
_______________
To inquire about a translation for this video message for a fee email: [email protected]
Category: Hizballah
New video message from Jabhat al-Nuṣrah: "Syrian Refugee Camps in Jarūd 'Arsāl Between the Bombings and Injustices of the Lebanese Army and the Iranian Ḥizb al-Lāt"

_______________
To inquire about a translation for this video message for a fee email: [email protected]
New video message from Jaysh al-Fataḥ: "Targeting a Car of Commanders of the Party of Satan With a Guided Missile and Killing All of Them in the Area of al-Rahwah"

_________________
To inquire about a translation for this video message for a fee email: [email protected]
Jihadology Podcast: Syria Status Update with Charles Lister
Charles Lister comes on the show to discuss a wide range of topics related to the current situation in Syria:
- The background and evolution of Jaysh al-Fatah
- What Jaysh al-Fatah has meant to rebel and Jabhat al-Nusra victories in Syria
- The recent formation of a Jaysh al-Fatah branch in the south and what the southern front in the war currently looks like
- How the regime, Iran, and Hizballah have reacted to the changing military dynamics on the ground
- The recent fighting between the Kurds and the Islamic State in northern al-Raqqah governorate
Links:
- Charles Lister (@Charles_Lister) on Twitter
- Aaron Y. Zelin (@azelin) on Twitter
- Charles’ forthcoming book “The Syrian Jihad: Al-Qaeda, the Islamic State and the Evolution of an Insurgency,” which comes out on September 24
The show is produced by Karl Morand. If you have any feedback you can email [email protected] or find us on Twitter: @JihadPod
You can subscribe to the show in iTunes or with the show’s RSS feed.
Download this Episode (46.5 mb mp3)
New video message from Jabhat al-Nuṣrah: "Damaging a 57mm Canon of the Iranian Ḥizb al-Lāt With a Guided Missile"

_____________
To inquire about a translation for this video message for a fee email: [email protected]
New video message from Jabhat al-Nuṣrah: "Damaging a Launching Pad for Cornet Missiles Belonging to Ḥizb al-Lāt in al-Thalājah Hill in Jarad Flīṭah"

_______________
To inquire about a translation for this video message for a fee email: [email protected]
New video message from Jabhat al-Nuṣrah: "Destruction of 57 mm Canon of the Iranian Ḥizb Allah"

________________
To inquire about a translation for this video message for a fee email: [email protected]
Hizballah Cavalcade: Hizballah al-Abrar: The Latest Hizballah Franchise in Iraq
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Hizballah al-Abrar: The Latest Hizballah Franchise in Iraq
By Phillip Smyth

