NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
—
Sariyya al-Tali’a al-Khurasani: A New Combat-Tested Shia Militia in Syria
By Phillip Smyth ([email protected])


Figure 1: The STK’s logo (left) and flag (right). The logo includes Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps’s symbol. A verse from the Quran, Quran 29:69 meaning, “And those who strive for us [in jihad] we will surely guide them to our [Islamic] ways”. Over the rifle the phrase reads, “The Islamic Resistance”.

Figure 2: Another logo used by the STK.
In late September, Sariyya al-Tali’a al-Khurasani (STK or The Vanguards of Khurasani Unit), also referred to as the Khurasani Unit, first made itself known to the world via Facebook. The group may draw their name from Abu Muslim al-Khurasani (A.K.A. Abu Muslim), an 8th century military leader who helped depose the Sunni Umayyad dynasty’s rule over the early Islamic caliphate.[1] The STK also claims to be based out of Arbil, Iraq, the capital of Iraqi Kurdistan. According to the Khurasani Unit’s own releases, it appears to exclusively operate in a military function in rural areas outside of Damascus, Syria.
Technically, the STK was first announced on September 24, 2013 on Facebook. However, it is possible the group’s first page was made “private” and another mirror page was setup in its stead. Thus, the initial announcement of the group’s existence was hidden. The mirror page which first helped formally announce STK’s creation was made on October 8, 2013. Both pages hold unique images from the group and promote the same general messages. As with other Shia militias in Syria, the group claims to defend the Sayyida Zaynab shrine and promotes general pro-Iranian pan-Shia narratives. The promotion of Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei and of their own Shia identity through the posting of photos showing Shia clerics in their ranks is a regular theme.
Most of the STK’s imagery was posted in October. In fact, there were days when eight new images were posted on both of their Facebook sites. STK has also released extensive footage showing its fighters in combat inside Syria. This footage has included numerous photos of its fighters, including those of wounded members, and videos of the group engaged in combat. A particular feature of STK propaganda has been images showing the fighters posing with the group’s flag. Only the Badr Organization’s Syria unit, Quwet Shahid Baqir al-Sadr, has also engaged in extensive posting of images featuring their organization’s flag with their fighters in Syria.
While Shia Islamist organizations fighting in and contributing fighters to Syria have done little to hide their connections to Iran, STK went the extra step and actually repackaged Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps’ logo as their own. Their blatant promotion of Iran’s Supreme Leader in many of their posts leaves no illusions to which Shia clerical leader or ideology to which the group swears loyalty.
Unlike other Shia militias (E.G. Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir, Liwa’a al-Imam al-Hasan al-Mujtaba, and Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas) fighting in Syria, the STK has not stated which (if any) Iraqi Shia organizations have contributed fighters to the group.
The number of fighters in STK’s ranks is unknown, though their leadership has been identified. STK, has been reported to be fighting around Damascus’s Sayyida Zaynab Shrine and in the rural area near Damascus called Ghouta. Videos showing engagements featuring their fighters went viral among Syrian rebel supporters and Shia militia supporters online. In part, this has been due to the fact that their videos appear less staged (e.g. Shia militiamen firing a few rounds from a sniper rifle) and are much longer than others produced.
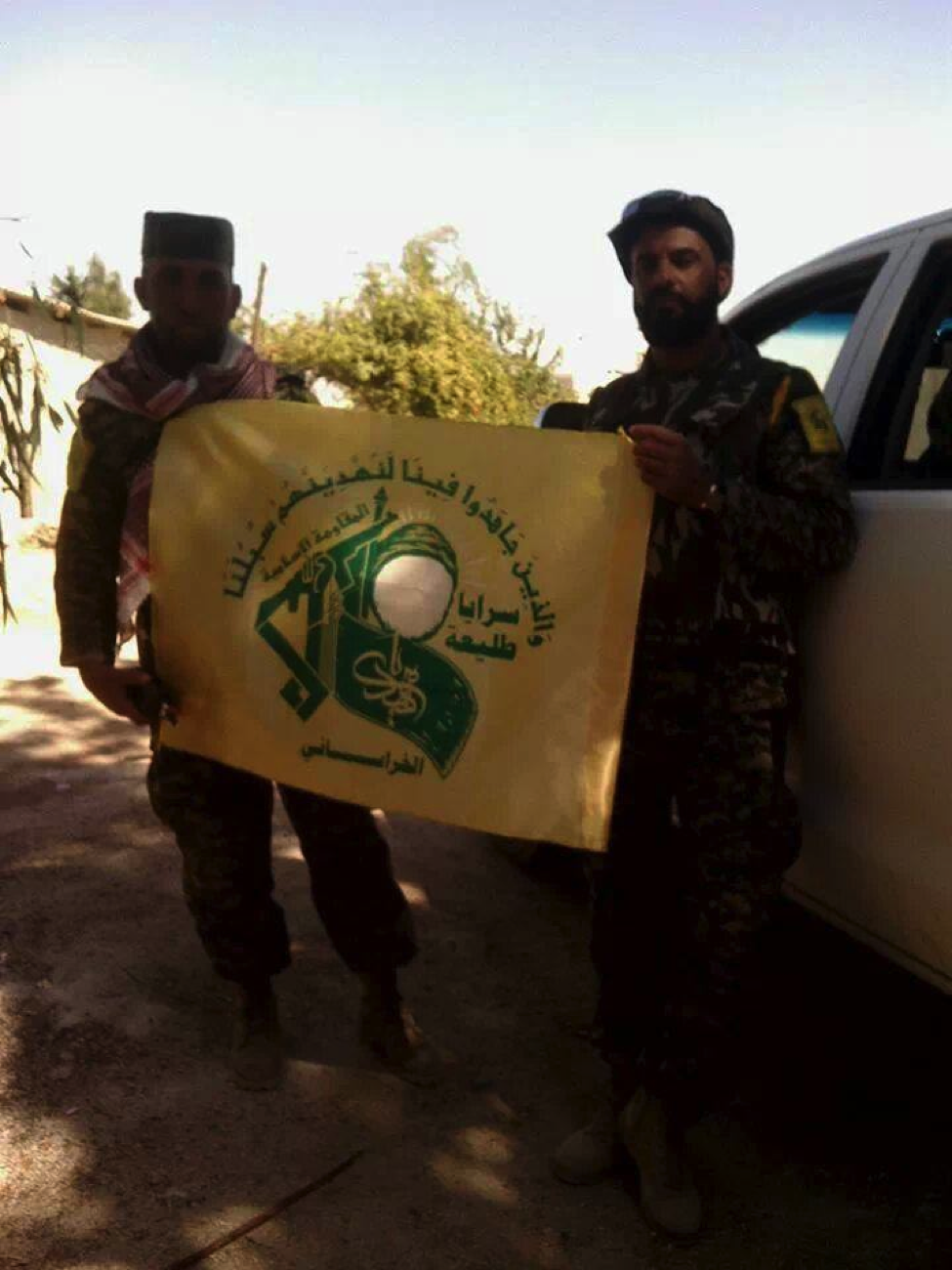

Figure 3: Two STK fighters pose in front of a truck holding the organization’s flag.
Ali al-Yasiri: The STK’s Commander
The immediate announcement of commanders for specific Shia fighting units in Syria is usually not a common theme. Less than two weeks after the first Facebook post made by the STK, it was announced by the group that their commander was named Ali al-Yasiri. Yasiri is shown in many photographs posted by the organization on its Facebook pages. Yasiri was also shown in photographs featuring Sayyid Muhammed Jawad al-Madrasi, a Shia cleric.[2]
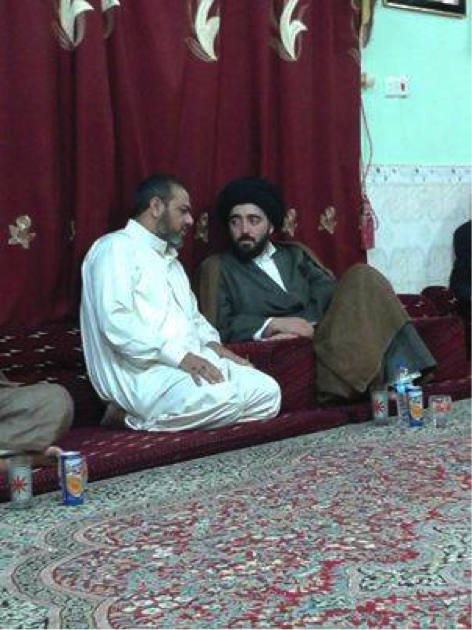

