
_____________
To inquire about a translation for this video message for a fee email: [email protected]
Category: Lebanon
New video message from Jabhat al-Nuṣrah: "Targeting a Group of the Militia Ḥizb al-Lāt With a Concourse Missile Killing More than 12 From Them – 'Arsāl"

_____________
To inquire about a translation for this video message for a fee email: [email protected]
New video message from Jabhat al-Nuṣrah: "Damaging a 57mm Canon of the Iranian Ḥizb al-Lāt With a Guided Missile"

_____________
To inquire about a translation for this video message for a fee email: [email protected]
New video message from Jabhat al-Nuṣrah: "Message From the Shī'ah Prisoners To the Children of Their People in Lebanon"

______________
To inquire about a translation for this video message for a fee email: [email protected]
al-Awzā’ī Foundation for Media Production presents a new statement from the ‘Abd Allah ‘Azzām Brigades: "Condolences to the Islamic Nation on the Death of the Mujāhid Shaykh Ibrāhīm al-Rubaysh"

Click the following link for a safe PDF copy: ‘Abd Allah ‘Azzām Brigades — “Condolences to the Islamic Nation on the Death of the Mujāhid Shaykh Ibrāhīm al-Rubaysh”
_____________
To inquire about a translation for this statement for a fee email: [email protected]
New video message from Jabhat al-Nuṣrah in Lebanon: "Our Appointment Day of the Funeral: The Martyr Usāmah Manṣūr Abū 'Umar Who Was Assassinated By Lebanese Intelligence in Tripoli – al-Tabbānah"

_____________
To inquire about a translation for this video message for a fee email: [email protected]
al-Awzā’ī Foundation for Media Production presents a new statement from the ‘Abd Allah ‘Azzām Brigades: "To the Lebanese People and the Lebanese Government and Its Army #2"

Click the following link for a safe PDF copy: ‘Abd Allah ‘Azzām Brigades — “To the Lebanese People and the Lebanese Government and Its Army #2”
_____________
To inquire about a translation for this statement for a fee email: [email protected]
Check out Phillip Smyth's new Policy Focus for The Washington Institute: "The Shiite Jihad in Syria and Its Regional Effects"

In 2012 and early 2013, media sources were widely reporting the imminent fall of Syria’s Bashar al-Assad regime to Sunni rebel groups. But not long thereafter, it began to show resilience, holding off further rebel advances and even retaking lost ground.
This turnabout was fueled largely by Iran-backed Shiite proxy groups fighting on Assad’s behalf. While these groups often invoked the defense of the Sayyeda Zainab shrine as their rallying cry, their influx into Syria was far from a spontaneous expression of Shiite unity. Indeed, it reflected instead a highly organized geostrategic and ideological effort by Iran to protect its Syrian ally and project power across the Middle East. When fighting spread to neighboring Iraq, many of the Iraq-based proxies regrouped across the border to defend their homeland against advances by The Islamic State.
The web of Iran-backed Shiite proxies is exceedingly complex, with much overlap and many changing aliases. In this new Institute study, Phillip Smyth — author of Hizballah Cavalcade and University of Maryland researcher — deftly navigates these many groups, exploring topics such as the narrative of pan-Shiite jihad, the range of Shiite clerical views on the jihad, recruitment techniques, and weapons used. His discussion compellingly shows why pursuing U.S. regional interests must involve targeting not only ISIS but also its Shiite adversaries.
Click here to read the entire report.
New statement from Jabhat al-Nuṣrah: "Indeed Our Solders Are Those Who Overcome"

Click the following link for a safe PDF copy: Jabhat al-Nuṣrah — “Indeed Our Solders Are Those Who Overcome”
________________
To inquire about a translation for this statement for a fee email: [email protected]
Hizballah Cavalcade: The Shia Militant Response to Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr’s Death Sentence
NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
The Shia Militant Response to Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr’s Death Sentence
By Phillip Smyth