Figure 1: Hizballah al-Abrar
Hizballah al-Abrar (HAA or the Party of God of the Righteous) follows in the footsteps of a long line of new Shia militia organizations which have been announced in Iraq since June 2014. These groups often model their symbolism, organizational structures, and ideological profile on Lebanese Hizballah. Additionally, these groups commonly have strong links and at times have shared commanders with other established Shia militia proxies of Iran.
HAA is no exception, utilizing the official logo of Lebanese Hizballah with the addition of a stylized map of Iraq in the globe section of the symbol. The group, mirroring other Iranian proxy Shia groups in Iraq, Lebanon, and Syria, also refers to itself as “al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya fi al-Iraq” (The Islamic Resistance in Iraq). HAA has done little to hide its connections to Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq (AAH). If anything, HAA actually promotes the links. Furthermore, its connections to other organizations promoting Iran’s Khomeinist ideology have been featured in other photos.
HAA’s secretary general, Sheikh Fadhel al-Khaz’ali, has been prominently featured in the group’s propaganda releases and has been used to show the group’s links to Iran’s Iraqi proxy groups. In one photo, Khaz’ali is shown receiving an award from the Imam Khomeini Relief Foundation. In others, Khaz’ali is shown standing under the AAH banner.
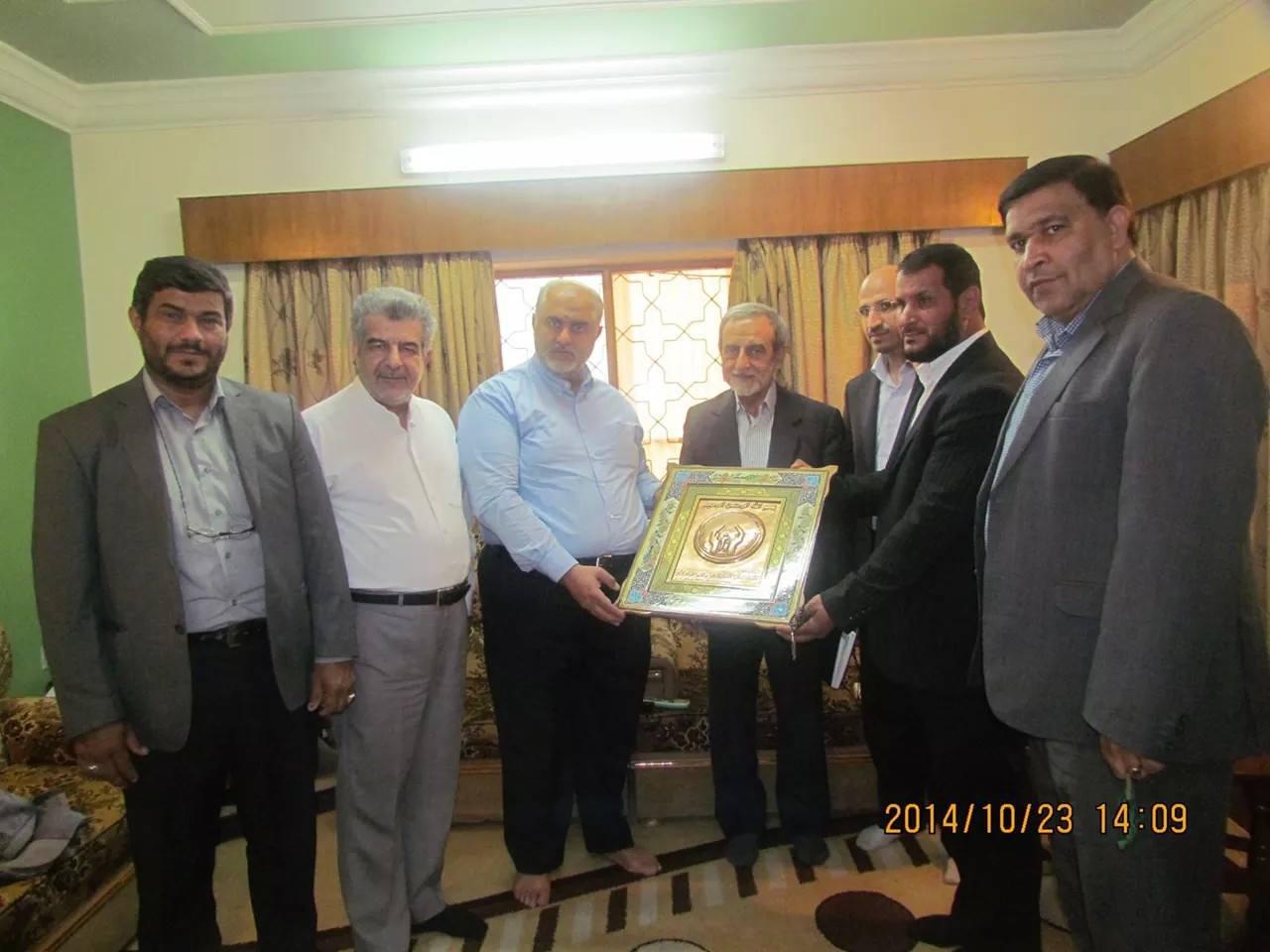

Figure 2: This photo claims to show Sheikh Fadhel al-Khaz’ali recieving an award from the Imam Khomeini Relief Foundation.
Following a social media model which had been replicated by other newer Shia militias in Syria and Iraq, HAA initially published easily created images showing the group’s new symbol. Later, photos claiming to show fighters from the group, a more official looking fighting force, complete with patches, flags, and official statements began to appear after the group’s initial appearance on Facebook in August.

