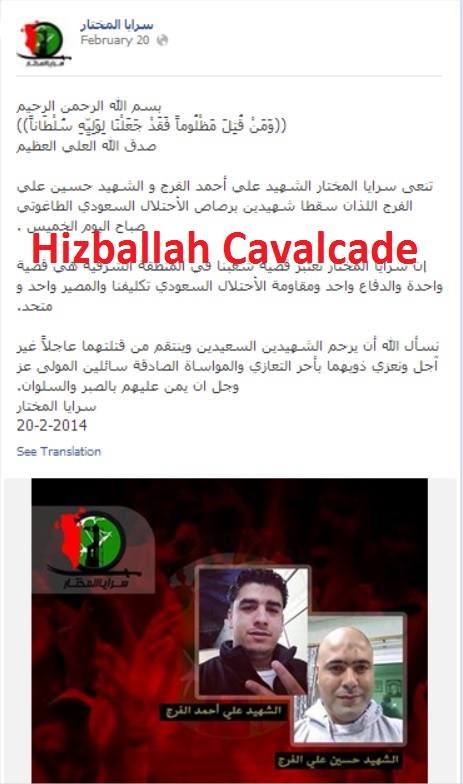
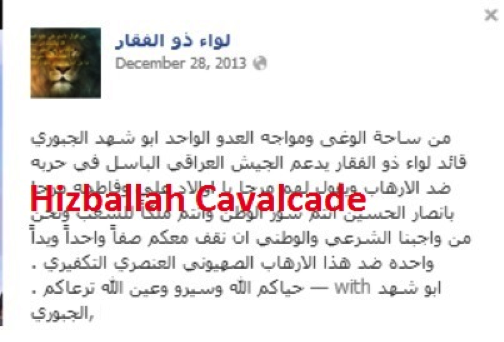
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
The Pearl & the Molotov: Bahrain’s Growing Militant Groups
By Phillip Smyth
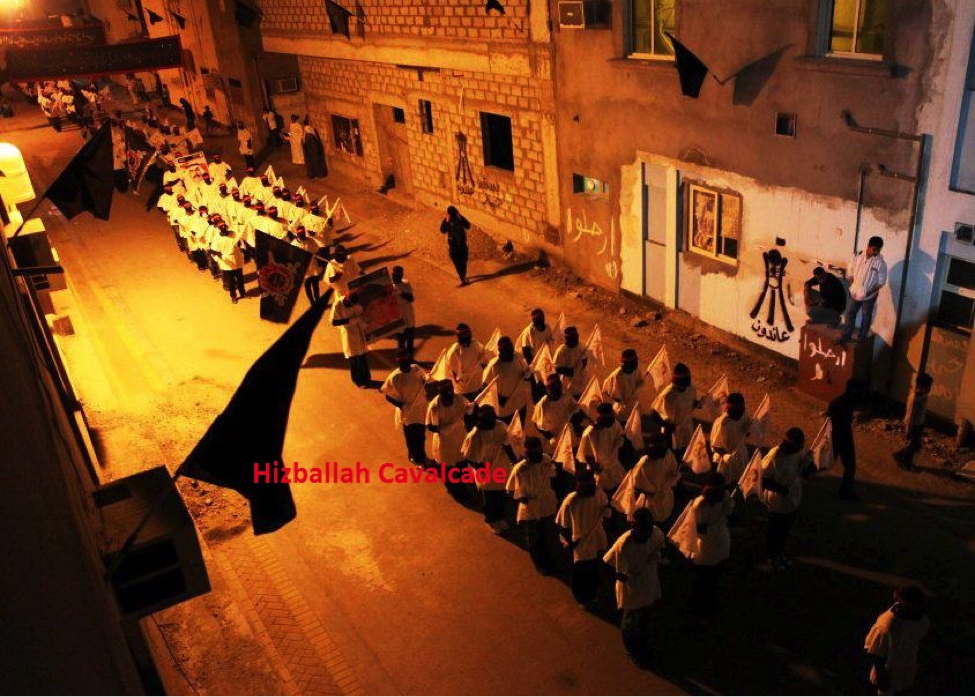

Figure 1: In a nighttime demonstration, members of Sariyya al-Muqawama al-Sha’bia (The Brigades of Popular Resistance) march wearing balaclavas and white burial shrouds. The shrouds exhibit their willingness to be martyred.
While a Shia jihad is being fought in Syria, Bahrain stands as another central conflict which continues to influence discourse, regional policies, and exacerbate sectarian tensions. For many Shia Islamists, particularly militant groups backed by Iran, Bahrain is a major political sore spot and focal point. Over the course of three years, the development of new militant groups within Bahrain has demonstrated that there is an increasing utilization of violent tactics. Since these militant groups are in the more rudimentary stages of development, there is the further possibility that they are increasingly viewing the conflict in Bahrain along regional and sectarian lines.