Ayatollah Sheikh Nimr Baqr al-Nimr, an outspoken radical Saudi Arabian Shia cleric, has been the center of controversy and brewing conflict between Shia protesters, militant Shia groups of Saudi Arabia and Bahrain, and their respective Sunni governments. According to a 2012 article by Toby Matthiesen, al-Nimr was, “long a peripheral figure in the local Shia power struggle but now seems to have become the most popular Saudi Shia cleric among local youth.”1 His cause and image is spreading across the Middle East as the latest example of Sunni oppression of Shia in the region and his recent death sentence has become a potent rallying cry for regional Shia militant organizations, particularly those with links to Iran.
Arrested in 2012, Nimr was accused by the Saudi government’s Special Criminal Court of making sectarian statements to cause strife, inviting foreign intervention (shorthand for Iranian influence), and disobeying the king. Following his 2012 arrest, thousands took to the streets and Saudi police shot and killed two protesters.2 In mid-October 2014, Nimr was sentenced to be “crucified”, a process where the sheikh will be beheaded and his body displayed.3
Protests in Saudi began in early 2011 and in part addressed anti-Shia discrimination suffered by the group in the Shia majority area in Saudi Arabia’s oil-rich Eastern Province; primarily zones around the Shia-majority towns and villages near the city of Qatif.4 Following the 2011 Saudi intervention in Bahrain, protests against the Saudi government increased in Bahrain and Saudi Arabia among Shia protesters.5 Following the 2011-2012 protests, links between Bahrain’s and Saudi Arabia’s protest movement spilled over into the more militant circles which actively promoted Nimr’s defiant stance and a hope to combine their fronts against common foes.
Of further interest are Nimr’s own ideological leanings and how they may relate to Shia militant responses. In Frederic Wehrey’s Sectarian Politics in the Gulf, the sheikh is described as a follower of the late Ayatollah Muhammad al-Shirazi.6 Shirazi was one of the founders of a radical Shia political school of thought referred to as the “Shiraziyya.” Shiraziyya clerics have been some of the most influential in the Arab Shia world. Initially al-Shirazi agreed with the Islamic revolutionary ideology of Ayatollah Khomeini, only to split from Khomeini over issues regarding how the new Islamic state (in Iran post 1979 revolution) should be led.7 In one BBC Arabic report, Nimr had been accused by Riyadh of attempting to spread Wilayat al-Faqih.8 Absolute Wilayat al-Faqih is the Khomeinist concept that serves as the basis for the Islamic Republic of Iran. Nevertheless, it was not clarified whether this was the type of Wilayat al-Faqih Nimr was accused of propagating.
Despite the history of strife between Shirazi’s school of thought and that of Ayatollahs Khomeini and Khamenei, al-Nimr appeared to increase public support for Tehran and send other more mixed messages. In 2008, he had also reportedly stated he supported Iran’s nuclear program by saying any attack against it should be met by a response from the Islamic world. That same year, he also said that Saudi Shia may need to call on foreign support (implying Iran) to help press their issues in Saudi Arabia.9 Later in 2009, Nimr reportedly called for secession, stating during a sermon, “Our dignity is more precious than the unity of this land.”10 His statement came as a response to discrimination against Shia in the kingdom and reflected possible repercussions if certain demands made by Shia protesters were not addressed.
Since 2013, in a piecemeal fashion, social media accounts associated with Iranian proxy groups in Iraq have promoted the images and other supportive statements for Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr.11 While this does not necessitate that Nimr is a true ally or proxy of Tehran, his message and influence is likely seen by Iran as a cause to be promoted in that country’s wider struggle for the leadership of Shia Islam and as a counter to Saudi Arabia.
Nimr’s deep links and strong voice within the Saudi Shia community, particularly among youthful radicals and other more non-violent protestors, has led to Shia militant groups championing his cause from Bahrain and Iraq. Even in Yemen, Shia supporters of Ansar Allah, more commonly known as the Houthis, even launched demonstrations for the jailed cleric.12 Some Bahraini militant groups, which view the struggle of their coreligionists in a geographically close region of Saudi Arabia, as part and parcel to their conflict with the Khalifa monarchy and their Saudi government supporters. Additionally, powerful Iranian proxy groups based in Iraq—which have also maintained anti-Saudi and anti-Bahraini government narratives—have taken to issuing stern threats against Riyadh for his sentence.
The Violent Replies From Saudi Arabia’s and Bahrain’s Militants
Bahraini militant groups demonstrated the most concerted effort in terms of orchestrating violent retorts to Nimr’s jailing and sentence. While other threats and attacks were conducted since the start of 2014, this piece will focus on more recent threats and attacks beginning in the summer of 2014.
Bahrain’s Saraya al-Mukhtar (SaM), a group which once said the Saudi Shia of the Qatif and the Shia of Bahrain constituted one people with common foes, launched the most attacks over the longest period specifically addressing Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr’s arrest, trial, and death sentence.
Starting in August, SaM attacked an electricity tower in Ar-Rifā near a Bahraini military base. The group filmed the attack and stated it had been a warning related to the imprisonment and trial of Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr. Around the same time, SaM also began an online countdown for the Nimr verdict and increased their threats against Saudi Arabia. The group also ratcheted up it’s pro-Nimr messaging with the release of numerous images.
This messaging coincided with Saraya al-Mukhtar making its first direct threat against U.S. military personnel in Bahrain on August 11. Through an image posted to Facebook, SaM stated that, “The American cover on al-Saud and Al_Khalifa crimes,,Marines in bahrain will pay the price. [sic]” The message essentially claimed that the U.S. was the real backer for the Khalifa and Saud monarchies. As a result, they bore equal responsibility and could be targeted.

Figure 1: Saraya al-Mukhtar’s anti-American message posted on August 11, 2014.

Figure 2: A Saraya al-Mukhtar photo for Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr posted on August 8, 2014. The poster reads: “Sheikh Nimr[‘s trial and poor treatment] will make us put all options on the table.”

Figure 3: A Saraya al-Mukhtar photo posted on August 10, 2014. This poster reads: [in the red box] “A warning from Saraya al-Mukhtar to the mafia of the Sauds [in white text] Harming Sheikh Nimr will make us put all options [on the table]. Harming the Faqih Nimr means every single Saudi national will enter our country in a coffin.”

Figure 4: A Saraya al-Mukhtar photo for Ayatollah Nimr al-Nimr posted on August 11, 2014. The poster reads: “Do not hesitate, Do not underestimate, No red lines.. after [the] discrimination [against] the Faqih al-Nimr.”
On September 16, SaM announced it had planted 6 explosive devices in retaliation for al-Nimr’s incarceration. Albeit, these bombs did not target U.S. interests and there was little confirmation as to whether any devices were actually planted.
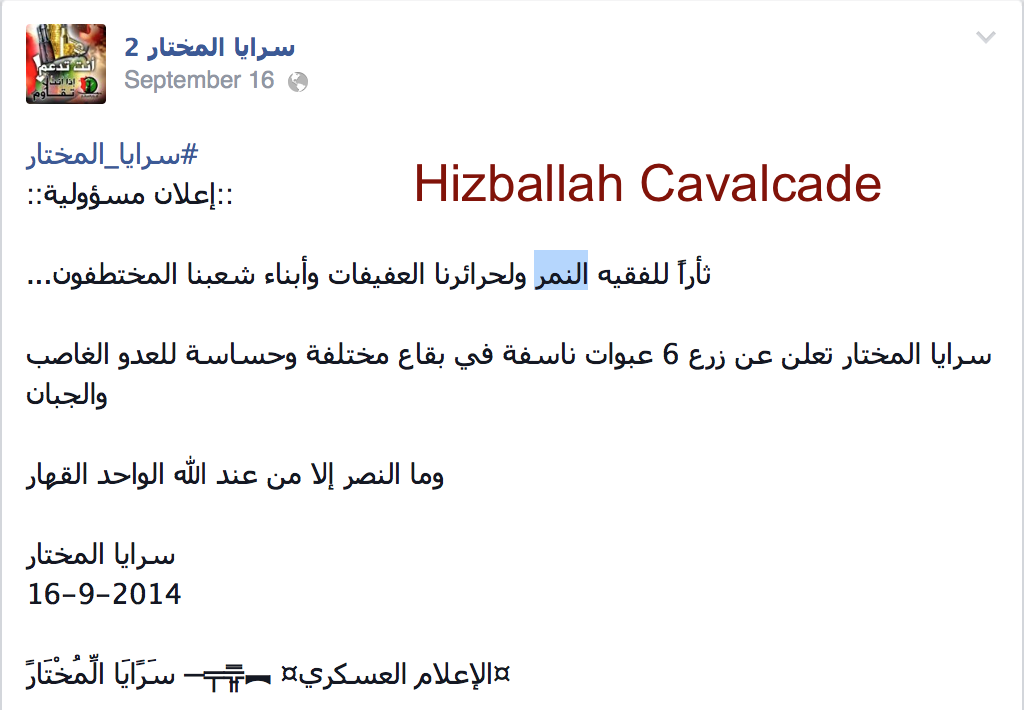
Figure 5: Saraya al-Mukhtar’s September 16 claim to have planted 6 bombs.