Figure 3: A HAA fighter holding the group’s flag. This picture claimed to show HAA fighters heading to the Battle of Amerli.
In terms of combat deployments, the group has claimed it sent fighters to Amerli, Diyala, Baghdad, and the key battlefront of Jurf al-Sakhr. In a video released on October 28, 2014, HAA combatants waved the group’s flag along with that of Karbala-based Shia militia, Firqat al-‘Abbas al-Qataliya – al-Dafa’ ‘an Muqadisat al-Iraq (The Abbas Fighting Group – Defenders of the Iraqi Holy Sites) in what appeared to be an impromptu celebration commemorating recent victories in Jurf al-Sakhr.
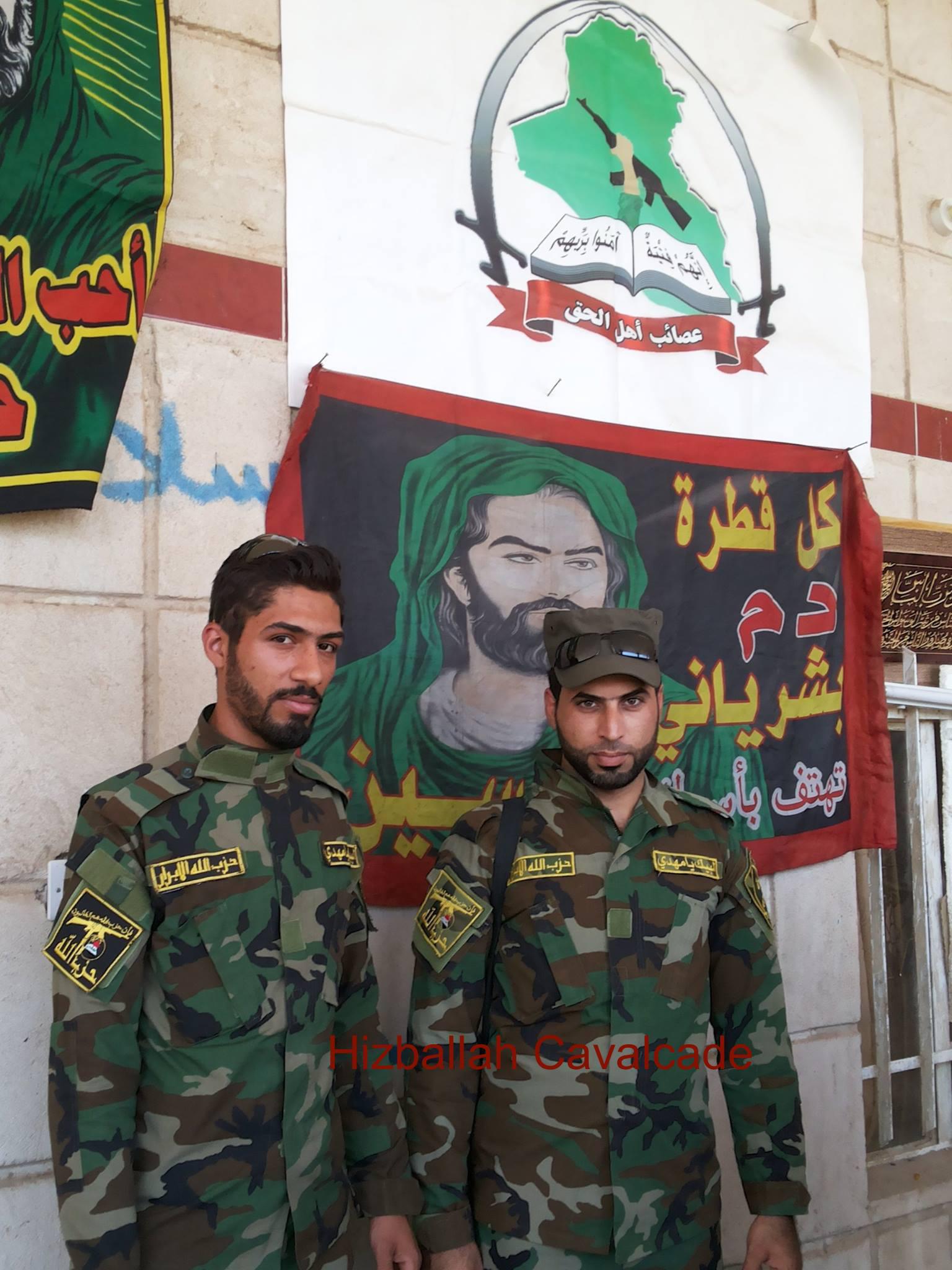

Figure 4: Two HAA fighters, Yasir al-Khazarji and Amir Sa’adi pose together under AAH and Shia religious banners. Note the HAA-specific arm patches.
Despite the fact that HAA has claimed to be positioned across diverse sections of Iraq, it has not stated the size of its force. Furthermore, the group’s quickly paced attempt to appear more professional online may demonstrate that the group will be further developed within Iraq’s Shia militia and political sphere. In fact, Sheikh al-Khaz’ali was pictured in an undated photograph with former Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki and other leaders from Iraq’s internal security forces and army.
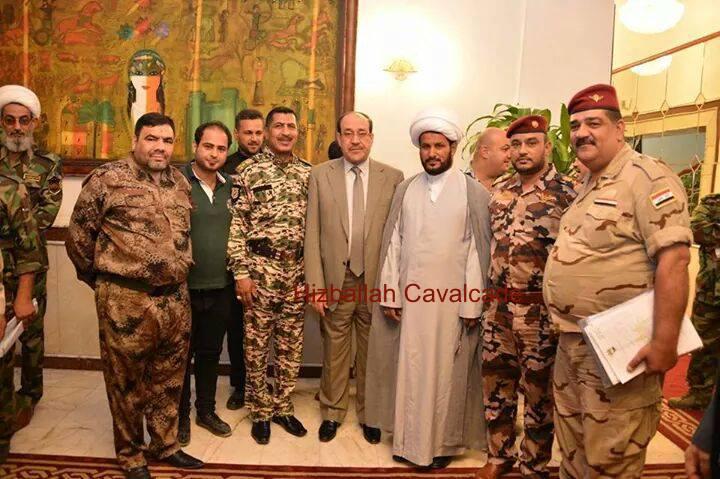

Figure 5(Right): Sheikh Khaz’ali is shown with a stylized Hizballah and Iraqi national flag.