Main Goals of Hizballah Cavalcade’s Bahrain Posts
Since violent Bahraini organizations have not received adequate profiling, it is the goal of Hizballah Cavalcade to clarify their positions using primary open source material. Thus main goals include, but are not limited to:
- Describing the established organizations, their claims, goals, and ideological orientations.
- Analyzing claims made by the groups.
- Attempting to establish whether the organizations in question may have a connection to external actors.
A Little Background
Since 2011, Shia-majority Bahrain, which is led by the Sunni Khalifa royal family, has been gripped by protests calling for (among other demands) the Khalifas to abdicate, democratic reforms, and greater access for Shia to government positions.[1] For the most part, protests have been peaceful and have at times included both Sunni and Shia Muslims. These protesters have been faced with a number of often violent government crackdowns and accusations of the use torture by authorities.[2]
Yet, the protests, deaths, and growing polarization in Bahrain has regularly been considered a sort of sideshow when compared to other major protests and civil wars in the Middle East. The BBC even referred to the protests as the, “Forgotten Spring.”[3] Still, it would appear that some within the protest movement and possibly external organizations, are bent on forming groups to achieve their ends via violence.
On February 14, 2014—to commemorate the first “Day of Rage” held by Bahraini protesters on the same day in 2011—massive protests, which included main opposition parties and independent groups were held throughout the country. For the most part, these protests were peaceful. Around this time Bahraini authorities also reported a “terror blast.”[4] While this was hardly the first act of violence by a group within Bahrain, the blast underlined a number of more violent actions carried out by new organizations, since 2012.
In December of that year, Reese Erlich of the Global Post noted that younger elements of the protest movement were increasingly turning to violence and were making it difficult for local traditional leaders to control their activities.[5] By the end of 2013, new armed organizations calling for the overthrow of the Bahraini government were announced and continue to claim new attacks within Bahrain. In a period stretching from September 2013-January 2014, most of these new groups adopted higher profiles and attempted to brand their narratives, claimed attacks, and group identities within their online communities and pages.
Understanding Bahraini Militant Rhetoric
Bahraini militant organizations utilize rhetorical phrases and terms found with other Shia Islamist militant groups operating in Syria and Iraq. Often, their enemies are referred to as, “the Khalifa mafia”, “mercenaries” or “Saudi agents”. Nevertheless, this type of rhetoric also draws heavily upon local issues.
There were reports as early as 2011 that Bahrain was recruiting Sunni foreigners to man the internal security apparatus.[6] This issue of naturalizing foreign Sunnis, particularly from Pakistan, is viewed by protest leaders and militants alike as a major sectarian, economic, and social issue.[7] As future posts will show, the utilization of foreign-born police and security personnel is showcased in Bahraini militant propaganda.
Additionally, Saudi Arabia and other Persian Gulf Arab states sent forces as part of the Peninsula Shield which sent troops to Bahrain in March 2011. In April 2013, Peninsula Shield established a further headquarters in Bahrain in order to better coordinate their forces in the country.[8] Bahraini outlets have also reported that as of January 2014 these military forces were still defending “key instillations” and claimed they were not involved in Bahrain’s “internal issues.”[9] The presence of Saudi forces has added to the charge by protesters and militants that the Khalifas are simply propped-up by outside forces. An underlying message, which combines both national and religious identity, is that outside Sunnis (namely those who subscribe to Wahhabism; A religious movement which at times has demonstrated a violent hatred for Shi’ism) are continuing to control what should be Bahraini Shia affairs.
At the time of this writing, none of the groups have overtly stated that their goals are directly related to Shi’ism. However, many of the organizations use Shia-centric imagery, and have almost exclusively Shia members. Moreover, a number of the organizations in question have adopted the moniker, “Al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya” (“The Islamic Resistance”), a term heavily utilized and favored by Iranian-backed organizations, particularly Lebanese Hizballah and Iraq’s Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq.
What About Iran?