Figure 4: Ali Yasiri is shown with Sayyid Jawad al-Madrasi. On Facebook, the group identified the cleric as, “Ajwad Madrasi”.
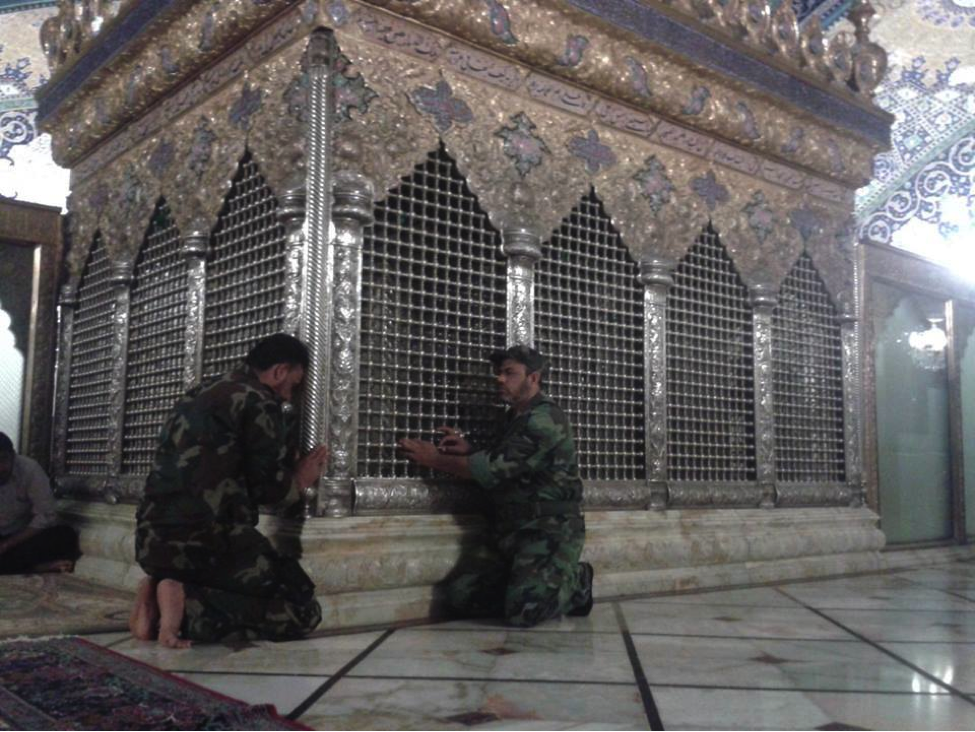

Figure 5: Yasiri and another unnamed STK fighter pose at Zaynab’s tomb.
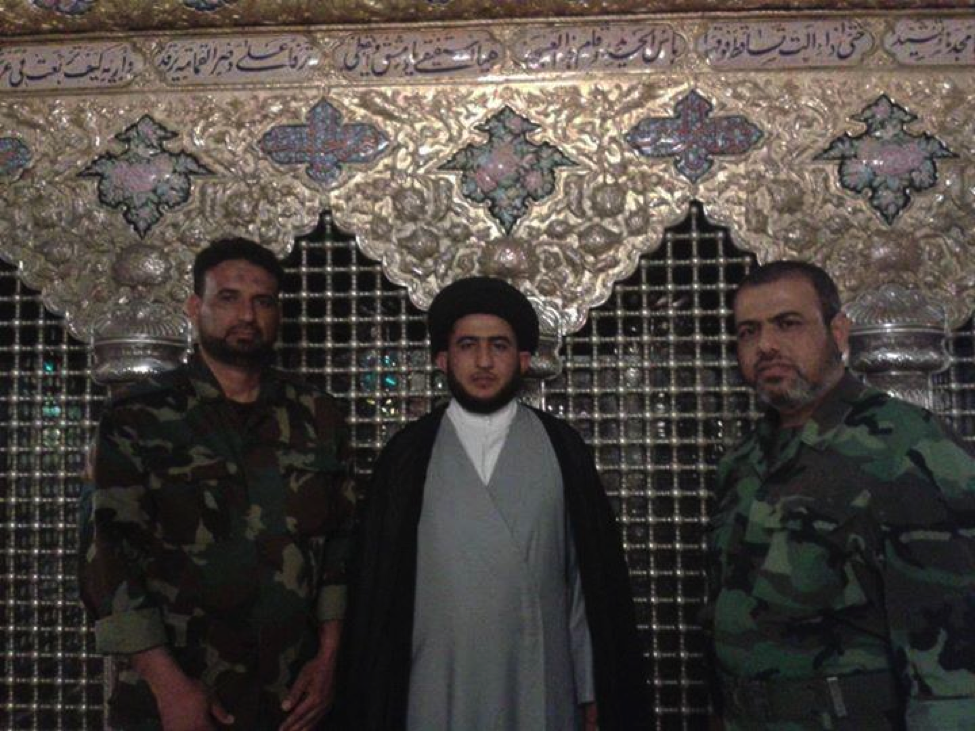

Figure 6: Yasiri and an unnamed fighter pose with an unnamed cleric at Zaynab’s tomb. All three figures have been featured in other photos released by STK.
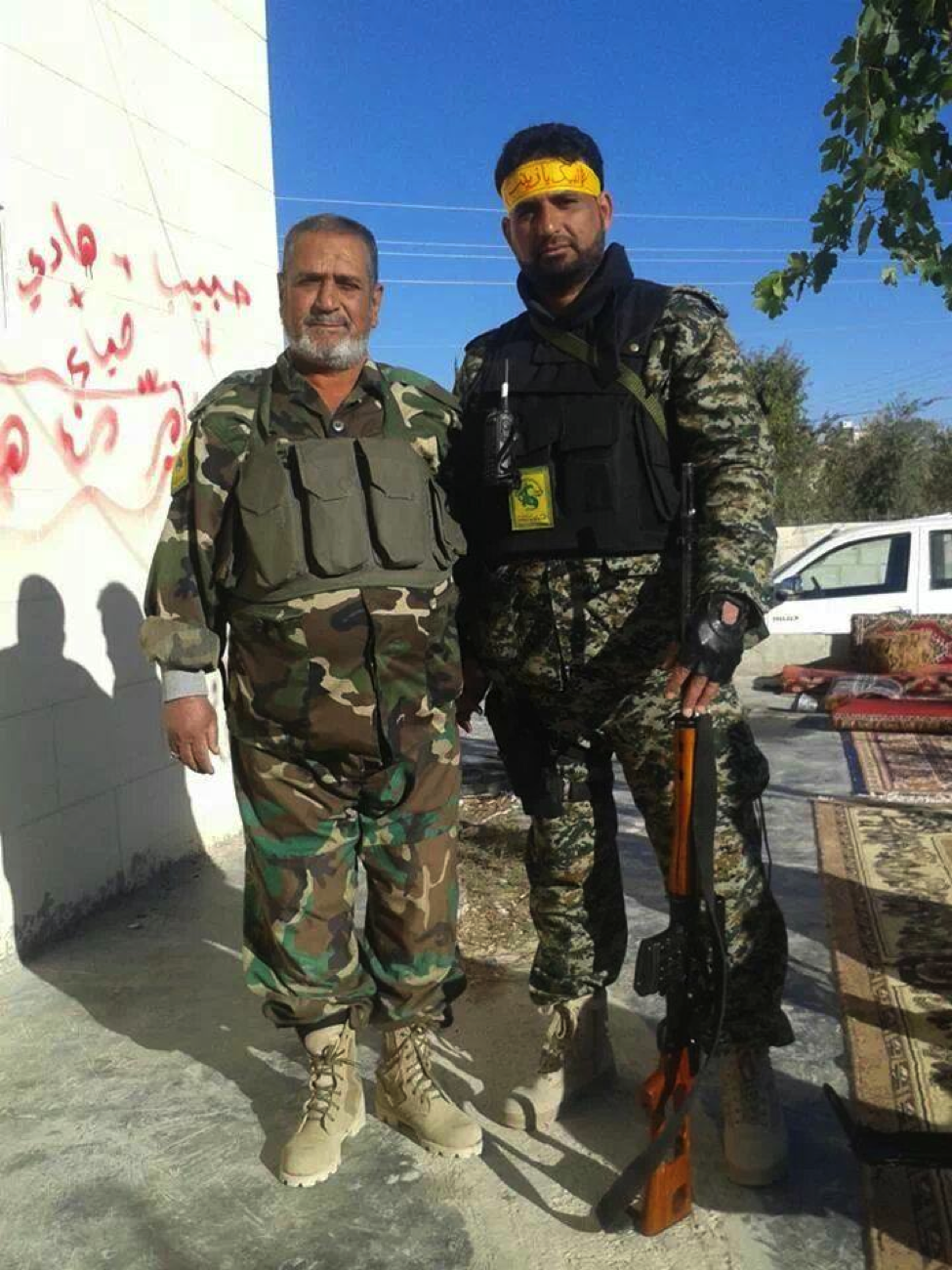