Figure 6 (Left): Sheikh Fadhel al-Khaz’ali poses with former Iraqi Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki and others.
Thus far, the group has released a number of official statements. Below, a translated version of one statement dealing with “rumors” about ISIS penetrations of Baghdad, gives insight into the group’s worldview, including their anti-U.S. positions and opinions on fighting ISIS.

Figure 7: HAA fighters gather for a photograph.

Figure 8: AAH and HAA leaders are pictured together.
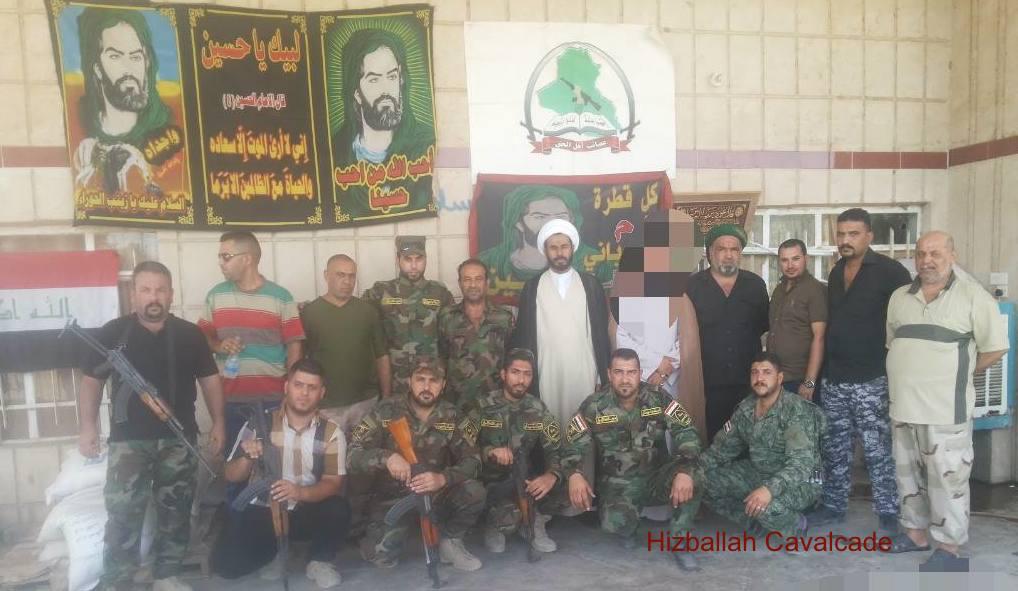

Figure 9: HAA central leadership and combatants pose under Shia religious and an AAH banner.

Figure 10: HAA announcement released on social media on October 18, 2014.
Translation of HAA’s October 18, 2014 Announcement*:
There are rumors on social media websites that ISIS is close to entering Baghdad and that there are tens of thousands [of ISIS fighters] steps away from the heart of the capital, while thousands of others are standing behind the gates. Rumors about Baghdad Airport being under fire, that the Americans were able to kick ISIS groups out from the outskirts of the airport, rumors that the belt of Baghdad will close up on the Sadr City and Al-Shu’ala, rumors that millions of residents will become refugees, and that the flag of ISIS will be set up in Khazimiya, in Sayyid Idris [an important Shia shrine south of Najaf] and in the area of Khamsa [a Baghdad neighborhood], Khamsin, or in Muzzafar Square [a central square in Sadr City]. Despite all of these rumors, the clowns, murderers, and killers from ISIS are not close to entering Baghdad. None of them [the rumors] represents a grain of truth.
These [rumors] represent a lost bet that aims to spread chaos, frustration, and misery among the majority of the Iraqi people. This fear mongering is an old method of psychological warfare, it also serves to allow certain material and symbolic games. Regarding the theory of ISIS closing up on Baghdad, the Americans might be the party that is the most excited along with ISIS, Arab countries, and members of the Sunni minority. What are the possibilities this gang will enter the capital and is there a possibility to achieve this?
By reviewing ground data in places where the terrorist organization has entered, such as Mosul, Anbar, some regions of Salah Ad-Din [province], and limited regions of Diyala, we find that it is impossible for ISIS to enter Baghdad, because Baghdad has taken the necessary security steps. Second, because the forces of the popular [militias] and jihadists groups, especially the Islamic Resistance in Iraq Hizballah al-Abrar in Baghdad, can send the terrorists back to hell within hours not days. The most important thing is that those who foster terror and sleeper cells in Baghdad, even if they move along with ISIS’s movement, will not be able to offer full strategic and security coverage for them, because those who foster these cells are based in limited areas which are under surveillance and observation.
Entering Baghdad is not easy and there is no way to be convinced that it will happen quickly and easily. Especially if we want to keep in mind all of the facts on the ground and take into consideration the strength of the defending group, especially since there is proof that crushing ISIS is a likelihood. As is the case in Amerli, Samarra, and areas inhabited by most of the Iraqi people, the main factors which helped ISIS to reach Nineveh [Province] and Ramadi and some regions here and there, is not the strength of ISIS but because of [their sneaky behavior] betrayal. They are betraying these regions by conspiring with murderers and criminals under sectarian and vengeful pretexts. ISIS cannot come close to the walls of Baghdad because the forces which are defending Baghdad and consisting of Hizballah al-Abrar, the forces of the popular movements, and the holy warriors in all jihadist cells, along with governmental and security forces, supported by the heroes of Iraqi Air Force, can confront any attempt to take Baghdad. The fate of ISIS will be failure, especially because the defenders of Baghdad have more privileges than the attackers…we ask God to protect us and the Iraqi people.
* Some sections have been edited so there is better flow in English. Additionally, ISIS is referred to as “Da’ish” in the original statement.
Hizballah Cavalcade: IRGC's First Martyr vs. ISIS in Iraq?
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
IRGC’s First Martyr vs. ISIS in Iraq?
By Phillip Smyth
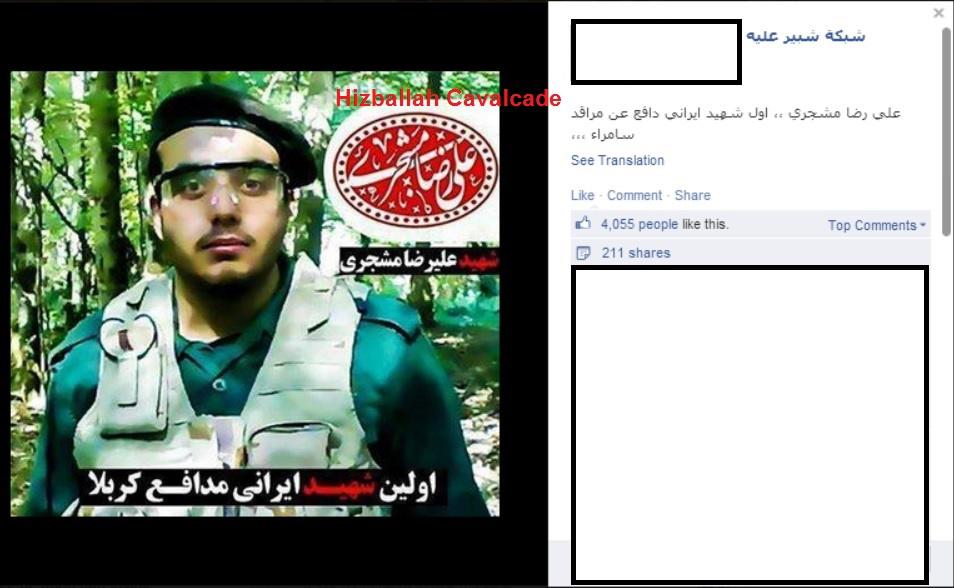
Figure 1: Post claiming the IRGC member was killed fighting in Samarra.
According to Iranian media outlets Ali Reza Moshajari, a member of Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), was reportedly killed in an accident on June 14, 2014.1 In another article written by the IRGC-linked Tasnim News, Moshajari was killed in “Western Iran” while on “a mission.” In all of the articles he is described as a “martyr” or “hero martyr.” However, his death was not such an open and shut case. In fact, Moshajari’s death may be further evidence of direct IRGC presence in Iraq.
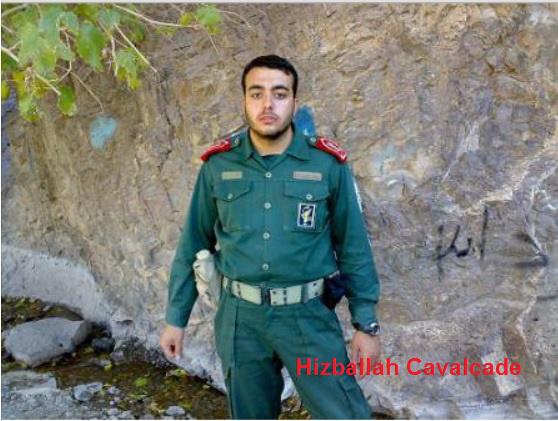