Bahraini authorities have regularly accused Iran of being a main driver behind the protests and in violent acts executed against security forces in the country.[10] As documented in other Hizballah Cavalcade posts, Iran makes no secret about its support for Shia jihadis in Iraq, Lebanon, and Syria. In fact, Iran has been a vocal supporter of the Bahraini protesters. In commemoration of 120 protesters killed in Bahrain, Iran opened a memorial for the “martyrs of the Islamic Revolution” in Tehran.[11]
In May 2013 Bahraini authorities banned political organizations within the country from contacting Lebanese Hizballah.[12] Later in December, Lebanese Hizballah’s Al-Manar TV station apologized for their coverage of events in Bahrain.[13] Shia Islamists in Iraq have also launched protests and issued very public criticisms of the situation in Bahrain. Iraq’s Muqtada al-Sadr has also been active in voicing his concern and support for Bahraini Shia protesters.[14]
Of course, Bahrain is not Syria and any claimed “jihad” would be hamstrung by the fact that Bahrain has strict gun control laws.[15] Smuggling of arms is also complicated by the presence of the US Navy’s Fifth Fleet (which is based in Bahrain) and by Bahraini units. As a result, many attacks have not used firearms, but instead utilize Molotov cocktails, hand grenades, homemade bombs, and other improvised weapons. In December 2013, Bahraini authorities claimed to intercept a shipment of “Iranian-made” explosives and other arms.[16]
Despite the many claims of Iranian involvement, there have been strong denials regarding the “Iranian hand” since the start of the protests.[17] Available information on armed organizations and their links to Iran is sparse and still developing. Additionally, some sympathetic to the protest movement have claimed these organizations are little more than fabrications by the Bahraini authorities. Regardless, this does not necessitate that Iran is not attempting to co-opt some of the more violent elements belonging to the anti-government ranks, create new militant organizations in Bahrain, or extend a more covert hand to those engaged in violence. Forthcoming posts will delve into these specifics in more detail.
[1] Some of their 2011 demands were listed in this Reuters piece:
https://www.reuters.com/article/2011/02/15/us-bahrain-protesters-idUSTRE71E3YN20110215.
[2] See:
https://www.reuters.com/article/2013/12/31/us-bahrain-torture-idUSBRE9BU0BY20131231.
[3] See:
https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/b01dms66.
[4] See:
https://www.reuters.com/article/2014/02/15/us-bahrain-uprising-anniversary-idUSBREA1E08P20140215.
[5] See:
https://www.globalpost.com/dispatch/news/regions/middle-east/121212/bahrain-protests-opposition-violence.
[6] See:
https://www.theguardian.com/world/2011/feb/17/bahrain-security-forces-sunni-foreign.
[7] See:
https://world.time.com/2011/03/11/what-lies-beneath-bahrains-new-citizens-fuel-unrest/.
[8] See:
https://gulfnews.com/news/gulf/bahrain/peninsula-shield-bahrain-headquarters-hailed-1.1172079.
[9] See:
https://www.gulf-daily-news.com/NewsDetails.aspx?storyid=368082.
[10] See:
https://gulfnews.com/news/gulf/bahrain/iran-must-stop-meddling-in-our-affairs-bahrain-1.1296492. Most recently, Bahraini authorities have also accused Iran of being behind training and equipping those who carried out bombings in the kingdom. See:
https://www.aljazeera.com/news/middleeast/2014/01/bahrain-accuses-iran-training-rebels-201413144049814960.html.
[11] See:
https://www.jahannews.com/vdcjhtetiuqexoz.fsfu.html,
https://www.e-heyat.com/fa/63/65610,%D9%BE%D8%B1%D8%AF%D9%87-%D8%A8%D8%B1%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B1%DB%8C-%D8%A7%D8%B2-%DB%8C%D8%A7%D8%AF%D8%A8%D9%88%D8%AF-%D8%B4%D9%87%D8%AF%D8%A7%DB%8C-%D8%A8%D8%AD%D8%B1%DB%8C%D9%86-%D8%AF%D8%B1-%D8%AA%D9%87%D8%B1%D8%A7%D9%86-%D8%AA%D8%B5%D8%A7%D9%88%DB%8C%D8%B1.aspx?AspxAutoDetectCookieSupport=1, and
https://www.tasnimnews.com/Home/Single/282308.
[12] See:
https://www.reuters.com/article/2013/05/27/us-bahrain-hezbollah-idUSBRE94Q0CR20130527. Bahraini authorities also went so far as to ban books they felt were connected to Lebanese Hizballah (
https://www.bna.bh/portal/en/news/579261) and restrict access to websites affiliated with the group (
https://www.bna.bh/portal/en/news/573944).
[13] See:
https://www.dailystar.com.lb/News/Lebanon-News/2013/Dec-08/240287-hezbollah-media-apologizes-over-bahrain-coverage.ashx#axzz2uHGo5rHE.
[14] Sadr organized rallies in 2011 in Basra and Baghdad. See:
https://www.reuters.com/article/2011/03/16/us-bahrain-iraq-idUSTRE72F4U220110316. In 2012 he also demanded the release of a German Shia prisoner jailed by Bahraini authorities
https://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5hdjuVY1N_2x3OsmZC0fOfUmOThbQ?docId=CNG.7e3f91968ac1c442282f98bc759b433d.3f1.
[15] In some cases, possession of illegal firearms could land one in prison for 15 years. See:
https://www.khaleejtimes.com/DisplayArticleNew.asp?xfile=/data/middleeast/2012/April/middleeast_April100.xml§ion=middleeast.
[16] See: