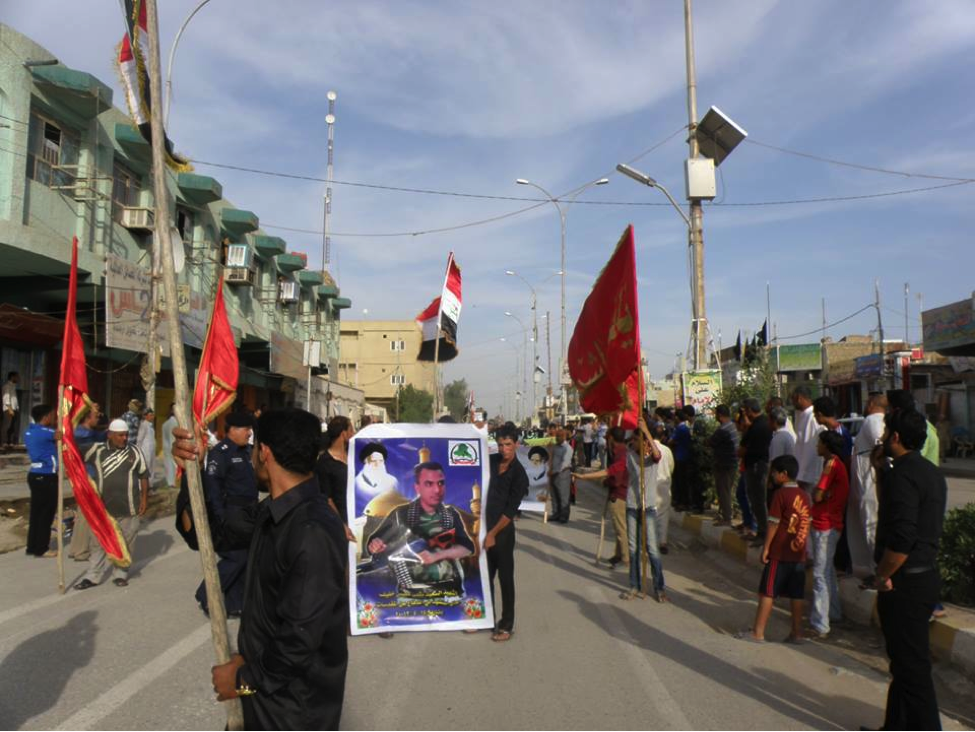
Name: Al-Sa’id Mutheneh ‘Abees Khafeef
Affiliated With: Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq/Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas
Death Announced: May 18, 2013 (via Facebook). The funeral was held on May 18, 2013 in Baghdad.
Notes: Khafeef’s funeral had an entire photo album on Facebook devoted to it. Additionally a video of the funeral was also posted to YouTube.
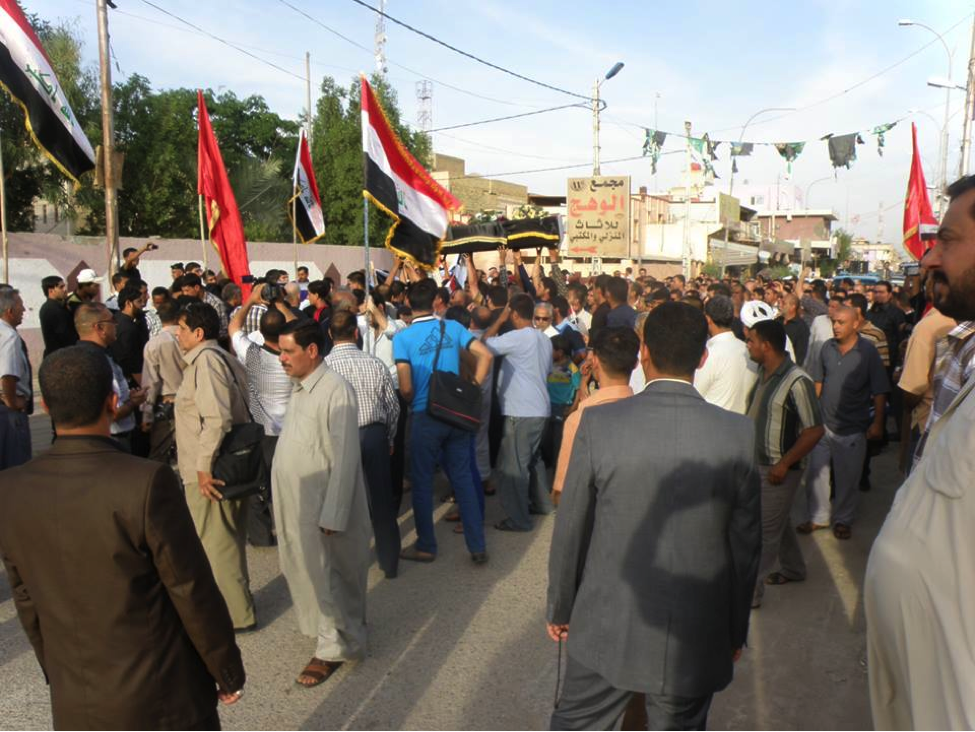