Figure 2: Moshajari in his IRGC uniform.
Before official announcements were made by groups such as Kata’ib Hizballah or Lebanese Hizballah stating they were both involved in fighting in Syria, both organizations would give vague explanations for the funerals of their members. The former would claim members had died due to illness or for other non-combat related reasons. Lebanese Hizballah would often only state that their fallen fighter had been “killed doing his jihadist duty.” Nevertheless, on social media run by many of these elements, it would be stated that the fallen fighters had in fact been killed in Syria. This may be the same type of structured announcement.
In some ways, this mirrors the announcements for the fallen IRGC member who was not only listed as a martyr for battle on a mission of some sort, but had competing accounts for how and where he died.
On Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps-linked (often these pages are run directly by the IRGC for internal and narrative purposes) social media networks–which run the gambit from Twitter and Facebook to Google Plus and YouTube—have cast Moshajari as an IRGC fighter who had been “martyred” in the IRGC deployment to Iraq.
It is possible that Moshajari was actually killed in an accident while deploying with IRGC units to sections of Iraq bordering Iran. CNN reported that 500 IRGC had been deployed to Diyala, an Iraqi province on the border with Iran.2 In Diyala Province, Kata’ib Hizballah and other Iraqi Shia Islamist groups backed by Iran have also reported being engaged in combat against units belonging to the Islamic State of Iraq and al-Sham (ISIS).
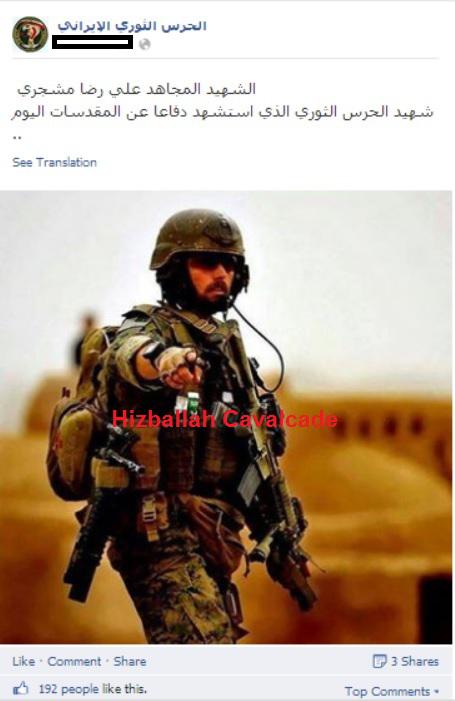
Figure 3: An IRGC Facebook page claiming Moshajari was the first IRGC martyr in Iraq while defending the shrines.
However, other Facebook-based sites with links to Iran’s regional Shia Islamist proxies and the IRGC also claimed that he had been involved in the “defense of Samarra.” Samarra has been a city of heavily publicized deployments by Iran’s Shi’a Islamist proxies within Iraq, mainly due to the fact that the holy Askari Shrine is located in the city.

Figure 4: Killed IRGC member’s martyrdom poster. The poster was circulated primarily on Facebook and Twitter. It claims he was an “Iranian defender of Karbala.”
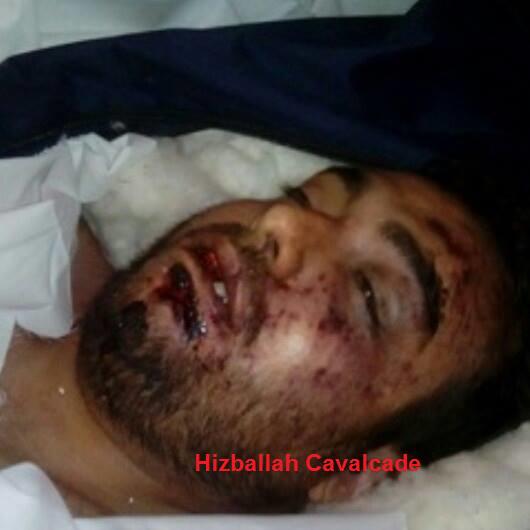