Figure 6: Saraya al-Mukhtar’s claim of 2 attacks on October 18, 2014.
Then on October 9, SaM claimed to conduct an attack in the town of Karana, Bahrain utilizing an improvised firearm. SaM’s claim of responsibility stated they attacked, “herds of mercenaries” (shorthand for Bahraini police and other security entities). On October 15, SaM claimed to have launched attacks in Sanabis and Aker, Bahrain targeting “mercenaries”. In another statement from that day, the group threatened, “The occupying mafia of al-Saud and al-Khalifa [would face]…consequences for the death sentence.” Later, on October 18, SaM claimed two attacks, referring to them as “Revenge of the Faqih [an expert in Islamic jurisprudence] Nimr.” SaM’s statement declared that it had injured “ranks of the enemy occupier.”
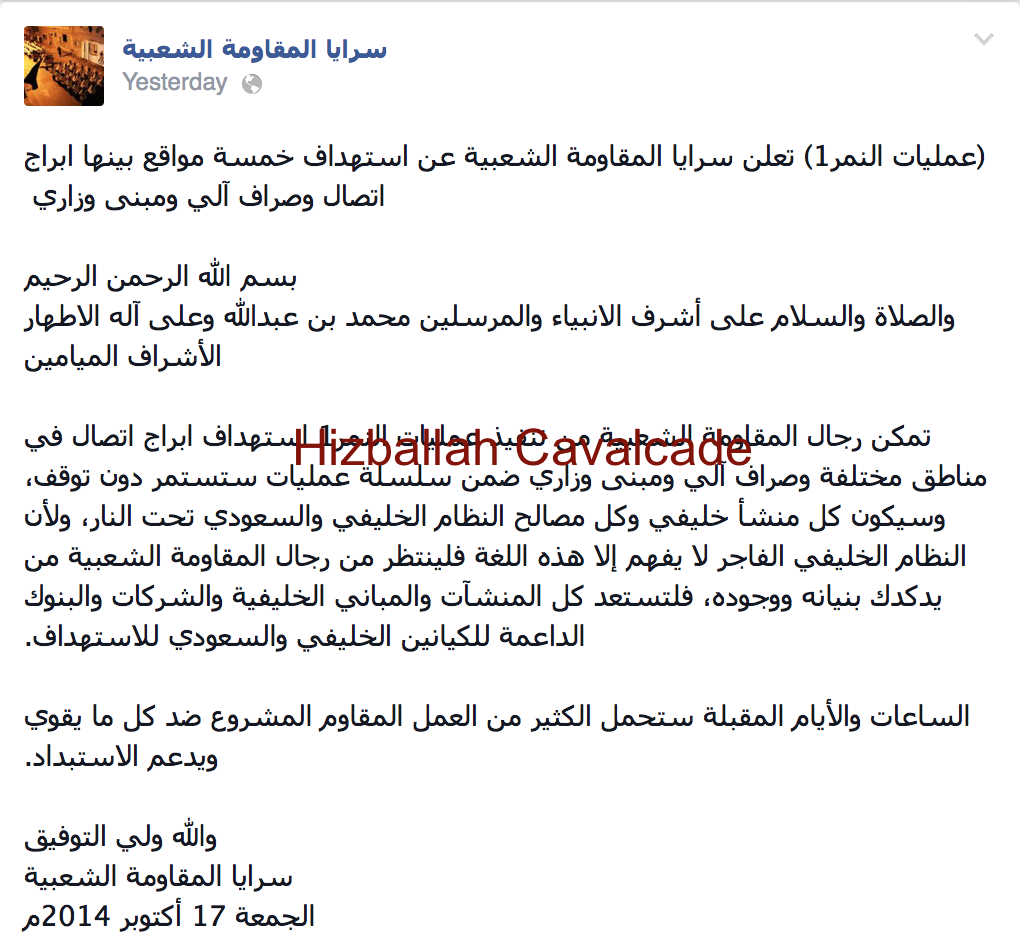
Figure 7: SMS’s claim of attack in honor of Sheikh Nimr.
Bahraini militant group, Saraya