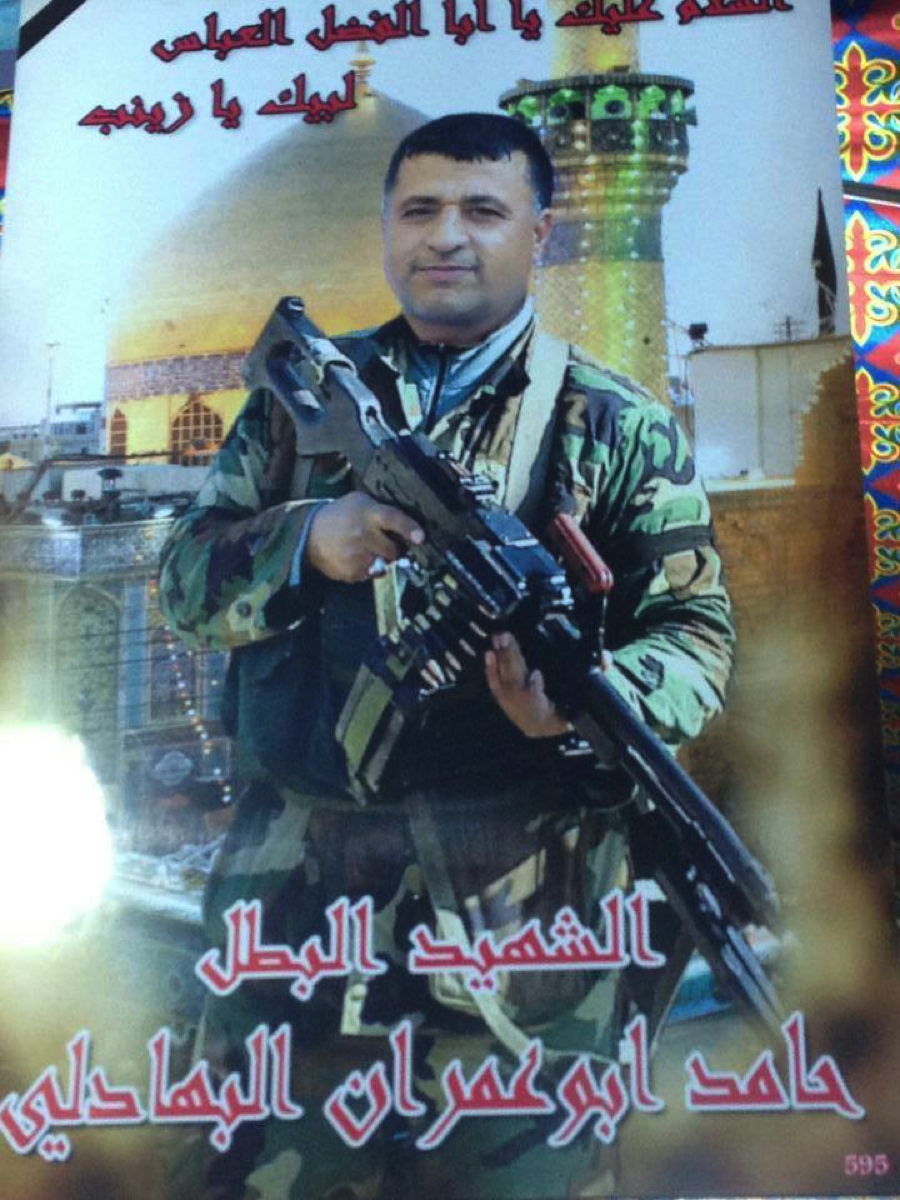
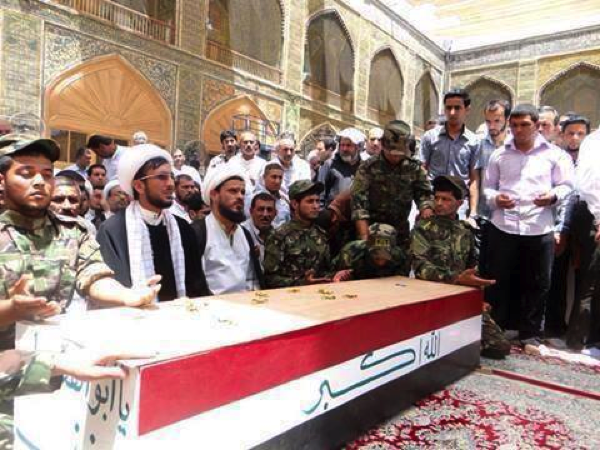
Name: Hamid Abu ‘Amran al-Bahadali (A.K.A. Abu ‘Amran/’Umran)
Affiliated With: Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas/Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq
Death Announced: May 26, 2013 (two Facebook pages claimed his death was announced on May 25th)
Notes: Bahadali was initially only claimed by Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas as a member. However, on May 28th it was announced on a prominent pro-Hizballah/pro-LAFA Facebook page that he also belonged to Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq. His funeral was reportedly held in Baghdad.