Figure 5: A photo of Moshajari’s face prior to his funeral.
_________
NOTES:
Hizballah Cavalcade: Singing Hizballah’s Tune in Manama: Why Are Bahrain’s Militants Using the Music of Iran’s Proxies?
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
–
Singing Hizballah’s Tune in Manama: Why Are Bahrain’s Militants Using the Music of Iran’s Proxies?
By Phillip Smyth
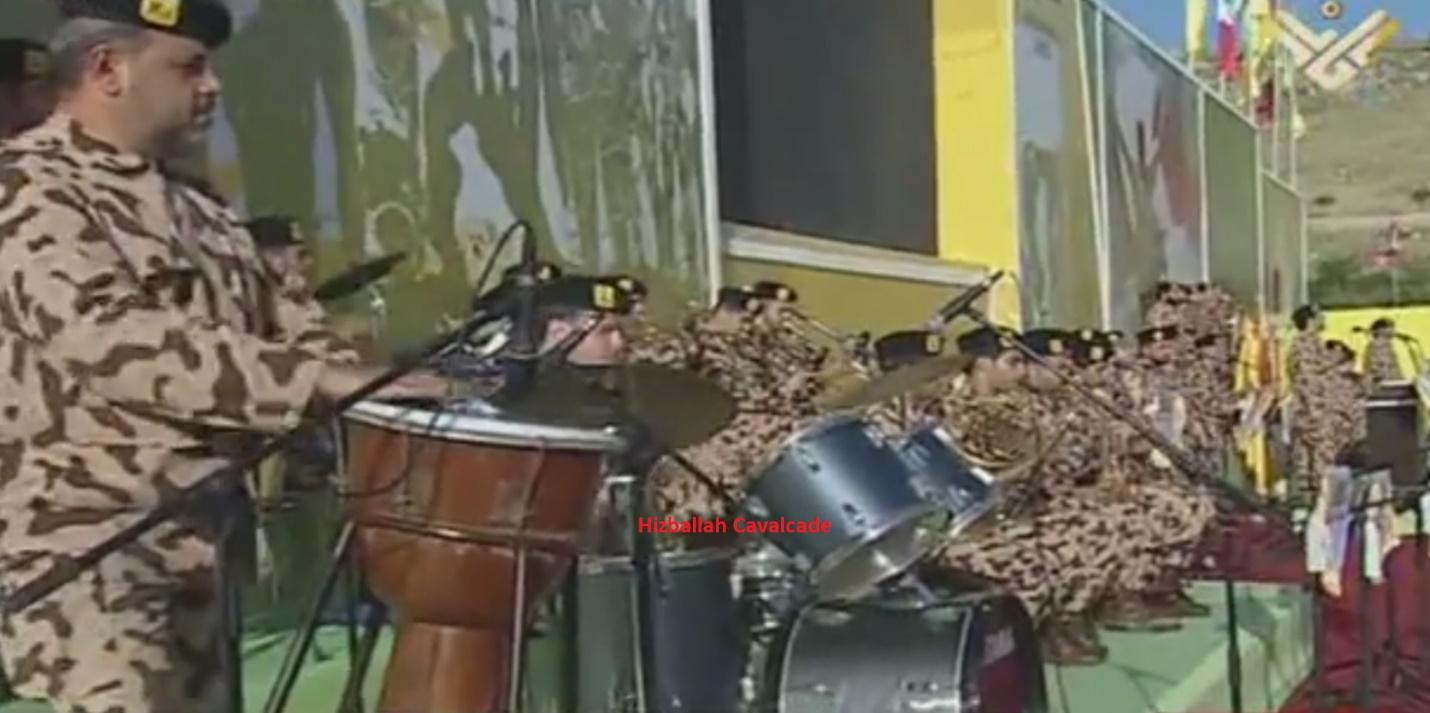