Figure 7: Yasiri (left) and the same unnamed fighter pose together for a photo. The fighter on the right holds an SVD type sniper rifle.
STK’s Fighters & Equipment
Little information is available on the numbers of fighters STK has operating in the field. Judging from their photographs, the group has over twenty members. The arms the group uses mimic the varieties used by other Shia militias. Most of these weapons are Kalashnikov-type rifles, SVD-type sniper rifles, RPG-7s, and the PKM-type machine guns. The group has also been recorded using light mortars in clashes in rural areas outside of Damascus.
In addition to their small-arms, the militia’s uniforms appear to include types of U.S.-style digitized camouflage. Some of the group’s uniforms include M81-type woodland camouflage and Desert Camouflage Uniform-type patterns. Also, other unidentified types of camouflage patterns have been seen on the STK’s fighters.
Interestingly, many of the same faces are featured in photographs of STK fighters. In fact, one in particular, that of a Shia Islamic cleric wearing a black turban, can be spotted in many photos of STK militiamen. His inclusion may be a way the group demonstrates their Shia Islamic identity. The Badr Organization has also included clerics in their militia photos in a similar effort.
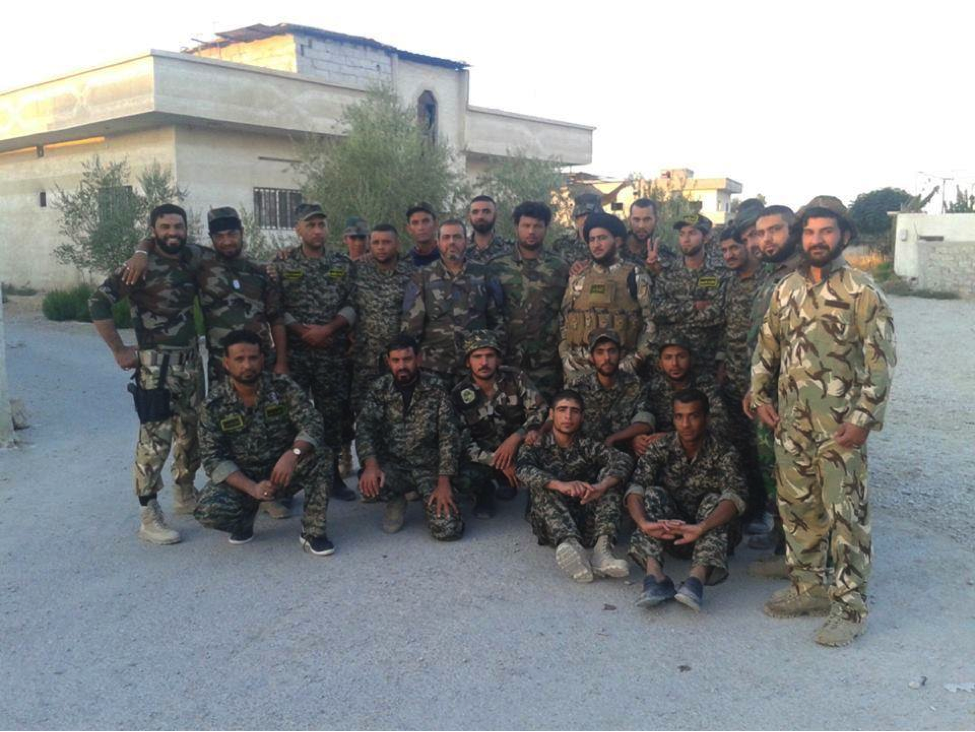

Figure 8: STK fighters pose for a photo in East Ghouta, Syria.
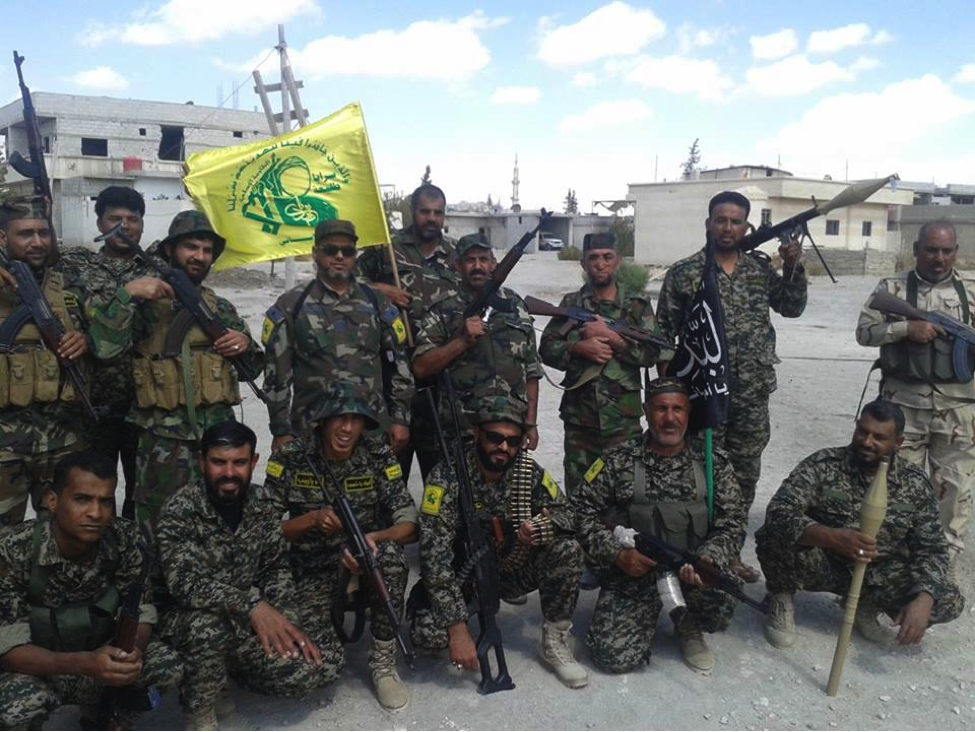

