Following the death of Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, I tracked the new bayat coming in for the new leader Abu Ibrahim al-Hashimi al-Qurashi. This post will do the same with the announcement of Abu Ibrahim’s death and Abu al-Hasan al-Hashimi al-Qurashi as the new leader of the Islamic State. As I said in the original post:
There are two main reasons for this: 1. pledges are leader-specific rather than group-specific and thus need to be renewed with each succession and 2. it is a way to legitimize al-Qurashi’s rule and create a media event so that the group can promote itself as it transitions to a new phase.
The first reason is also something that IS pointed to when it began to overtly feud with al-Qaeda (AQ) in 2013, by saying that following Abu Mus’ab al-Zarqawi’s death, his successor Abu Hamzah al-Muhajir gave baya to the newly created Islamic State of Iraq’s leader Abu ‘Umar al-Baghdadi and even after Abu ‘Umar was killed, when Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi took over in 2010 and then Usamah Bin Laden was killed in 2011, Abu Bakr never publicly gave baya to Ayman al-Zawahiri, even if al-Zawahiri claims he gave it to him privately. Therefore, from the perspective of IS this whole process is not trivial, but important for legitimacy of its leadership and to potentially weed out any insubordination before it manifests into something larger as it already did in the past vis-a-vis AQ.
This post will be updated with the latest official pledges.
—
March 11, 2022:
Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – Karkūk




























Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyyah – Lake Chad Basin

























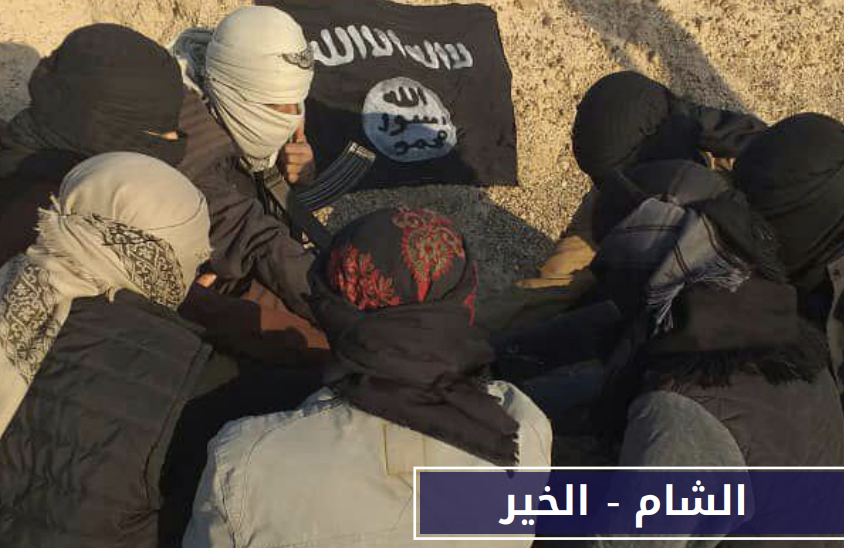
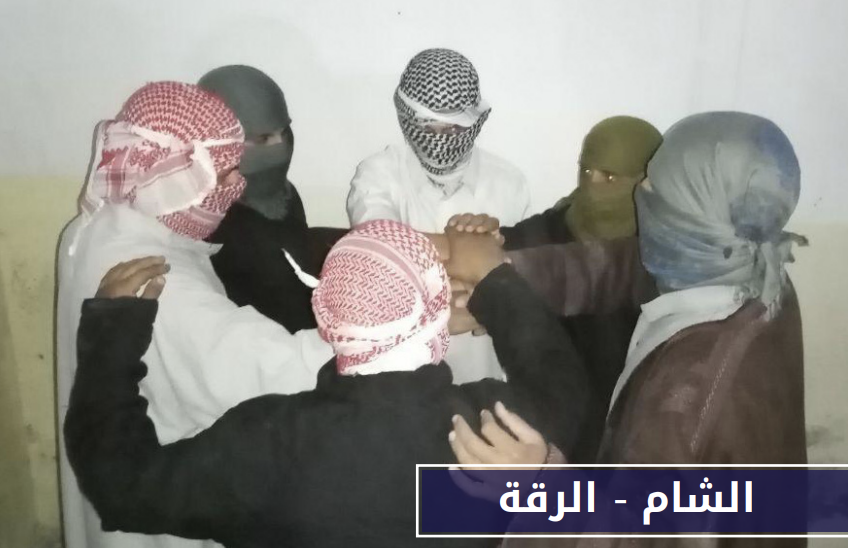
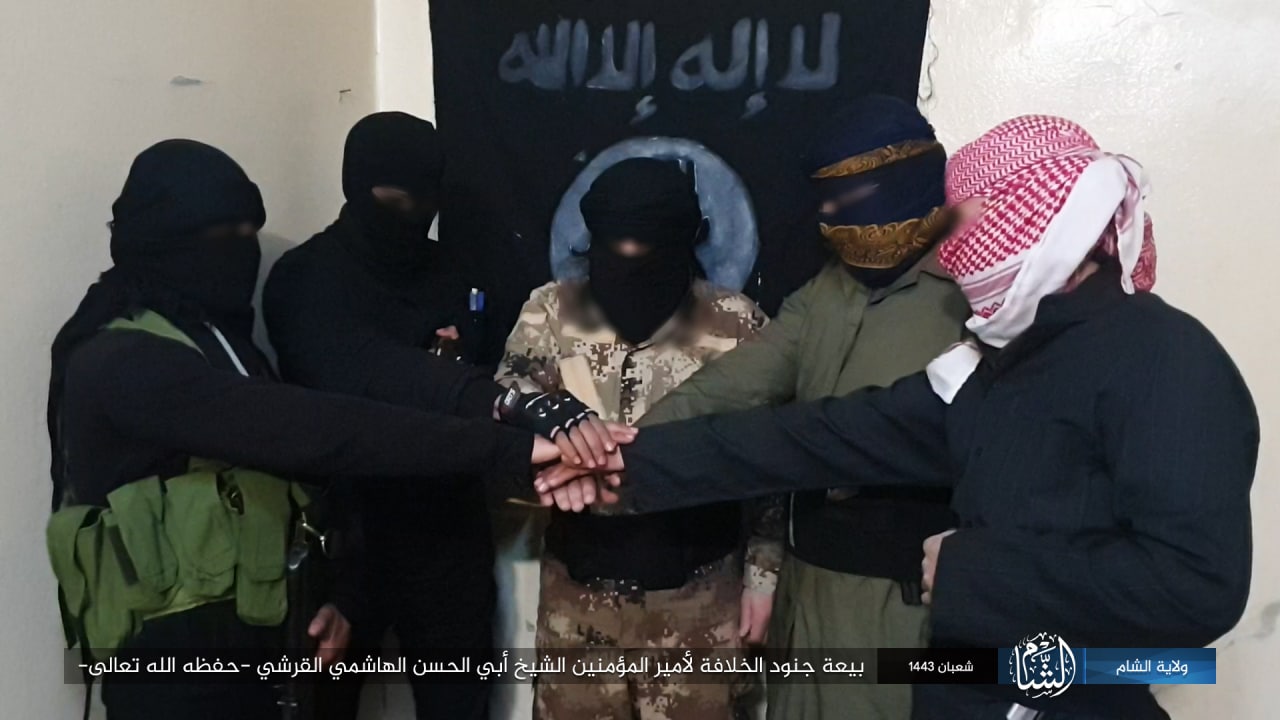
Wilāyat al-Shām


