Figure 1: A screenshot of a Hizballah musical band performing at the 2013 “Resistance and Liberation Festival”
Bahraini officials have repeatedly accused anti-government militants and protesters in the country of being supplied, trained, and supported by Iran and its numerous regional proxies. Still, the government of Bahrain has done little to bolster their claims of deep and intrinsic links between Bahraini militants and Tehran. Along with official Iranian denials, the issue of Iran-Bahraini militant links is still quite hazy. Nonetheless, this does not mean that within the material released by Bahraini militant organizations that there are not hints of some level of Iranian influence. One of the more intriguing pieces pointing to influence from Iranian-backed organizations comes from the utilization of specific types of music in the many propaganda videos released by Bahraini militants, their sympathizers, and amplifiers.
Numerous instances of Bahraini militants producing propaganda videos with different varieties of music created and utilized by Iranian-backed proxies could indicate a connection with Iran’s proxies. Nevertheless, this type of overlap should not be viewed as a “smoking gun” affirming Iranian involvement. However, it does assist in piecing together direct and indirect influences.
The pieces of music in question were originally developed and used by Iranian proxy organizations, particularly Lebanese Hizballah, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq (AAH), and Kata’ib Hizballah. In fact, some of the songs that have been promoted fit a long standing media strategy employed by the aforementioned groups and Iran when manufacturing narratives and perceptions for themselves and other armed groups.
The use of music as a transferable propaganda medium follows a very formulaic strategy used by Iran and its “Islamic Resistance” proxy organizations for many years. Often, songs produced for one group are repackaged for newer organizations in other geographic locations. The songs are then altered in a way to make them appeal to the populations and target audience where the new group is located.
Possible Reasons for Using Specific Songs
Why would Bahraini militant groups utilize Hizballah and its Iraqi clones’ music and with such frequency? Some possible answers include:
- Direct Iranian influence or assistance provided to the developing militant groups.
- Video editing/production was offered to Bahraini militants by Iran and/or its proxies as a means to influence and shape militant organizations and to encourage the adoption of a more bellicose strategy to the broader (and more peaceful) protester audience.
- Bahraini militants sympathize with Iranian-proxy groups, their exploits, and with the general concept of “Al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya” (“The Islamic Resistance”). The hope to be as successful, feared, and/or respected as those organizations has led them to adopt the same varieties of music.
- Thumbing their nose at the government: With the government of Bahrain accusing protesters and militants of being Iranian proxies, militant groups may use the material as a way to subtly frighten or encourage speculation among Bahraini government and other observers.
- Narrative Goals: One song by Lebanese Hizballah’s Ali al-Attar called “Wa’ad al-Asra” or “The Prisoner’s Promise” was written to celebrate the release of prisoners Hizballah sought to free during the 2006 Hizballah-Israel War. While the song makes clear references to Lebanese Hizballah and themes related to the 2006 war, the same song was employed by some Bahraini protesters (as background music for their uploaded clips) when they protested the government’s detention of key protest-leaders.
Auto-Tuning the Revolution: Examples of the Musical Overlap
In March 2014, a music video which was claimed to have been produced by “Saraya al-Bahrainiyya al-Muqawama” or the Bahraini Resistance Brigades, (which is likely another name used by The February 14 Youth Coalition’s Saraya al-Muqawama al-Sha’biya [Popular Resistance Brigades]) was posted by the popular Revolution Bahrain’s YouTube Channel. The video featured a montage of edited clips, which purported to show Bahraini militants engaged in training. The music video also included a number of videos of bombings orchestrated by militant Bahraini organizations.
Yet, the music used was strikingly familiar in the circles of Iranian-backed Shi’a Islamist groups. In fact, Iranian-backed Iraqi group, Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq had released the exact tune back in 2011 to commemorate attacks the group orchestrated against U.S. targets to demonstrate solidarity with Bahrain’s protesters. Later in 2011, when fellow Iranian proxy Kata’ib Hizballah released footage of attacks it had also launched in solidarity with Bahraini protesters, it too used the same song.
However, the song was neither originally Bahraini nor Iraqi, instead its origins were rooted father to the west, in Lebanon. The original song, “Risalat al-Thuwar” (“Message of the Rebels”), was performed by one of Lebanese Hizballah’s official bands, Firqat al-Fajr (The Dawn Band), following the 2006 Hizballah-Israel War. It first appeared on the band’s 2007 “Lahan al-Turab” or “Melody of the Soil” album. Still, the rendition dealing with Bahrain was not the only version of the song. Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq had their own Iraq/Grand Ayatollah Muhammad Muhammad Sadiq Sadr (as opposed to Sayyid Hassan Nasrallah) themed “Risalat Thuwar” produced in 2011.
“Risalat al-Thuwar” is not the only Hizballah song which has been adopted and rebranded by Bahraini militants and their amplifiers. Another song used by Bahraini militants also comes from Firqat al-Fajr. The song, “Ya Wa’ad Allah” (“O Promise of God”) can be found on the group’s 2008 album, “Sharit Wa’ad Allah” (“Take the Promise of God”). The song has been released in different formats, with more recent music video varieties showcasing the assassinated Hizballah terror-mastermind Imad Mughniyeh. The album also included an instrumental version of the song. Both versions have been prominent features on productions done by Hizballah’s Al-Manar TV network.
In Bahrain, “Ya Wa’ad Allah” was used as background for clips released to the popular (particularly with militant groups) Revolution Bahrain’s YouTube account. One of these videos included the firebombing of an armored car used by Bahraini government forces.
It is not just the polished music video-quality material finding its way into Bahraini militant propaganda productions. Bahraini militant group Saraya al-Mukhtar released a video of their April 2014 targeting of Bahraini police with an improvised explosive device. Another bomb attack in Bani Jamra also utilized the same background music.
The musical selection in the background matched with instrumentals used by Iraq’s Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq. This music was first featured on the AAH-affiliated Al-Ahad TV in the late summer/fall of 2013 to commemorate Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq members killed fighting in Syria. Further pointing to some level of Iranian or Iranian proxy influence, is highly unlikely that this particular musical element could find its way into so many pieces of released footage. This may indicate some Bahraini militant footage being sent abroad (possibly to Iraq) where the footage is re-edited and put back together for a later introduction.
Another similar instrumental used by Bahraini militants with Saraya al-Mukhtar and Saraya al-Ashtar was also the same exact tune utilized in a number of Kata’ib Hizballah video releases (see: 00.17-00.40 on “Kata’ib Hizballah Anti-America Video”).
The use of the last two instrumentals create further questions. Why would these groups, which have resorted to using a variety of improvised weapons, and exist under increasing heavy security crackdowns, spend the time to find, edit, and utilize background instrumentals which already have obscure points of origin. Why pick these two exact instrumentals, which have only been found in the repertoire of Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq and Kata’ib Hizballah? Other Bahraini protest organizations have utilized a variety of different musical accompaniments. Thus, the use of these particular musical pieces seem out of place when compared to the rest of what has been released.
Whatever the reasons, closely assessing the propaganda published by these organizations may provide insight into rather opaque organizations. While assessing the musical selections may appear to be a tangential escapade, AAH, Kata’ib Hizballah, and Lebanese Hizballah have all demonstrated their strategy of using this material as another method to push the narrative of the “Islamic Resistance.”