Figure 9: STK fighters pose with the group’s flag and light weapons.
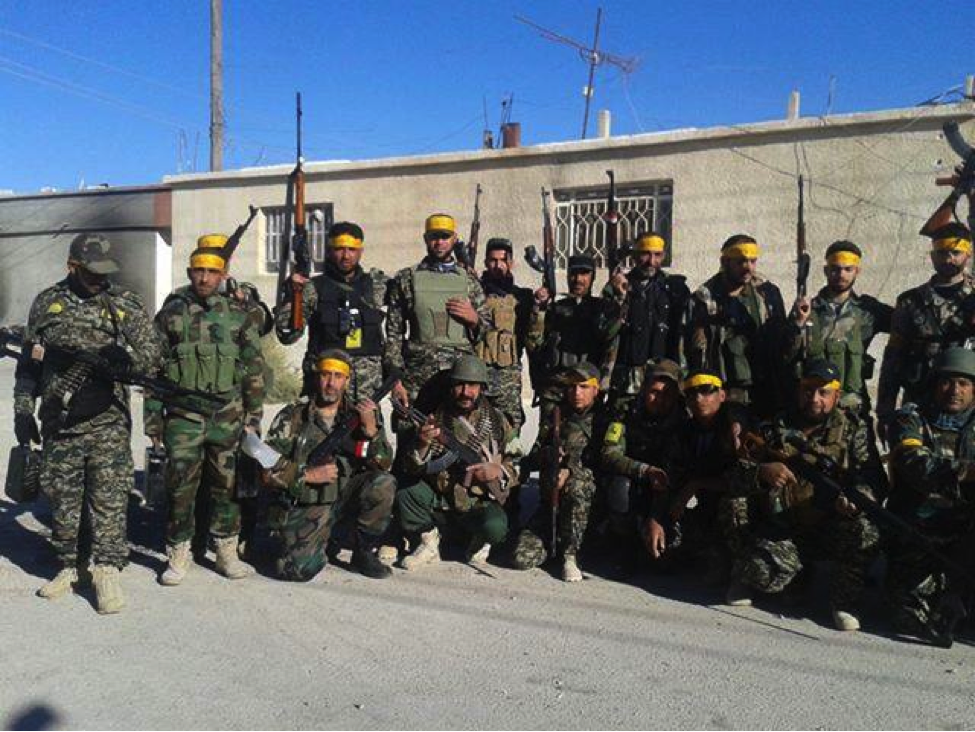

Figure 10: STK fighters pose in their uniforms and headbands.
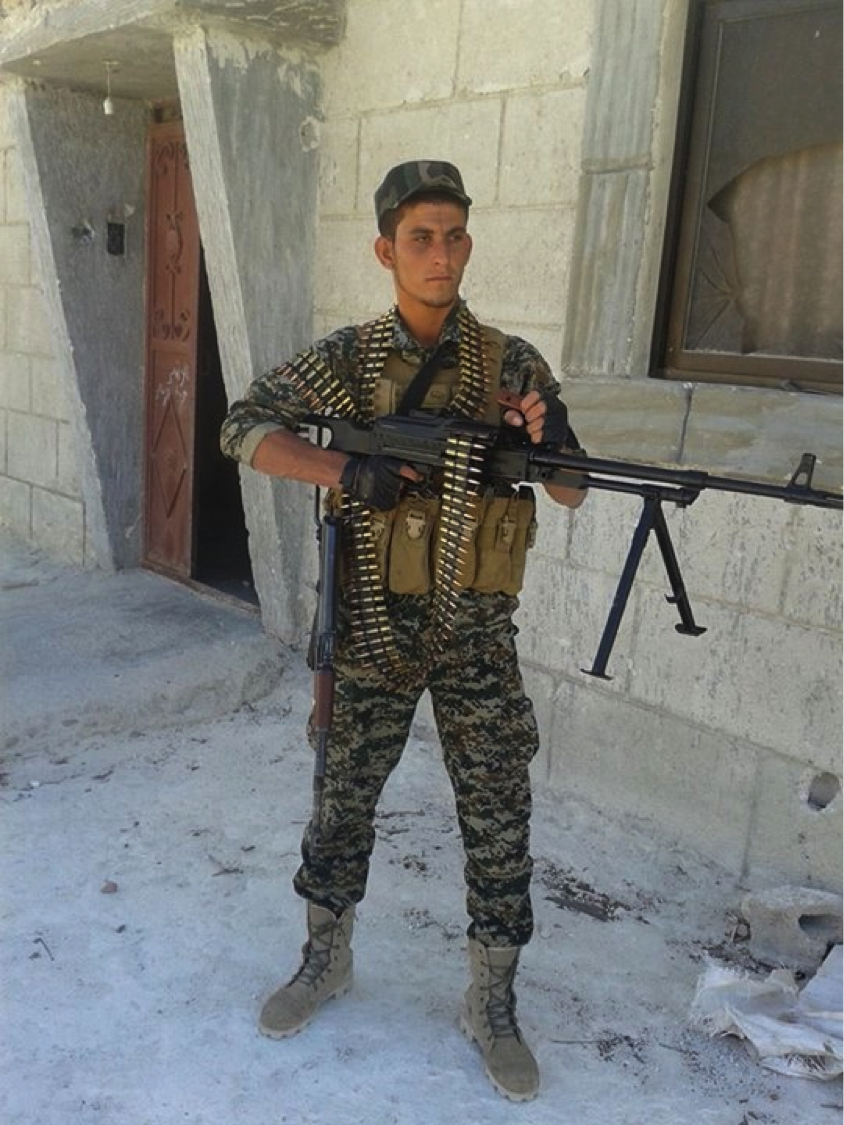