Wilāyat al-Ṣūmāl








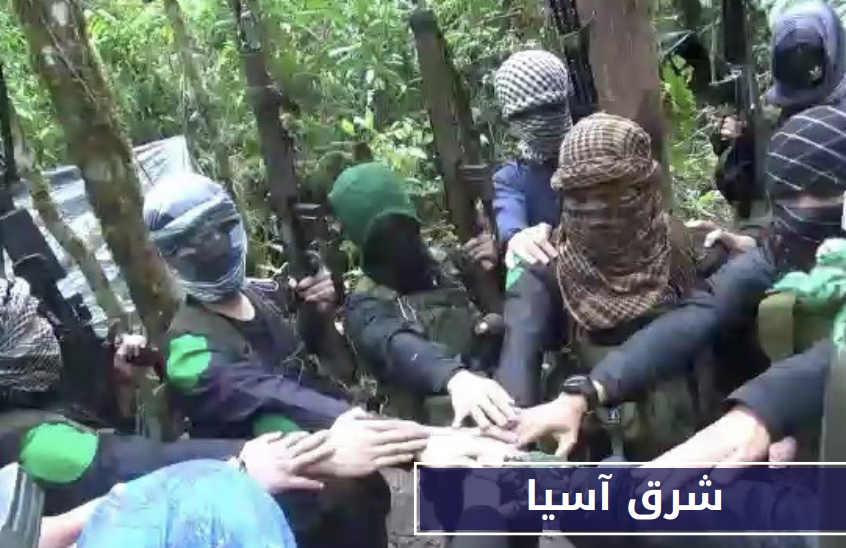
Wilāyat Sharq Asīā






March 12, 2022:
Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – al-Ānbār












Wilāyat al-Yaman




Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – Ṣalāḥ al-Dīn














Wilāyat Khurāsān






























Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyyah – al-Faruq Region













Wilāyat Lībīyā



Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyyah – Sambissa








Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyyah – Sahel Region
























Wilāyat Gharb Ifrīqīyyah – Kerenoa Region





Wilāyat Bākistān









Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – Shamāl Baghdād


Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – al-Janūb


Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – Diyālā
















Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – Nīnawā


Wilāyat al-Hind








Wilāyat al-‘Irāq – Dijlah




Wilāyat Saynā’












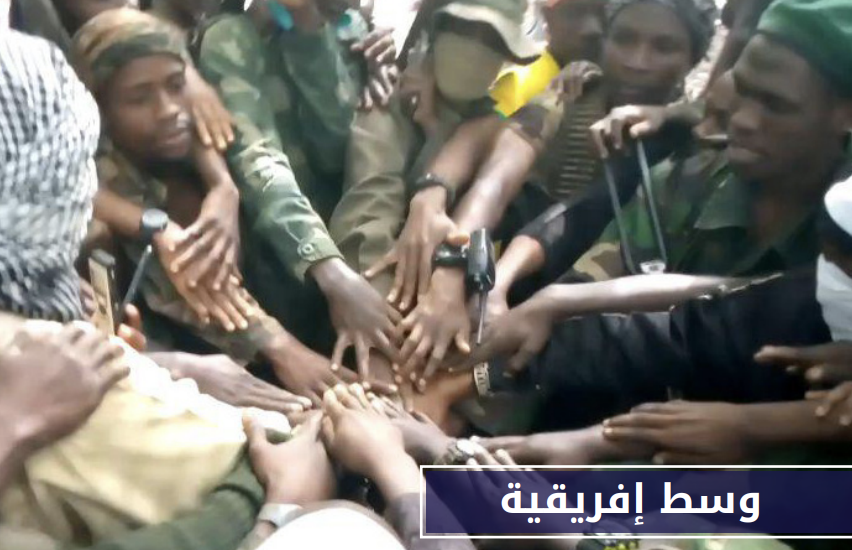
Wilāyat Wasaṭ Ifrīqīyah