Name: Dergham Hisham al-Sa’di al-Baya (A.K.A. Dergham al-Sa’di)
Affiliated With: Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq/Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas
Death Announced: May 23, 2013. Funeral was held (in Iraq) on May 24, 2013.


Name: Iyad Fadhl Matar al-Sarifawi
Affiliated With: Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq
Death Announced: May 28, 2013, (reportedly killed on May 26, 2013)
Notes: This is the first Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq martyrdom poster (for a member killed in Syria) to feature Iraq’s late Grand Ayatollah Muhammed Sadiq al-Sadr (left) and Iranian Supreme Leader, Grand Ayatollah Khamenei (right) as bereaved over the loss of a fighter. Al-Sarifawi’s death could only be confirmed on two pro-Hizballah Facebook pages. Since all other Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq members killed in Syria have also fought under the banner of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas, it is probable that Sarifawi fought as a member of that organization. However, any affiliation with LAFA has not been publicized.

Name: Haidar Jabari Salman al-Jazari
Affiliated With: Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada/Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas
Death Announced: May 24, 2013 (via YouTube video posting). Funeral was held in Basra, Iraq on May 23, 2013.
Notes: In the video for Jazari, it is claimed he was a “Commander” for the “Sacred defense” of the Zaynab Shrine in Damascus. Jazari’s claimed affiliation with Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada (on his martyrdom poster) is another important facet of his background. The group was first mentioned in late-April during a funeral for an Iraqi Shia in Basra. Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada may be a new organization used to vector volunteer fighters to fight at the Zaynab Shrine. As with other Iraqi Shia killed in Syria, Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas also claimed Jazari as a member.

Name: Maytham Khalaf al-‘Aqabi (A.K.A. Ghayth al-‘Asab)
Affiliated With: Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq/Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas
Death Announced: May 9, 2013
Notes: As with most other killed Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq members, ‘Aqabi’s poster features Iraq’s late Grand Ayatollah Muhammed Sadiq al-Sadr (left) and Iranian Supreme Leader, Grand Ayatollah Khamenei (right). His Iraqi roots were not hidden, with Iraq’s flag and the symbol for Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq pictured between the two ayatollahs.
 [1] “Hezbollah leader Nasrallah vows victory in Syria”, BBC, May 25, 2013, https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-middle-east-22669230.
[2] See: “Analysis Of The History And Growth Of Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq, The League Of The Righteous, An Interview With Institute for the Study of War’s Sam Wyer”, Musings On Iraq Blog, January 7, 2013, https://musingsoniraq.blogspot.com/2013/01/analysis-of-history-and-growth-of-asaib.html
[3] Note: As with Lebanese Hizballah, Iraq’s Kata’ib Hizballah has never officially announced its members were being killed in Syria. Instead, the group claimed its fighters were killed while performing their, “Jihadist duties”.
[1] “Hezbollah leader Nasrallah vows victory in Syria”, BBC, May 25, 2013, https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-middle-east-22669230.
[2] See: “Analysis Of The History And Growth Of Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq, The League Of The Righteous, An Interview With Institute for the Study of War’s Sam Wyer”, Musings On Iraq Blog, January 7, 2013, https://musingsoniraq.blogspot.com/2013/01/analysis-of-history-and-growth-of-asaib.html
[3] Note: As with Lebanese Hizballah, Iraq’s Kata’ib Hizballah has never officially announced its members were being killed in Syria. Instead, the group claimed its fighters were killed while performing their, “Jihadist duties”.