Figure 11: An STK machine gunner.
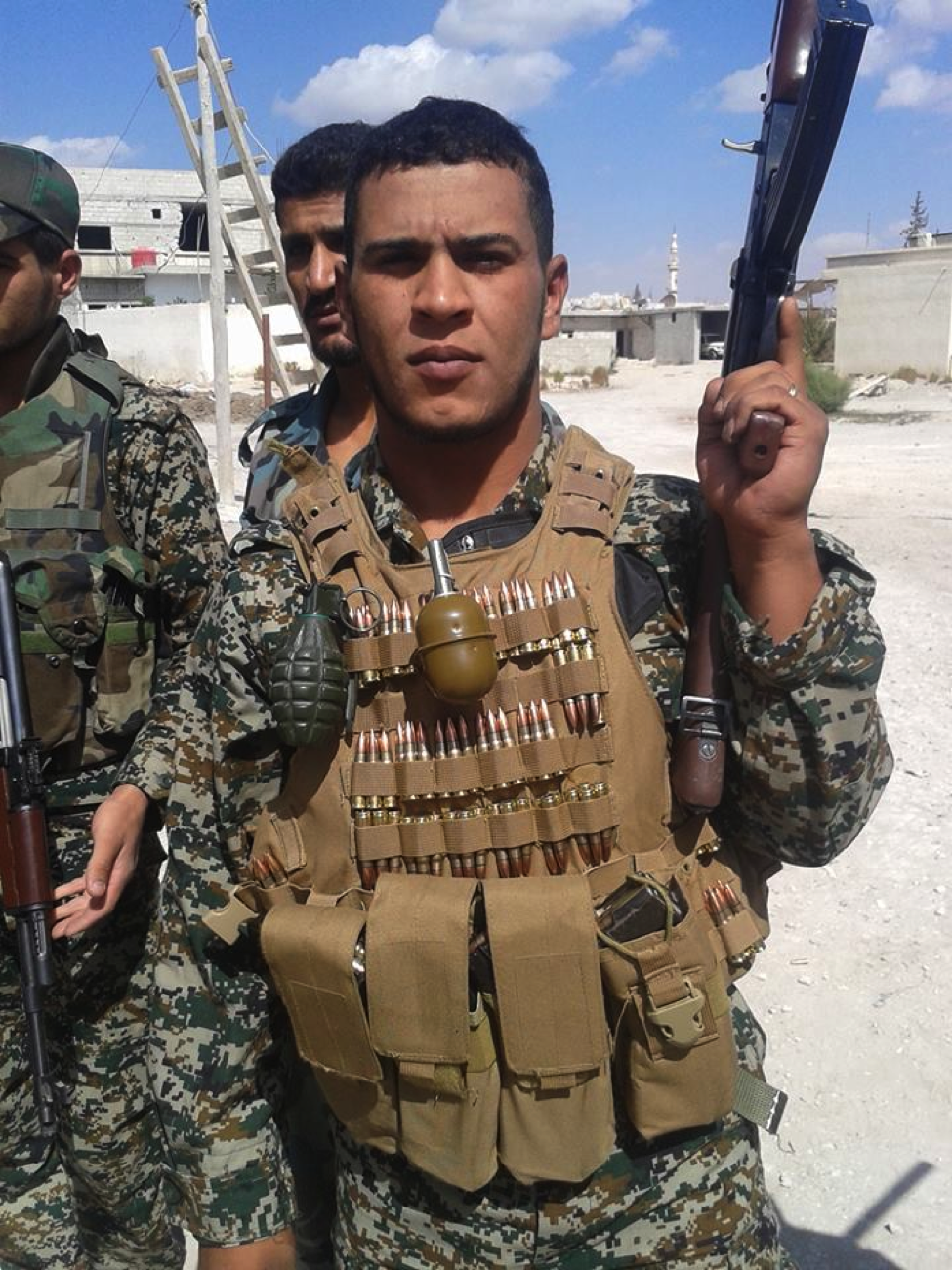

Figure 12: An STK fighter holds his rifle as he stands with other members of his organization.
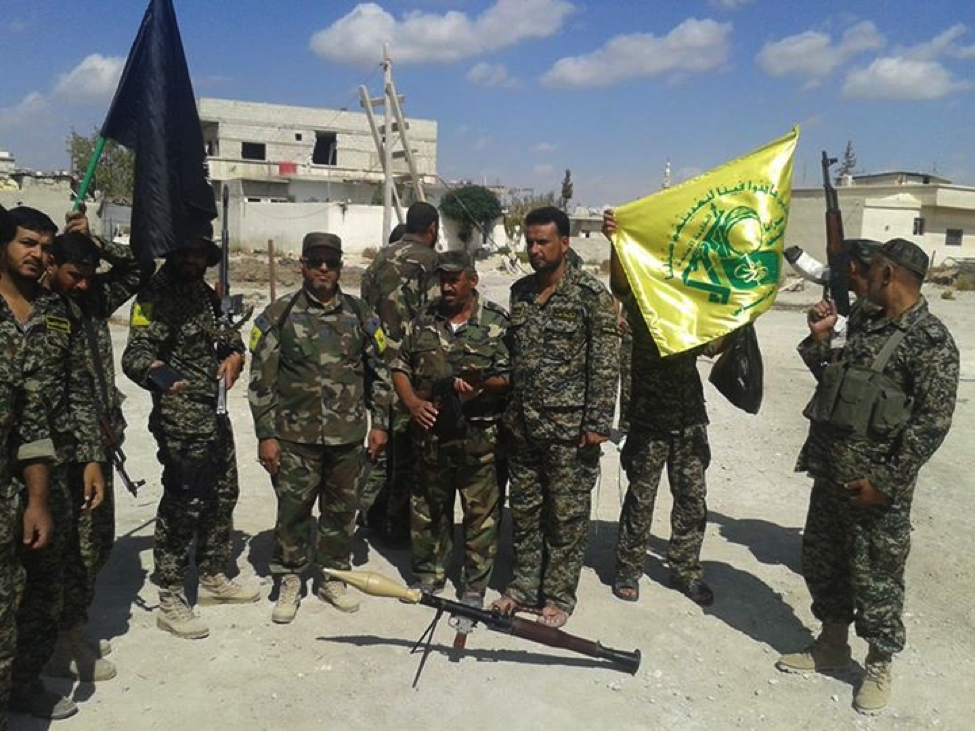

Figure 13: STK fighters pose around an RPG-7 and the group’s banner.
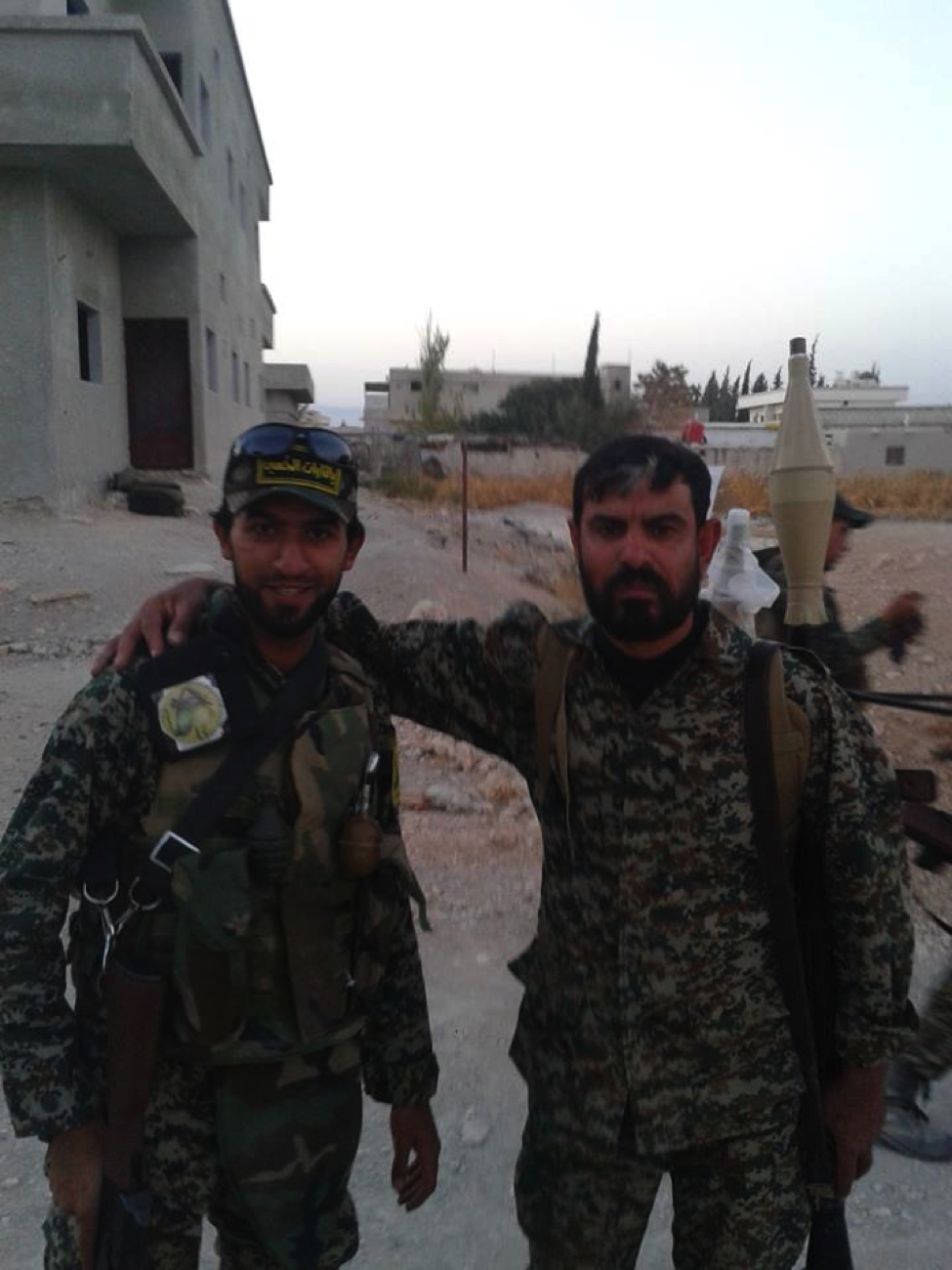

Figure 14: STK militiamen pose for the camera. The fighter on the right holds an RPG-7.
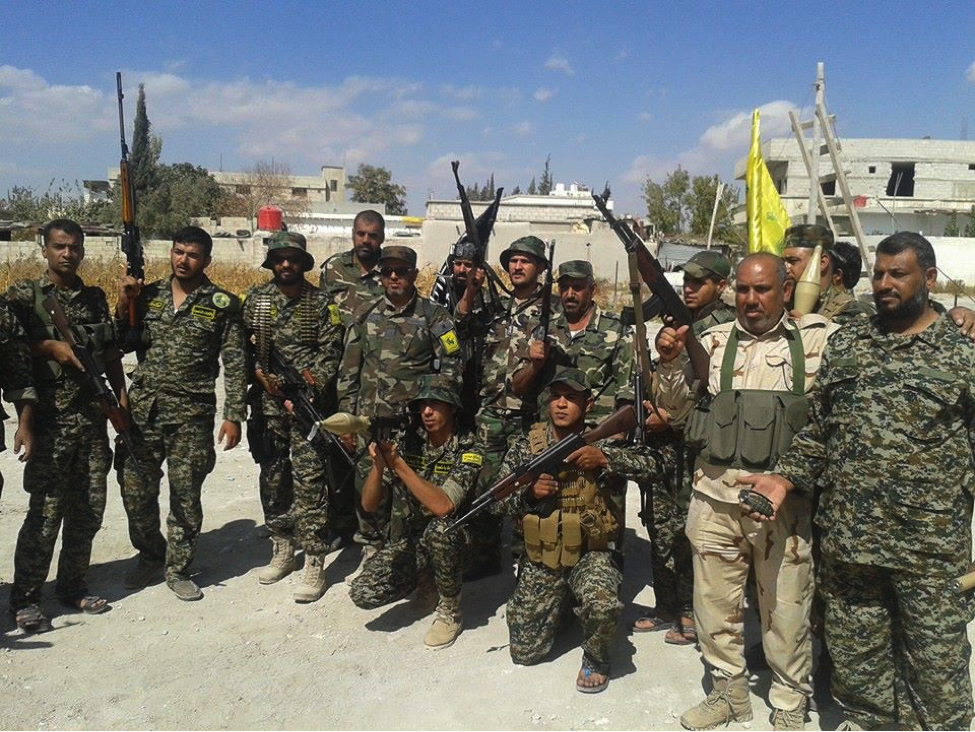

Figure 15: STK fighters stand and kneel together with their weapons as they pose for photographs.
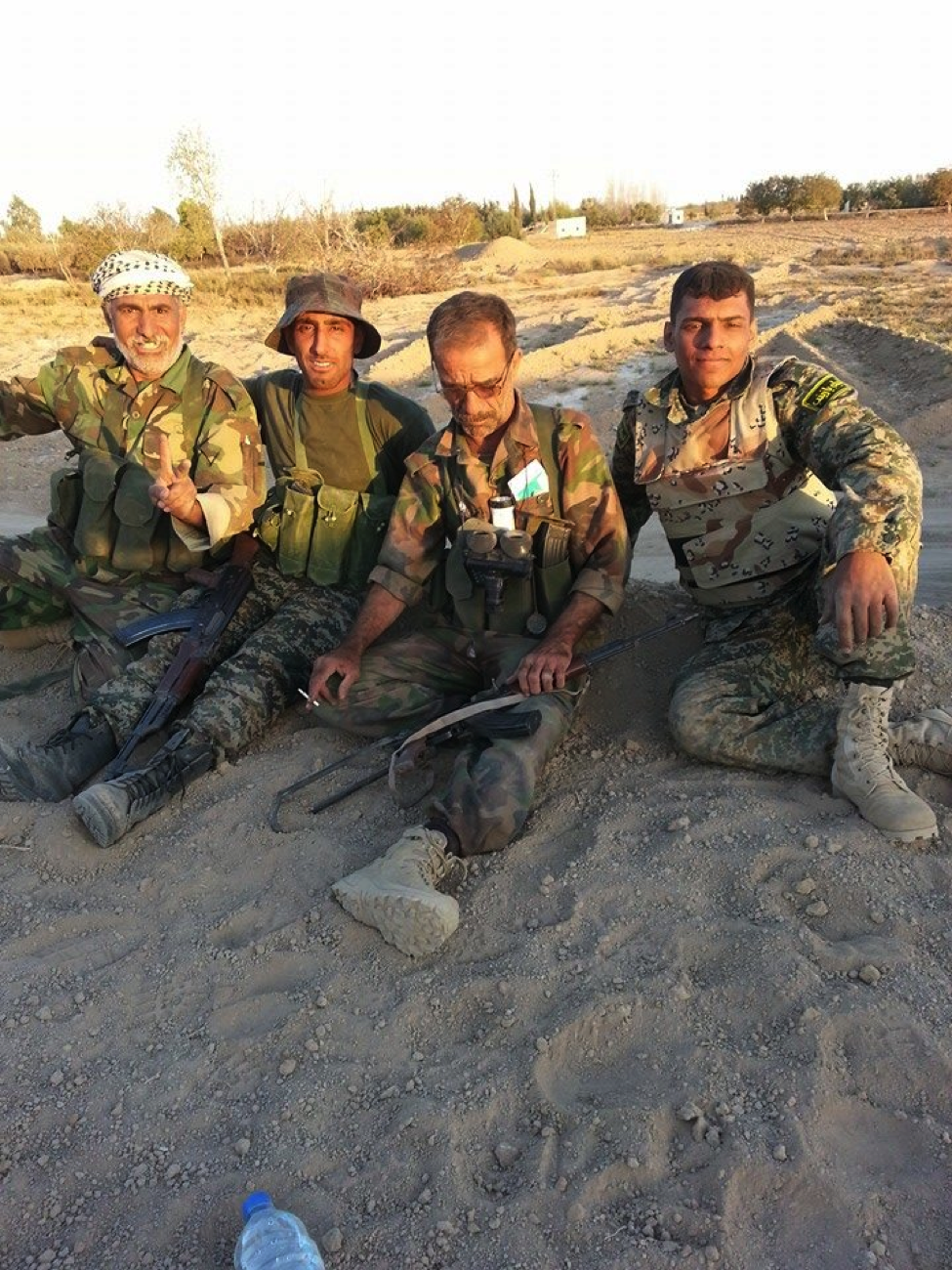

Figure 16: Older and younger fighters sitting together in Rif Dimashq.

Figure 17: STK fighters take a break during fighting. The photo appears to be taken in the same area where some videos of STK combat engagements occurred.
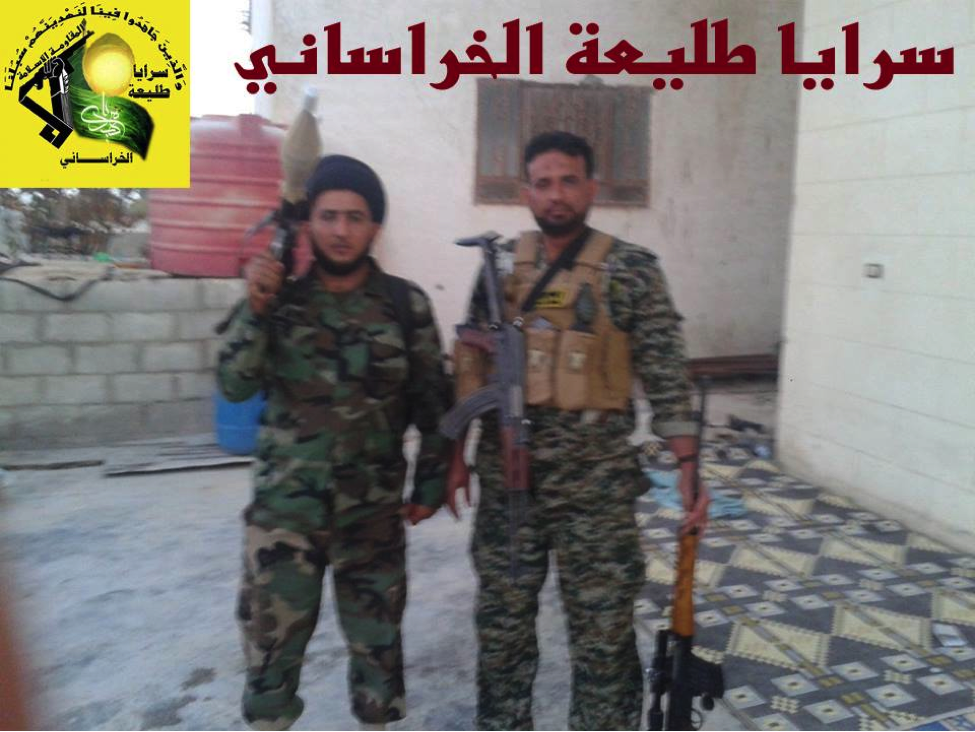

Figure 18: STK fighters, one appearing to be a Shia cleric, hold a mixture of small-arms.
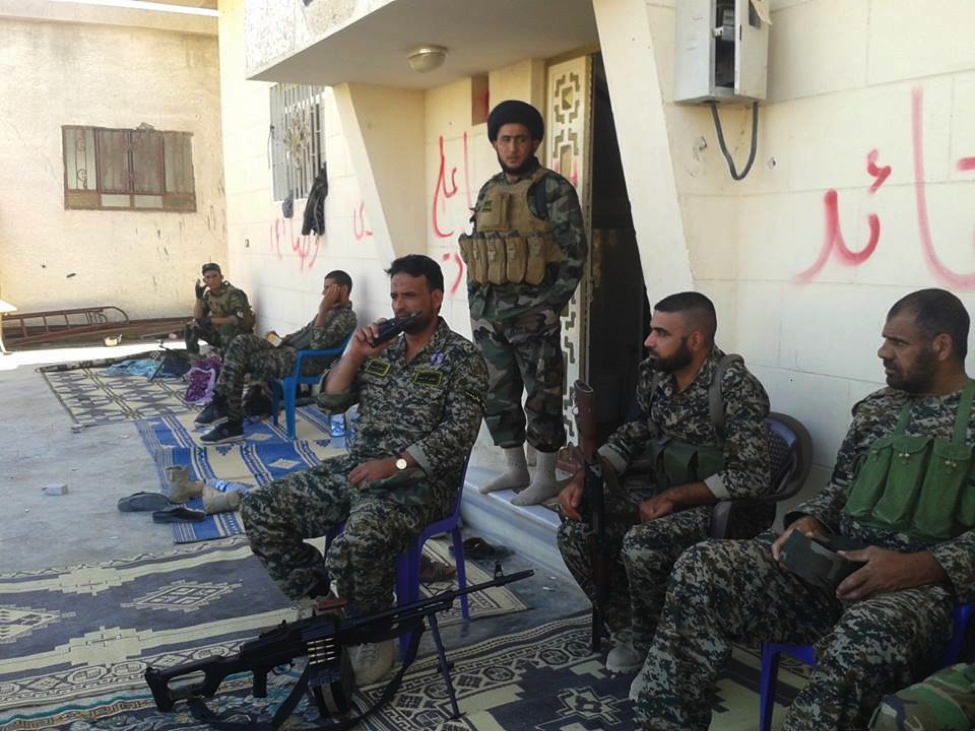

Figure 19: STK militiamen and a fighter in a black turban (signifying clerical status and descent from the Islamic Prophet Muhammed) relax in Rif Dimashq.
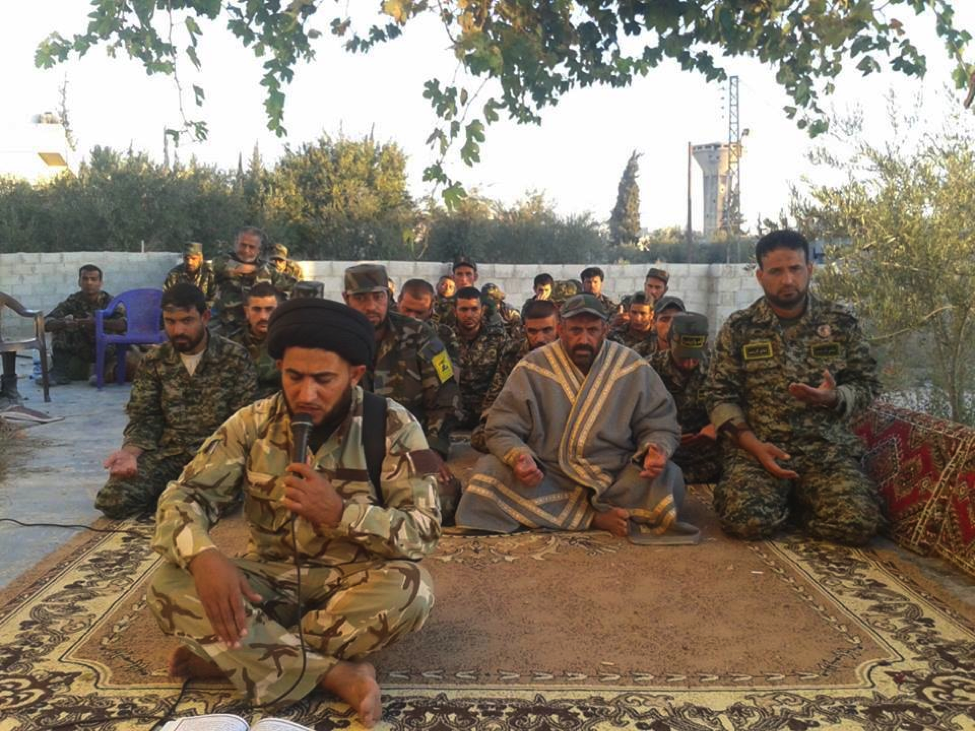

Figure 20: STK fighters at prayer time.
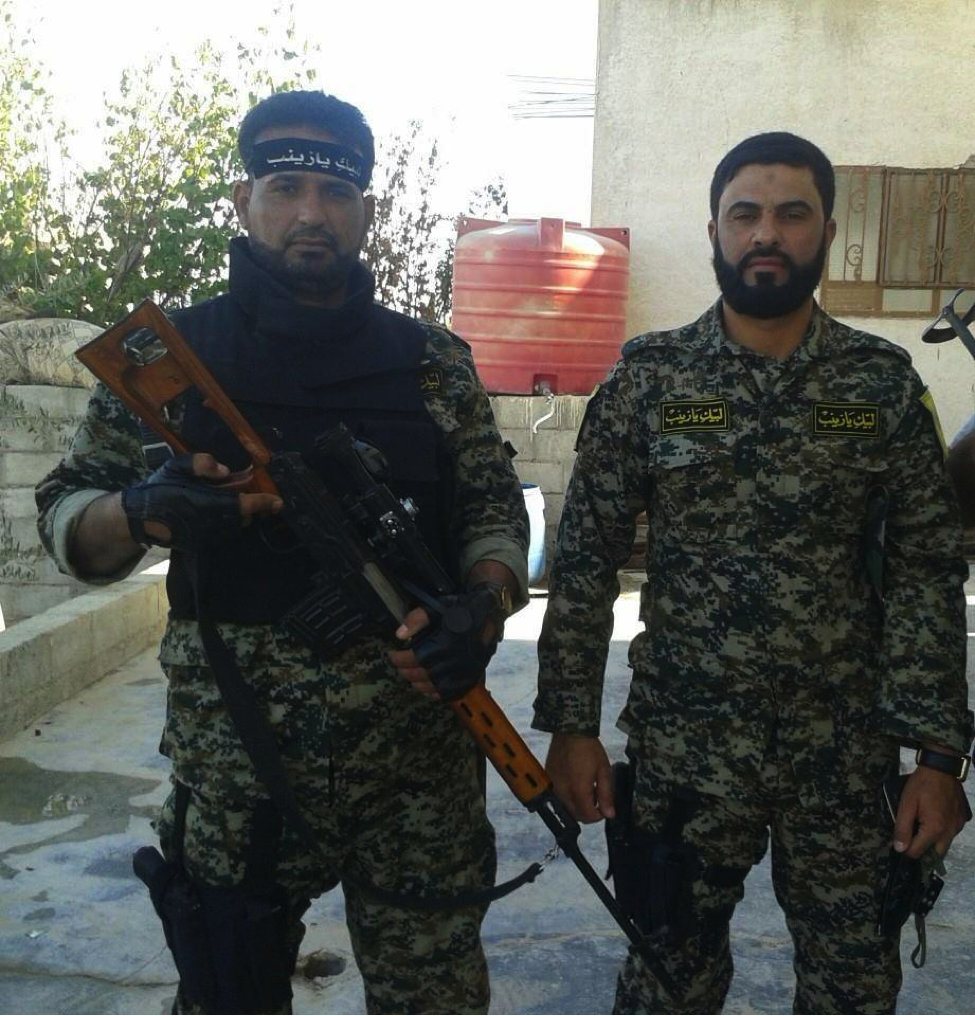

Figure 21: STK fighters. The fighter on the left has an SVD-type sniper rifle.
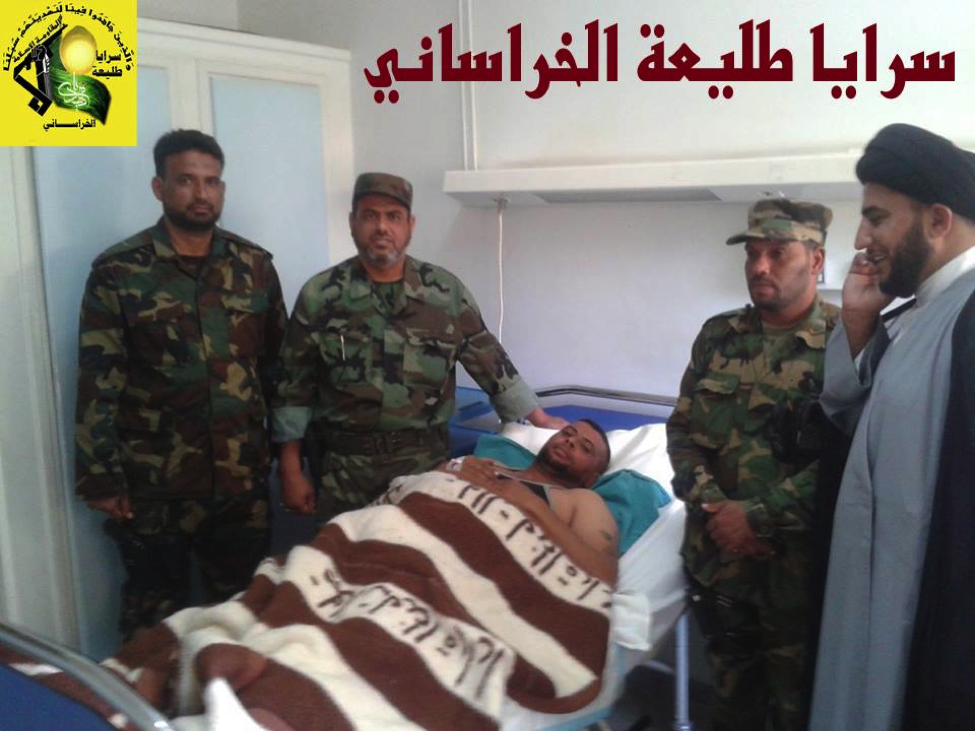
Figure 22: An injured fighter is shown with his compatriots and a Shia cleric.
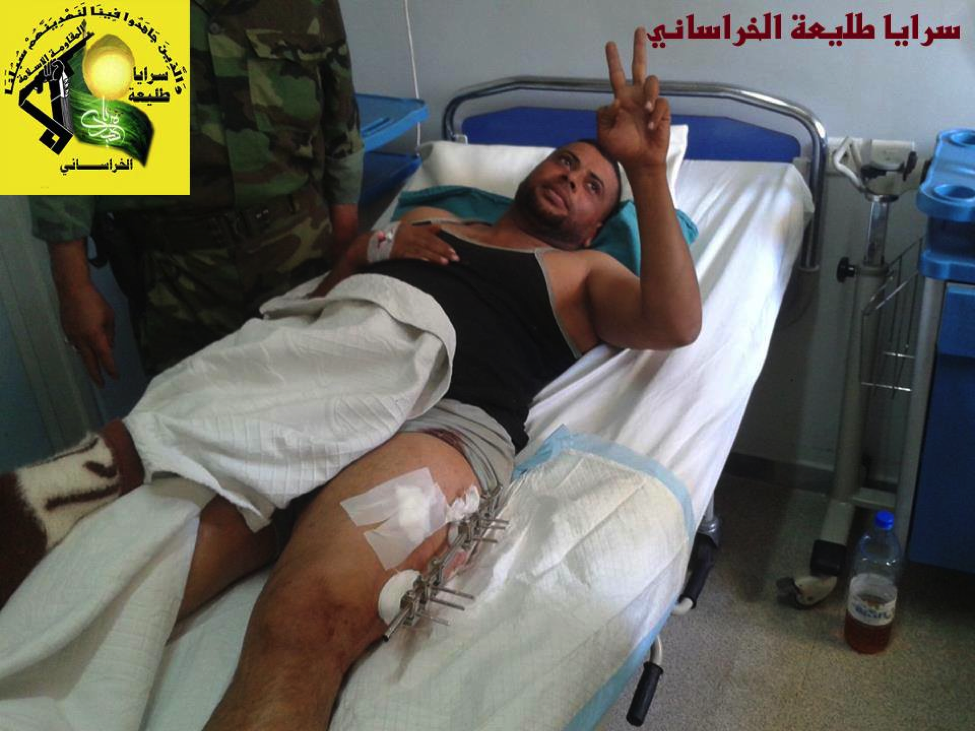
Figure 23: The same injured fighter flashes a “V for victory” symbol from his bed.
STK on Film
STK’s combat videos were first released in October and were quickly disseminated on Shia militia social media. When Syrian rebels came across the films in the weeks after their release, often the fighters were incorrectly branded as members of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas.
The first of the videos STK released shows the group fighting from a structure in Rif Dimashq. Save for the caption and titles on the videos posted, there was nothing which identified the fighters in the film as members of STK. In two other combat videos it show STK militiamen operating in East Ghouta section of Rif Dimashq, firing mortars, RPGs, rifles, and other weapons.
Hizballah Cavalcade: Sariyya al-Tali’a al-Khurasani: A New Combat-Tested Shia Militia in Syria
Posted on
[1] Matthew S. Gordon, The Rise of Islam, (Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, 2005), Pp. 47-48.
[2] See al-Madrasi’s Facebook page: https://www.facebook.com/pages/%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B3%D9%8A%D8%AF-%D9%85%D8%AD%D9%85%D8%AF-%D8%AC%D9%88%D8%A7%D8%AF-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D8%AF%D8%B1%D8%B3%D9%8A/178591738857323 The page has not been updated since 2012 and little information is available about the cleric online.
